Heart health may be impacted by the bacteria in your gut.
Heart health may be impacted by some gut bacteria, particularly certain strep species that are typically found in the mouth and digestive tract.
Gut bacteria in particular, according to researchers, may be connected to the development of plaque, which can result in clogged arteries.
According to experts, the new research expands on other studies that suggest a connection between gut flora and cardiovascular health. A new study reveals that the mouth and gut may be the origin of several cardiac issues.
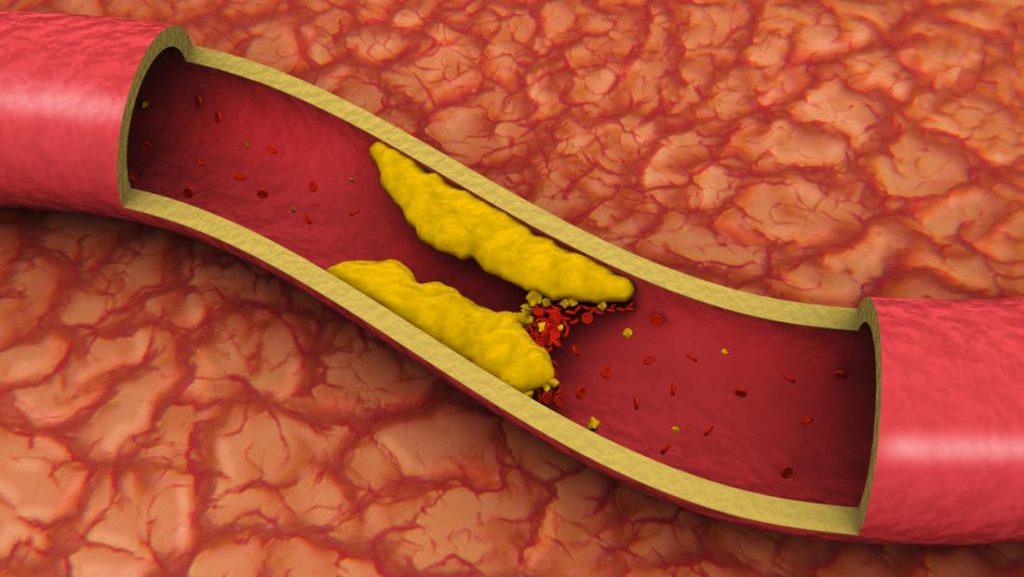
A key contributor to heart attacks are deposits of fat, cholesterol, and other chemicals called atherosclerotic plaques, also referred to as clogged arteries.
According to Swedish researchers, a higher prevalence of these plaques is linked to the presence of specific oral bacteria, mainly Streptococcus, in the gut.
The research, conducted by scientists at Uppsala and Lund University and reported in the journal Circulation, was based on an examination of the gut flora and cardiac imaging of 8,973 persons between the ages of 50 and 65 who had no history of heart disease.
“We found that oral bacteria, especially species from the Streptococcus genus, are associated with increased occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques in the small arteries of the heart when present in the gut flora,” said Dr Tove Fall, a study author and professor of molecular epidemiology at the department of medical sciences and the SciLifeLab at Uppsala University.
Information from the gut bacteria and heart health study
The development of plaque in the blood arteries of the heart was detected early by researchers using cutting-edge imaging technologies.
They coupled the details with genetic sequencing information on a variety of bacteria that live in the stomach (as well as the mouth and throat).
In addition to the link between Streptococcus anginosus and atherosclerotic plaque, researchers also noted that Streptococcus oralis appeared to be connected to plaque accumulation.
According to the study’s findings, levels of some Streptococcus species in the mouth and the gut were associated with fatty deposits in the arteries.
Dr. Marju Orho-Melander, a senior author of the study and a professor of genetic epidemiology at Lund University, said, “We have just begun to grasp how the human host and the bacterial community in the various compartments of the body affect one other.”
According to our study, people who carry streptococci in their stomach have changed cardiovascular health. We must now look into whether these bacteria have a significant role in the emergence of atherosclerosis, she added in a press release.
Plaque buildup is facilitated by two different bacteria species.
One of the most important links the researchers discovered after looking at cardiac imaging and gut flora was with two particular bacteria.
Streptococcus species and indicators of systemic inflammation in the blood have a close relationship. Researchers connected the bacteria with diseases of the oral cavity because they were the same species that were discovered in the mouth.
According to Mesilhy, “Streptococcus anginosus and Streptococcus oralis subsp. Oralis were the most prevalent in [this study group] patients with coronary atherosclerosis.”
Mesilhy continued, “Previous research in mice suggest that oral exposure to Streptococcus species induces plaque formation.
How do gut microbes affect heart health?
Dr. Kezia Joy, an advisor for the UK-based online healthcare company Welzo who was not involved in the study, said that “emerging evidence suggests that alterations in the composition and function of the gut microbiota, commonly referred to as dysbiosis, may contribute to various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases.”
According to studies, specific gut bacteria can create metabolites such as trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), which has been linked to the onset and development of atherosclerosis. “TMAO has been linked to increased oxidative stress, atherosclerotic plaque development, and inflammation. Furthermore, the development of physiological systems including lipid metabolism, inflammation, and immunological responses all of which are important contributors to the development of cardiovascular diseases can be influenced by the gut microbiota.”
Dr. Bina Joe, chair of the physiology and pharmacology department at the University of Toledo in Ohio and founding director of the school’s Centre for Hypertension and Precision Medicine, stated that “the strength of this study is that it’s a large cohort [of participants], the researchers have done a very careful analysis of them at an early stage of cardiovascular disease, and the use of biomarkers” to identify particular gut bacteria that may contribute to plaque formation.
The significance of studying gut microbes
The Swedish study, according to Joe, who has previously led research into the connections between gut bacteria and high blood pressure, is a significant advancement in a field of study where the link between bacteria and cardiovascular illness is more hypothesized than established.
For instance, flossing is now recommended by dentists as a technique to reduce the buildup of mouth germs that may increase the risk of heart disease.
“We don’t know why, but it works,” said Joe.
Further investigation into the exact bacteria that affect cardiovascular disease and the execution of longitudinal studies that could demonstrate a causation rather than an association between gut flora and heart health are questions for future study, according to Joe.
Streptococcus bacteria, for instance, present in both the mouth and the gut, but it’s doubtful that just one strain is to blame for plaque formation because bacteria cannot thrive in both an anaerobic environment like the gut and an oxygen-rich one like the mouth.
Joe remarked, “It’s unclear whatever species of Streptococcus [the researchers] are referring to. In the end, a large community of bacteria may be at play rather than a specific strain.
Summary
A link between gut flora and coronary atherosclerotic plaques has been demonstrated by a recent study.
Researchers studied gut flora and cardiac imaging, and the results showed a strong connection between two different kinds of bacteria.
The study also demonstrated a connection between certain of the species linked to levels of the same species in the mouth and the accumulation of fatty deposits in heart arteries. These findings imply that microorganisms affect several biological systems.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health-news/your-gut-bacteria-may-impact-your-heart-health-heres-how
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gut-bacteria-can-increase-plaque-buildup-in-heart-arteries
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JAHA.122.026036
For Heart disease medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?cPath=77_99