Important parameters of Cervical cancer women need to know.
What Is Cervical Cancer?
Women’s cervix, which connects the uterus and vagina, is where cervical cancer develops when cells in the cervix alter. The deeper tissues of their cervix may be affected by this cancer, and it has the potential to metastasis (spread to other parts of the body), most frequently the lungs, liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum.
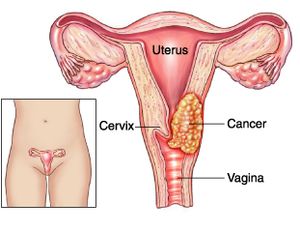
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, which is avoidable with a vaccine, is the main cause of cervical cancer. Since cervical cancer develops slowly, it is typically detectable and treatable before it poses a major threat. Thanks to better screening through Pap tests, it claims fewer and fewer lives of women every year.
The majority of cases are women between the ages of 35 and 44. However, women over 65 make up more than 15% of new cases, particularly those who haven’t been undergoing routine exams.
Different Types of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer comes in several different forms.
- Squamous cell carcinoma. This develops in your cervix’s lining. Up to 90% of cases have it.
- Adenocarcinoma. This develops in the mucus-producing cells.
- Mixed cancercarcinoma. This possesses traits from the other two categories.
Cervical cancer stages
Your doctor will determine the stage of your cancer after a diagnosis has been made. The stage reveals if and how far the cancer has spread if it has. Your doctor can identify the best course of treatment for you by staging your cancer.
There are four phases of cervical cancer:
- Stage 1: A little cancer. There’s a chance the lymph nodes were affected. It hasn’t spread to other body areas.
- Stage 2: The tumour has grown. It can have reached the lymph nodes or spread beyond the uterus and cervix. It hasn’t yet spread to other areas of your body.
- Stage 3: The malignancy has gone to the pelvic or the lower vagina. The ureters, which are tubes that transfer urine from the kidneys to the bladder, may be blocked as a result. It hasn’t spread to other body areas.
- Stage 4: The cancer may have spread to other organs, such as your lungs, bones, or liver, from the pelvis.
Signs and symptoms of cervical cancer
Early stages of cervical cancer are typically difficult to diagnose because they lack symptoms. It may take several years before cervical cancer symptoms appear. The greatest strategy to prevent cervical cancer is to find abnormal cells during testing for the disease.
Stage 1 cervical cancer symptoms and signs might include:
- Vaginal discharge that is either bloody or watery, may be heavy, and may smell bad.
- Vaginal bleeding following sex, in between cycles, or following menopause.
- Periods of menstruation could be heavier and longer than usual.
Symptoms of cancer that has spread to adjacent tissues or organs include:
- urination that is painful or difficult, occasionally with blood in the pee.
- diarrhoea, abdominal pain, or bleeding when you poop.
- fatigue, weight loss, and appetite loss
- a state of general disease
- a dull backache or leg swelling.
- abdominal and pelvic pain
You should have a comprehensive gynaecological exam, which includes a Pap test, if you suffer abnormal bleeding, vaginal discharge, or any other unexplained symptoms.
Cervical cancer causes
The sexually transmitted human papillomavirus is the primary factor in most occurrences of cervical cancer (HPV). Genital warts are brought on by the same virus.
There are over 100 distinct HPV strains. Cervical cancer is only caused by specific types. HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the two strains that cause cancer the most frequently.
Cervical cancer is not a guarantee even if you have an HPV cancer-causing strain. Most HPV infections are cleared up by your immune system, frequently within two years.
In both men and women, HPV can lead to other malignancies. These consist of:
- vulvar cancer
- vaginal cancer
- penile cancer
- anal cancer
- rectal cancer
- throat cancer
Cervical cancer risk factors
The greatest risk factor for cervical cancer is HPV. Additional elements that may raise your risk include:
- HIV
- chlamydia
- smoking
- obesity
- a history of cervical cancer in the family
- consuming little fruit and veg
- using contraceptive tablets
- being pregnant three times at term
- being under the age of 17 when you first became pregnant
You are not destined to develop cervical cancer even if you have one or more of these risk factors.
How is cervical cancer treated?
One member of the team treating cervical cancer is a gynecologic oncologist (a doctor who specialises in cancers of female reproductive organs). The stage of the disease, your age and general health, and whether or not you intend to have children in the future all play a role in the recommended course of therapy for cervical cancer.
Radiation, chemotherapy, surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are all options for treating cervical cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Your cervix’s cancerous cells are destroyed by energy beams used in radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is available in two different forms:
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) uses a machine outside the body to direct powerful radiation towards tumours.
- Radiation is applied directly to or near a malignancy during brachytherapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemo) kills cancer cells by administering medications by injection into your veins or oral ingestion. It enters your circulation and kills cells effectively throughout your body. Chemotherapy uses a variety of medications, some of which can be combined. Cycles of chemotherapy are frequently administered.
Surgery
Cervical cancer is treated with a variety of surgical procedures. The most typical procedures used to treat cervical cancer include:
- Laser procedure
- conical biopsy
- an easy hysterectomy
- Trachelectomy
- Pelvic enlargement
- Targeted treatment
Specific cancer cells are eliminated by targeted medication therapy without harming healthy cells. It functions by focusing on proteins that regulate how cancer cells proliferate and spread.
Immunotherapy
In immunotherapy, drugs are used to activate your immune system’s capacity to detect and eliminate cancer cells. Cancer cells can also signal to avoid being attacked by your immune system. Targeting these signals with immunotherapy makes it so cancer cells can’t deceive your body into believing they are healthy cells.
Clinical trials are yet another form of treatment. Some people supplement their cancer therapy with complementary therapies like nutrition, herbs, acupuncture, and other practises. Speak with your healthcare practitioner about alternative practises that promise to lessen the symptoms of cancer. Some may be beneficial, while others may be dangerous.
Cervical cancer prevention
Screening with a Pap smear or a hrHPV test on a regular basis is one of the simplest strategies to avoid cervical cancer. Precancerous cells are detected during screening so they can be treated before they progress to malignancy.
Most occurrences of cervical cancer are caused by HPV infection. With the help of the vaccines Gardasil and Cervarix, the illness can be avoided. The best time for vaccination is before a person starts acting sexually. Boys and girls can both receive the HPV vaccine.
You can lessen your risk of HPV and cervical cancer by doing the following additional things:
- Do not have too many sexual partners.
- When engaging in vaginal, oral, or anal intercourse, you should always use a condom or another barrier device.
You may have precancerous cells in your cervix if your Pap smear results are abnormal.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/cervical-cancer
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cervical-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20352501
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12216-cervical-cancer
- https://www.webmd.com/cancer/cervical-cancer/cervical-cancer
For more details, kindly visit below.