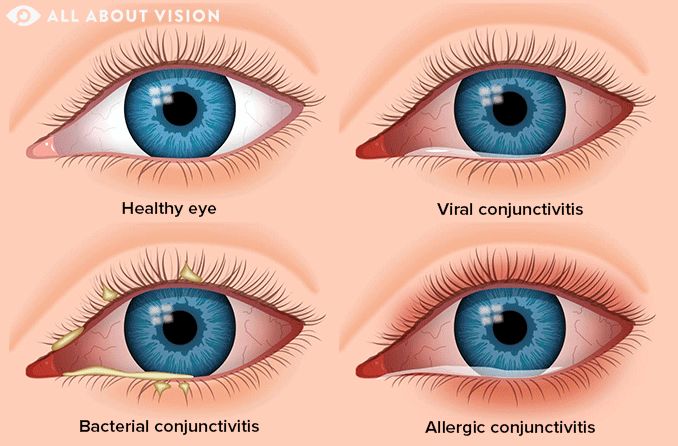
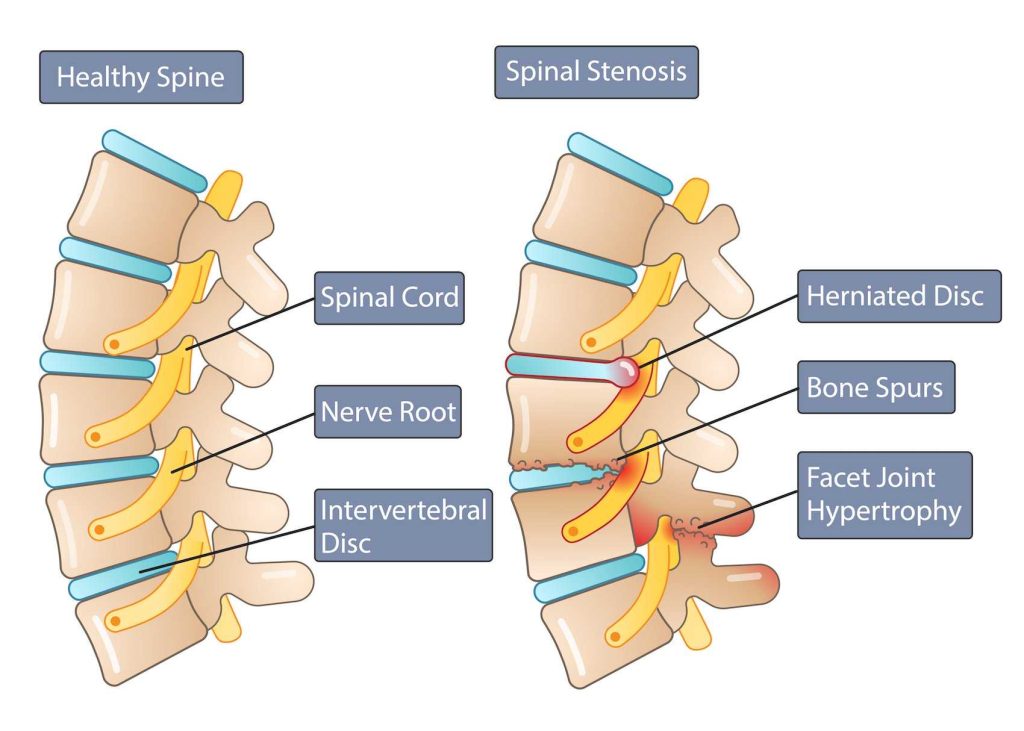
Lets explore the breathing problems you shouldn’t ignore.
Breathing issues occur when you feel as though you are not getting enough air, your chest feels extremely tight, you are out of breath, or you are being suffocated.
If you are fat or have just engaged in vigorous exercise, you can have shortness of breath. Extreme temperatures or being at a high altitude might also cause it. If you experience breathing issues for any other cause, it is likely a sign of a medical condition.
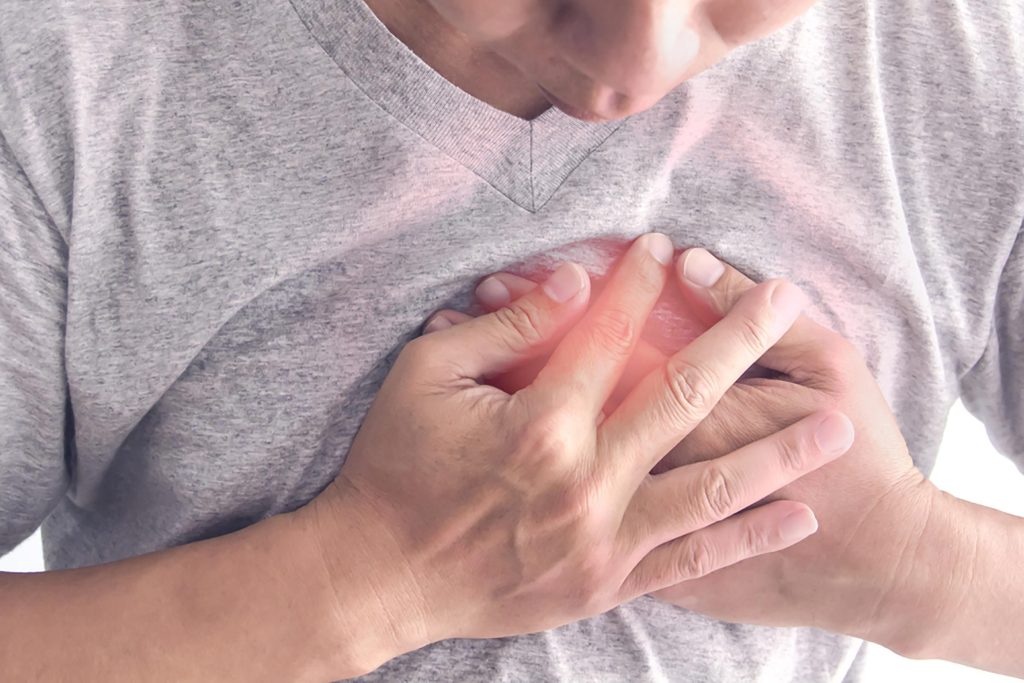
If untreated, you run the risk of developing major respiratory problems like pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax, issues with your trachea, bronchi, or other airway system components. As well as any other conditions that could harm your nerves or muscles that regulate your breathing.
When it comes to breathing, the warning symptoms listed below should never be disregarded.
Emergency tips
Contact the medical emergency or ambulance service if:
- You can’t speak in complete phrases because you’re out of breath.
- You also experience pain in your jaw, arm, or chest.
- feeling weak or ill.
Schedule a visit with your physician or think about visiting an emergency room if you are also gasping for air and:
- have swelling ankles or feet
- when you’re lying down, you feel more out of breath
- have a cough, fever, and chills
- possess blue fingertips or lips
- utter noises when breathing
- must use a lot of effort just to breathe
- are deteriorating
What to do while waiting?
Try to be calm while you wait. Make sure you are upright and, if at all feasible, that someone is with you.
Take 4 puffs of your blue or grey relief puffer if you have asthma. Every four minutes, take four more puffs until assistance arrives.
What causes breathing problems?
These are typical reasons for feeling out of breath:
- asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are examples of lung conditions (COPD)
- cardiovascular diseases and heart failure are two examples of heart issues
- airway infections include croup, bronchitis, pneumonia, COVID-19, the flu, and even the common cold
- an anxiety or panic attack
Some reasons for feeling out of breath unexpectedly include:
- allergy symptoms
- lung failure
- a clot-induced obstruction of one of the blood arteries in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
- uncommon lung conditions
- some illnesses, such COVID-19
Some people experience chronic shortness of breath. This may be brought on by:
- smoking
- not being fit
- getting fat
- anaemia
- heart disease or another issue with the heart
- lung disease
What other symptoms might I have?
You can also experience a cough, fever, sore throat, sneezing, blocked or runny nose, and overall congestion if your breathing issues are brought on by a cold or chest infection.
You may experience nausea, lightheadedness, and chest pain if the issue is with your heart. Take your medication exactly as prescribed if you have been given an angina diagnosis. Take a second dose after waiting five minutes.
If asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the cause of your symptoms, you may also experience excessive mucus production, a wheezing sound when you breathe, and a worsening of your symptoms with activity or at night.
In addition to a rapid heartbeat, shaking, sweating, nausea, and a sense of impending doom or danger, you might also experience these symptoms if you are experiencing a panic attack.
How are breathing problems treated?
The level of illness, how quickly it started, and any underlying illnesses you might have will determine the type of treatment you require.
If you visit a doctor, you might undergo the following tests:
- tests on blood
- scans and x-rays
- tests for breathing
- Treatments include of:
- If you smoke, support to stop
- medications, such as pills and inhalers
- Physical therapy and workouts
Can breathing problems be prevented?
Use puffers or any other breathing aids you may have in accordance with your pharmacist’s or doctor’s instructions. Also possible
- Look after yourself and any underlying issues causing your shortness of breath.
- Keep your cool and posture upright as you stand or sit so that the air can flow more freely.
- reduce pollution
- anything you are allergic to, avoid
- If you are overweight, lose weight.
- Plan ahead on what to do if circumstances worsen.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/breathing-problems
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/copd/ss/cm/telltale-signs-eight-breathing-problems-you-shouldnt-ignore?
For more details, kindly visit below.