How bacteria can occupy the skin and elevate eczema growth?
Researchers looked into how bacteria might impact the histology of eczema in a recent study. They claimed that S. aureus bacteria change in eczema patches, speeding up their spread.
Eczema, the most prevalent type of atopic dermatitis, is an itchy, dry skin condition that is not communicable. In the US, 30% of the population is affected by the illness.
Although there is no known cure for eczema, there are drugs available to treat its symptoms. These include topical emollients, topical immunosuppressants, and topical corticosteroids.
Eczema is believed to result from a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. A flare-up of eczema may occur when the immune system is triggered by irritants found in soaps and surface cleansers, for instance.
Variants in the gene that makes the protein filaggrin may cause lower production in eczema patients. Filaggrin is crucial for boosting skin elasticity.
People who have eczema may have breaks in their skin, which bacteria can enter and develop in. The immune system may try to stop this colonization by escalating the inflammation, which aggravates the itching and further damages the skin.
The creation of new medications to treat eczema may be aided by knowing more about how germs grow into eczema sufferers’ skin and how it causes inflammation.
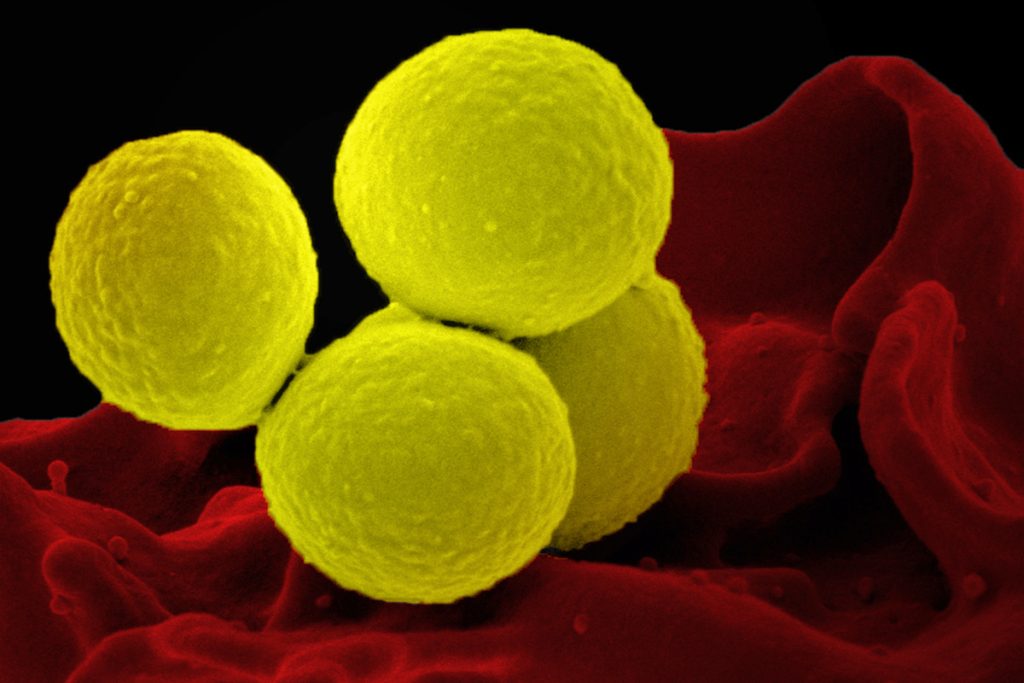
Recent studies looked into how Staphylococcus aureus adjusts to the skin of eczema sufferers. They claimed that the bacteria undergo alterations that cause them to lose their cellular capsule, allowing them to grow more quickly on the skin.
Dr. Alain Michon, the medical director of Project Skin MD Ottawa in Canada and a non-participant in the study, was consulted by specialists over the results.
What kind of bacteria is S. aureus?
According to earlier studies, S. aureus can frequently be found on the skin of eczema sufferers. Their eczema tends to be more severe the more bacteria they have.
By secreting toxins and drawing in immune cells, S. aureus is hypothesised to contribute to the pathophysiology of eczema and worsen the condition of the skin barrier.
S. Aureus is present in the nasal passages of up to 30% of persons. While the majority of infections are not serious, they can result in pneumonia, bone and joint infections, and serious bloodstream infections.
Information from the study on bacteria and eczema
The 23 children in Mexico between the ages of 5 and 15 who had moderate to severe eczema were the subjects of this longitudinal study by the researchers.
Standard medical care, such as topical steroids, emollient moisturisers, and bleach baths, were given to all of the subjects.
The children’s skin microorganisms were sampled by the researchers once per month for three months, and then again at nine months. Samples were collected from common eczema-affected areas such as the inside of the elbows and the backs of the knees. Additionally, they collected samples from the noses and forearms, which are often unaffected by the bacterium.
After that, the scientists cultivated S. aureus cells from every location, producing nearly 1,500 different colonies. This allowed them to more closely track the evolution of the certain cells.
At the end of the trial, they discovered that the majority of participants had only one lineage of S. aureus, indicating that new strains did not develop over time from the environment or other participants. However, they observed that throughout the trial, each lineage underwent significant mutation.
A gene called caps, which codes for an enzyme required for synthesizing polysaccharide a capsule-like shell that protects S. aureus from immune cells suffered several changes that lowered or abolished function, the researchers found in particular.
In a third of the subjects, the researchers discovered that capD mutations completely dominated the S. aureus microbiome population over the course of the study.
The researchers initially identified four distinct capD mutations in one youngster. By the time the trial was through, one of the variations had taken over and had expanded throughout the entire microbiome.
Increased eczema immunodetection
Dr. J. Wes Ulm of the National Institutes of Health, who was not involved in the study, was interviewed by Medical News Today about how mutations that make S. aureus more detectable by the immune system increase the spread of the bacteria and eczema on the skin.
Ulm remarked that from some angles, S. aureus becoming more readily identifiable by the immune system could appear to be a drawback. But he went on to say that if capD expression is lost or reduced, the bacteria may be better able to grow and spread since the energy that would have been used to create a useful capsule can now be used to fuel development.
Additionally, the absence of a capsule would make it simpler for the bacterium to adhere to the skin’s surface, improving its ability to spread throughout the skin.
Its lack of capD makes it easier for the immune system to detect and target the capD-deficient strain when it becomes more prevalent on the [skin’s] microbiome, Ulm said. Consequently, “and this, in turn, can enhance the immune response and magnify the inflammatory reaction giving rise to the characteristic rash and symptoms of eczema.”
Problems with the eczema research
The study’s tiny sample size, according to Michon, limits how broadly these results may be applied to other populations.
The results, he continued, might have been impacted by the fact that certain individuals’ microbiomes may have changed among those who took antibiotics both before and during the trial.
Other restrictions were also mentioned by Cameron K. Rokhsar, FAAD FAACS, a dermatologist and fellowship-trained cosmetic and laser surgeon in Manhattan and Long Island, New York, who was not associated with the study.
The drawback of these discoveries, according to Rokhsar, is that bacterial overgrowth only accounts for a portion of the overall puzzle. “The malfunctioning barrier specific to these people is the real problem with atopic dermatitis. Antibiotics are given to patients to reduce atopic dermatitis flare-ups, but they do not treat eczema.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-bacteria-can-colonize-skin-and-accelerate-eczema-growth#Limitationsof-the-eczema-study
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7317931/
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/04/230412131104.htm
For Skin disease medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?therapy=27