Deadly Brain Cancer: Understanding Glioblastoma and the Fight for Survival
Glioblastoma: Symptoms, Risks & Treatment Guide
Learn about glioblastoma, an aggressive form of brain cancer. Discover its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options to better understand this serious condition.
When we talk about deadly brain cancer, we’re primarily talking about glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) —the most aggressive and lethal form of brain cancer in adults. Accounting for approximately 45% of all primary malignant brain tumors, glioblastoma has a devastating prognosis that has remained stubbornly poor despite decades of research .
The statistics are sobering: the five-year survival rate for glioblastoma is only 8% , and median survival after diagnosis is just 14-18 months with standard treatment . In the United States alone, an estimated 24,820 new cases of brain and other nervous system tumors will be diagnosed in 2025, with approximately 18,330 deaths expected .
This article explores what makes glioblastoma so deadly, current treatment approaches, and promising research that offers hope for better outcomes.
What Makes Glioblastoma So Deadly?
Aggressive Growth Pattern
Glioblastoma is classified as a Grade IV tumor by the World Health Organization (WHO)—the highest grade possible. These tumors are characterized by:
- Rapid proliferation: GBM cells divide quickly and uncontrollably
- Diffuse infiltration: The tumor sends tentacle-like projections into surrounding brain tissue, making complete surgical removal nearly impossible
- Extreme heterogeneity: Even within a single tumor, cancer cells vary dramatically, making them moving targets for treatment
- Angiogenesis: GBM stimulates growth of new blood vessels to fuel its expansion
Treatment-Resistant Nature
Several factors make GBM exceptionally difficult to treat:
The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from infection but also blocks many cancer drugs from reaching tumor cells . Even when drugs penetrate this barrier, GBM cells employ multiple resistance mechanisms to survive chemotherapy and radiation.
The tumor microenvironment is described as immunologically “cold” —it actively suppresses the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells . This explains why immunotherapies that revolutionized other cancers have struggled against GBM.
Molecular Complexity
GBM harbors numerous genetic mutations that influence treatment response. The most clinically relevant include:
- IDH1/IDH2 mutations: Present in some gliomas; patients with these mutations have better prognoses
- MGMT promoter methylation: Predicts better response to temozolomide chemotherapy
- EGFRvIII mutation: Occurs in 25-30% of GBM patients and is associated with treatment resistance
- 1p/19q codeletion: Associated with better outcomes in certain glioma types
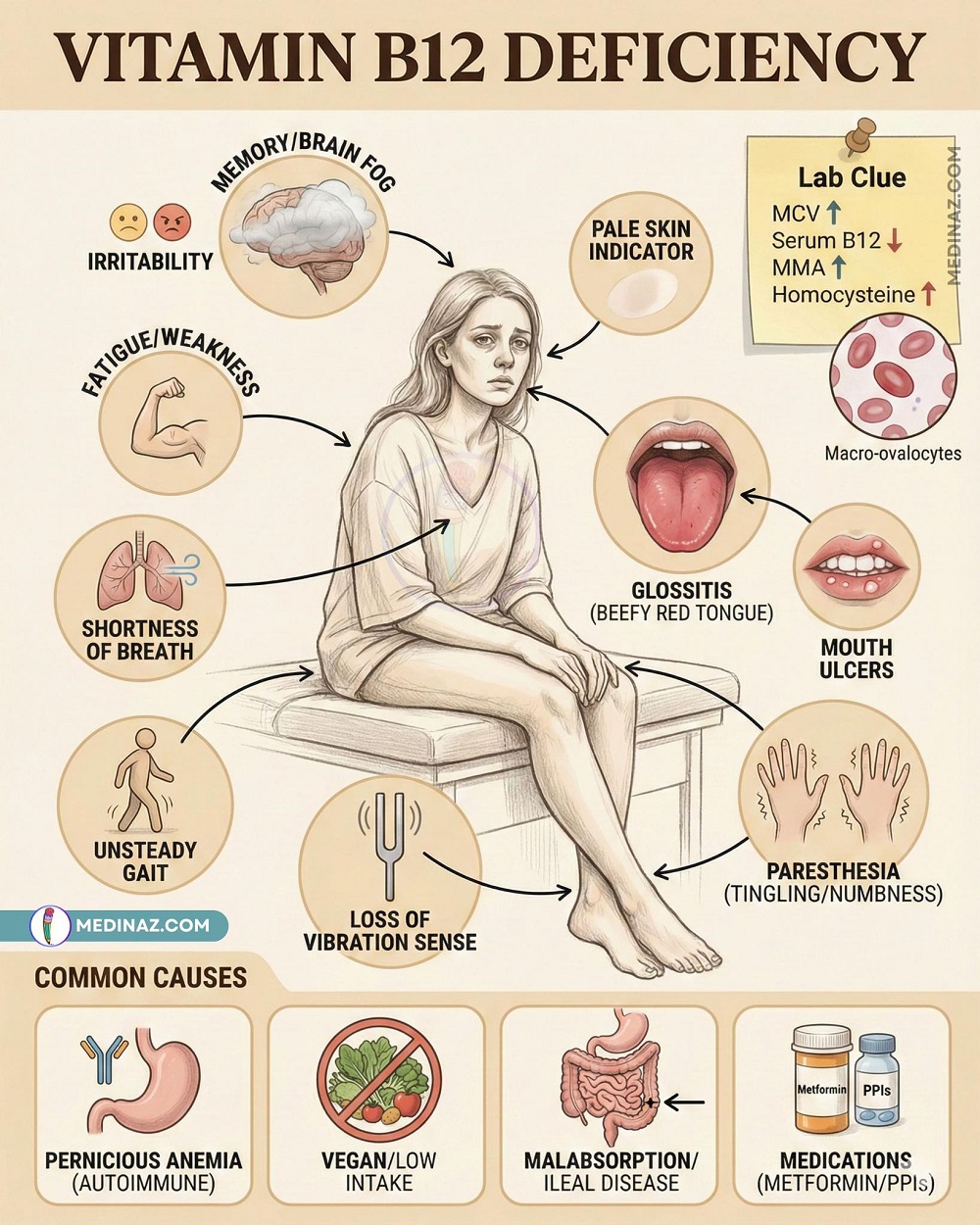
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Brain Cancer
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size and location but commonly include :
- Headaches (especially persistent or worse in the morning)
- Seizures (occurring in about 20% of patients at presentation and up to 70% over the disease course)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Vision changes (blurred vision, double vision)
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty walking or balance problems
- Speech and language difficulties
- Memory loss and confusion
- Personality changes
If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Current Treatment Landscape
Standard of Care: The Stupp Protocol
For newly diagnosed GBM, the established treatment approach includes:
- Maximal safe surgical resection: Removing as much tumor as possible while preserving neurological function
- Radiation therapy: Typically 60 Gy delivered over 6 weeks
- Temozolomide chemotherapy: The only FDA-approved drug for GBM, given concurrently with radiation and then as maintenance therapy
Despite this aggressive approach, tumors nearly always recur.
Surgical Innovations
Awake brain surgery (brain mapping) allows neurosurgeons to remove tumors near critical brain regions controlling speech, language, and movement. Patients remain awake during part of the procedure, providing real-time feedback that helps preserve vital functions .
Supratotal resection —removing more tissue than just the visible tumor—has shown promising results in some studies .
Emerging Treatments
Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields): This innovative therapy uses low-intensity electric fields to disrupt cancer cell division. It’s approved for both newly diagnosed and recurrent GBM and has shown improved survival when combined with temozolomide .
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT): A minimally invasive technique that uses heat to destroy tumor cells, particularly useful for recurrent or hard-to-reach tumors .
Breakthrough Research: Hope on the Horizon
Immunotherapy Advances
A groundbreaking 2019 study (with long-term follow-up reported in 2025) showed that administering the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda) before surgery significantly improved survival in recurrent GBM patients .
Key findings:
- Patients receiving neoadjuvant pembrolizumab had median survival of 13.9 months versus 7.5 months for those receiving it after surgery
- The pre-surgery approach allows T cells to recognize and attack a larger tumor burden, creating a broader and more durable immune response
- Tumors from the neoadjuvant group showed increased T-cell infiltration and suppression of cancer proliferation pathways
While experts caution that larger trials are needed before this becomes standard of care, the results represent one of the most promising advances in years.
Targeted Therapies for EGFRvIII-Positive GBM
For the 25-30% of GBM patients with EGFRvIII mutations, a 2025 network meta-analysis identified rindopepimut (a targeted vaccine) combined with bevacizumab as the most promising regimen for recurrent disease . This combination showed the best outcomes for overall survival, progression-free survival, and objective response rate, with the lowest incidence of severe side effects.
Personalized Medicine Through AI
Researchers at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center have developed scFOCAL —a computational framework that uses single-cell RNA sequencing to predict how individual tumors will respond to different treatments . This approach could eventually enable truly personalized therapy, identifying drug combinations tailored to each patient’s unique tumor cell populations.
Immune-Stimulating Wafers
Scientists at the University of Cincinnati are developing a delayed-release wafer containing interleukin-15 (IL-15) that would be placed in the surgical cavity after tumor removal. IL-15 activates immune cells to recognize and kill residual cancer cells . The team is testing this approach using “glioblastoma-on-a-chip” technology before moving to human trials.
Organ-on-a-Chip Technology
This innovative platform creates 3D models of human brain tumors that incorporate immune cells—something traditional cell cultures lack. It allows researchers to test therapies more accurately before reaching patients and could eventually predict individual patient responses to immunotherapy .
Risk Factors and Prevention
Unlike many cancers, there are no known lifestyle-related or environmental risk factors for primary brain tumors . This means there’s currently no proven way to prevent them.
Known Risk Factors
- Radiation exposure: Therapeutic radiation to the head (rare)
- Family history: Certain inherited syndromes increase risk:
Factors with uncertain or unproven effects include cell phone use, exposure to vinyl chloride, and certain occupational chemicals .
Living with Glioblastoma: Support and Outlook
Prognostic Factors
Several factors influence individual prognosis :
- Age: Younger patients generally fare better
- Tumor genetics: IDH mutations and MGMT methylation predict better outcomes
- Extent of resection: More complete removal improves survival
- Performance status: Overall health and function at diagnosis
The Importance of Clinical Trials
Given the limited treatment options, all GBM patients should consider clinical trial participation at every stage of their disease. Trials are investigating:
- Novel drug combinations
- Immunotherapy approaches
- Targeted therapies based on tumor genetics
- Innovative delivery methods to bypass the blood-brain barrier
Support Resources
A glioblastoma diagnosis affects the entire family. Important resources include:
- Neuro-oncology teams that include social workers and patient navigators
- Support groups for patients and caregivers
- Palliative care to manage symptoms and maintain quality of life
- Rehabilitation services (physical, occupational, speech therapy)
Conclusion: Progress Amidst Challenges
Glioblastoma remains one of medicine’s most formidable challenges. Its aggressive nature, treatment resistance, and molecular complexity have thwarted countless therapeutic attempts. Yet the research landscape is shifting.
From immunotherapy timing that makes biological sense to personalized AI-driven treatment selection, from immune-stimulating wafers to targeted vaccines—genuine progress is being made. While we don’t yet have a cure, each study brings us closer to understanding how to outsmart this deadly cancer.
For patients and families facing this diagnosis, the message is one of cautious hope: research is accelerating, clinical trials are expanding, and the scientific community remains relentlessly committed to finding better treatments.
References:
- National Foundation for Cancer Research. Brain Cancer Statistics and Facts. 2024.
- Comparative efficacy and safety of therapeutic strategies for EGFRvIII positive recurrent glioblastoma. ScienceDirect. 2025.
- Georgetown University Medical Center. Method developed to identify best treatment combinations for glioblastoma. EurekAlert! 2026.
- National Cancer Institute. Central Nervous System Tumors Treatment (PDQ®). 2025.
- Neurology Today. Immunotherapy Administered Before Surgery for Recurrent Glioblastoma Leads to Better Survival Outcomes. 2025.
- Drug Target Review. Organ-on-a-chip tests immune wafer for glioblastoma. 2026.
- NUHS. Brain Cancer – Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. 2025.
- Editora da Universidade de Vassouras. Glioblastoma multiforme: What’s new in relation to established therapeutics? 2025.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a brain tumor, consult a healthcare provider immediately. Treatment decisions should always be made in consultation with qualified medical professionals.