Complications of Sickle cell disease and its treatment.
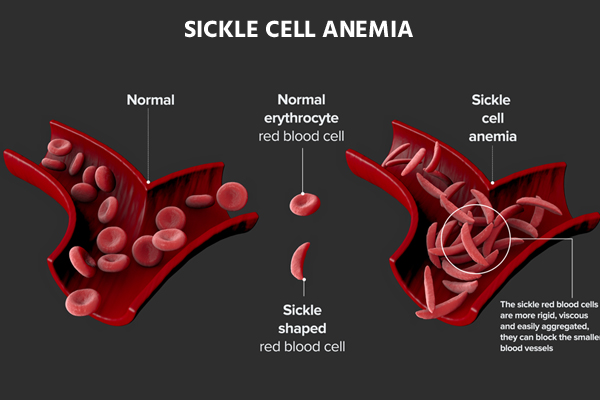
An umbrella term for a collection of hemoglobin-related hereditary diseases is sickle cell disease. There are techniques to control the symptoms of many conditions, even though they can be fatal. Hemoglobin, a substance found in red blood cells, transports oxygen to the body’s tissues. Hemoglobin issues in sickle cell disease result in sticky, C-shaped red blood cells that resemble sickles.
They may therefore become stuck in the cardiovascular system. Additionally, they are unable to adequately distribute oxygen. The body may be impacted in several ways by this.
The only known treatment for sickle cell disease is a stem cell transplant, but groups like the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America are attempting to increase public awareness of the condition and support financing for future research.
Sickle cell disease disproportionately affects “people whose ancestors come from Africa; Mediterranean countries such as Greece, Turkey, and Italy; the Arabian Peninsula; India; and Spanish-speaking regions in South America, Central America, and parts of the Caribbean,” according to Genetics Home Reference.
Types of Sickle cell disease
The protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells is called haemoglobin. It typically consists of two beta chains and two alpha chains. Different mutations in these genes are what lead to the four basic forms of sickle cell anaemia.
SS-hemoglobin disease
The most prevalent form of sickle cell disease is haemoglobin SS disease. It happens when both of your parents pass along copies of the haemoglobin S gene to you. As a result, Hb SS haemoglobin is produced. People with the most severe form of SCD also tend to exhibit the worst symptoms more frequently.
Hemoglobin SC disease
The second most prevalent form of sickle cell disease is haemoglobin SC illness. It happens when you receive both the Hb S and Hb C genes from one parent. Similar symptoms can be seen in those with Hb SC and Hb SS. The anaemia is less severe, though.
Hemoglobin SB+ (beta) thalassemia
The generation of beta globin is impacted by haemoglobin SB+ (beta) thalassemia. Less beta protein is produced, which results in smaller red blood cells. Hemoglobin S beta thalassemia is a condition that can be inherited if the Hb S gene is present. The symptoms are not as bad.
Hemoglobin SB 0 (Beta-zero) thalassemia
The fourth variety of sickle cell disease is known as sickle beta-zero thalassemia. Additionally, the beta globin gene is involved. It has signs like Hb SS anaemia. However, beta zero thalassemia might occasionally present with more severe symptoms. It’s linked to a worse prognosis.
Hemoglobin SD, hemoglobin SE, and hemoglobin SO
These sickle cell diseases are more uncommon and typically do not present with severe symptoms.
Sickle cell trait
Sickle cell trait refers to individuals who only have one parent have a mutant gene (haemoglobin S). They could have no symptoms at all or fewer symptoms.
Causes of Sickle cell disease
A genetic disorder is sickle cell disease. It can only be inherited from one or more defective genes from a person’s biological parents.
A person will have sickle cell trait but not sickle cell illness if they only inherit a defective gene from one parent. A person will develop sickle cell disease if they receive a defective gene from each parent.
How does sickle cell anemia affect people?
Sickle cell anaemia in newborns can last months without showing any signs. When they do, anemia-related symptoms such as severe fatigue or irritability, excruciatingly swollen hands and feet, and jaundice manifest. Injuries to the spleen in babies might impair their immune systems and increase their vulnerability to bacterial infections.
Older sickle cell anaemia sufferers may change and experience more severe medical complications as a result of the lack of oxygen reaching organ tissues. Sickle cell anaemia patients are more likely to suffer from liver, lung, kidney, spleen, and renal damage.
Symptoms and complications of Sickle cell disease
Numerous symptoms and issues may develop if the body’s cells do not obtain adequate oxygen. These can occur at any age and differ from person to person.
Compared to healthy red blood cells, sclerotic cells degrade more quickly. Anemia, or reduced amounts of red blood cells, may develop from this.
Early signs could include:
- Jaundice, also known as a yellowing of the skin and eye whites
- fatigue
- Hands and feet ache and edoema
Additional signs and issues might include:
- occurrences of pain
- the hands and feet swelling
- chest pain suddenly
- seeing less
- increased spleen
- leg sores
- stroke
- profunde vein thrombosis
- harm to the liver, heart, or kidneys
- gallstones
- malnutrition (in young people)
- infertility (in males)
- Priapism, which is a term for a protracted and uncomfortable erection
- Blood pressure that is too high in the lungs is known as pulmonary hypertension.
- blood arteries that feed the lungs
- heart disease
- bone and joint injury brought on by inadequate blood flow
- a greater chance of infections, which could present with serious symptoms
- fever
For further information on some of the most common signs and side effects of sickle cell disease, see the list below:
- Pain: Sickle cells become caught during a pain episode and block the flow of blood to a specific area of the body. The intensity and duration of the discomfort might vary, from minor to severe.
- Infections: The CDC cautions that, regardless of age, people with sickle cell disease may be more susceptible to developing a serious infection from COVID-19.
- Chest symptoms: Acute chest syndrome symptoms include chest pain, coughing, fever, and breathing difficulties.
- Enlarged spleen: Symptoms of an enlarged spleen include weakness, pale lips, rapid breathing and heartbeat, extreme thirst, and stomach pain.
Anyone who exhibits any of these symptoms requires immediate medical attention. They could also need to stay in the hospital for some time.
In children
Sickle cell illness is present before birth since it is inherited. If the problem is present at birth, a normal blood test will reveal it.
Aplastic crises, in which the bone marrow stops generating red blood cells and causes severe anaemia, can occur in infants in extreme cases. Due to red blood cell entrapment, they could also have an enlarged spleen. Low appetite and sluggishness are symptoms.
Sickle cell anemia Treatment
There are several different SCD treatments available, including:
- Intravenous fluid rehydration aids in the normalisation of red blood cell function. If you’re dehydrated, your red blood cells are more prone to swell and take on the sickle shape.
- Infections that are underlying or related with the crisis must be treated since the stress of an infection might cause a sickle cell crisis. An infection could develop as a crisis’s side effect.
- Transfusions of blood facilitate the delivery of nutrients and oxygen when necessary. Patients receive packed red cells that have been extracted from donated blood.
- Through a mask, more oxygen is administered. It facilitates breathing and raises blood oxygen levels.
- During a sickle crisis, painkillers are used to reduce the pain. You might require over-the-counter medications or potent prescription painkillers like morphine.
- (Droxia, Hydrea) aids in boosting foetal haemoglobin synthesis. The necessity for blood transfusions might decline.
- Immunizations can aid in illness prevention. Immunity is typically reduced in patients.
- Sickle cell anaemia has been treated by a bone marrow transplant. The best candidates are children under the age of 16 who have serious difficulties and have a matching donor.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/sickle-cell-anemia
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/315801
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sickle-cell-anemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355876
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/sickle-cell-disease/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4579-sickle-cell-anemia
For more details, kindly visit below.