Important types of Typhus disease you need to know about.
What is typhus?
One or more rickettsial bacteria infections are the main cause of typhus. When they bite you, fleas, ticks, lice, or mites (chiggers) spread it. Arthropods are a class of invertebrate animals that include fleas, mites, lice, and ticks.
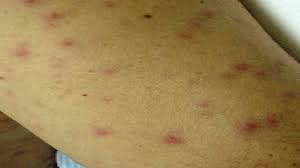
Arthropods that are harbouring rickettsial bacteria when they bite people can spread the bacterium that causes typhus. Scratching the bite causes the skin to become more irritated, which gives the bacteria easier access to the bloodstream. The germs continue to thrive and proliferate once they are in the bloodstream.
Typhus comes in three separate forms:
- epidemic (louse-borne) typhus
- endemic (murine) typhus
- scrub typhus
Depending on what bit you, you may contract a particular strain of typhus. Typically, arthropods spread a strain of typhus that is exclusive to their species.
Cause of typhus
Similar to how a cold or the flu are not spread from person to person, typhus is not. There are three distinct forms of typhus, each of which is brought on by a distinct bacterium and spread by a distinct arthropod.
Epidemic/louse-borne typhus
This type is brought on by Rickettsia prowazekii, which is also conveyed by ticks and potentially by body louse. Although it can be found anywhere in the world, including the United States, it is more frequently found in densely populated regions with subpar cleanliness, where the environment encourages the infestation of lice.
Endemic typhus
This form, often known as murine typhus, is brought on by the rat flea or cat flea and is brought on by Rickettsia typhi. Worldwide, endemic typhus is a problem.
It might be present in people who have frequent interaction with rats. Although cases have been reported in a few locations, particularly Texas and southern California, it is not frequently encountered in the United States.
Scrub typhus
This type is brought on by Orientia tsutsugamushi and is spread by chigger-like mites in their larval stage. The Pacific Islands, Papua New Guinea, Australia, and Asia are where this particular strain of typhus is more frequently discovered. Additionally known as tsutsugamushi sickness.
When a louse, flea, tick, or mite feeds on the blood of an infected person (epidemic typhus) or an infected rodent, they become carriers of the bacteria (any of the three typhus forms mentioned above).
You can get sick in a few different ways if you come into contact with these bacteria-carrying arthropods, such as by sleeping on bed linens with lice on them. In addition to being spread by their bites through your skin, the germs can also be spread through their excrement. The bacteria in their faeces can enter your bloodstream through the microscopic wounds on your skin if you itch a part of your body where lice or mites have been eating.
Symptoms of typhus
The symptoms of each kind of typhus are slightly different, although there are several symptoms that are present in all three varieties, including:
- headache
- fever
- chills
- rash
Epidemic typhus symptoms typically manifest abruptly and include:
- terrible headache
- higher than 102.2°F fever
- an expanding rash that starts on the back or chest
- confusion
- stupor and a lack of awareness of reality
- reduced blood pressure (hypotension)
- strong light sensitivity of the eyes
- significant muscular ache
Although less severe in most cases, the symptoms of endemic typhus last for 10 to 12 days and are strikingly similar to those of epidemic typhus. They consist of:
- wet cough
- nauseous and dizzy
- diarrhoea
Scrub typhus patients typically experience the following symptoms:
- an enlarged lymph node
- tiredness
- At the biting location, the skin may have a red lesion or sore.
- cough
- rash
The illness typically takes five to fourteen days to incubate. This indicates that symptoms typically don’t show up for five to 14 days after being bitten. If typhus is contracted while travelling overseas, symptoms may not appear until the traveller returns home. Therefore, if you have any of the aforementioned symptoms, it is crucial that you let your doctor know about any recent travels.
Treatment for typhus
The most typical antibiotics used to treat typhus include:
- Doxycycline is the recommended medication (Doryx, Vibramycin).
- Chloramphenicol is an alternative for women who are not pregnant or nursing.
- Adults who are unable to take doxycycline are prescribed ciprofloxacin (Cipro).
Complications of typhus
The following are a few typhus side effects:
- Hepatitis is a liver infection that causes inflammation.
- intestinal bleeding, also known as gastrointestinal haemorrhage
- A reduction in the volume of blood fluid is known as hypovolemia.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/what-is-typhus
- https://www.britannica.com/science/typhus
- https://www.healthline.com/health/typhus
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001363.htm
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/327505
For more details, kindly visit below.