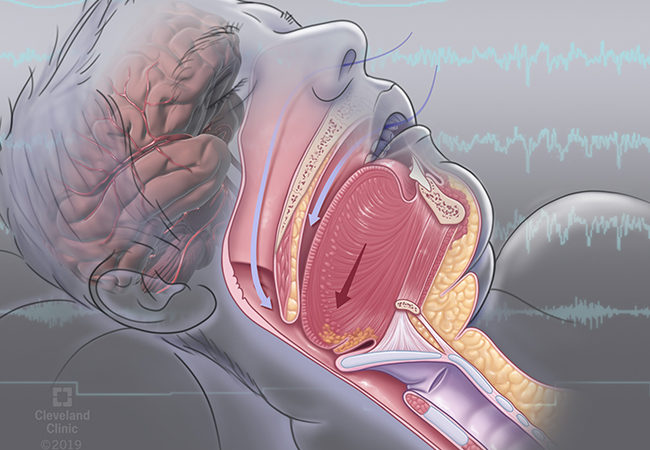
Obstructive sleep apnea & cardiovascular disease links.
According to a recent study, a major contributing component in the association between obstructive sleep apnea and elevated cardiovascular risk may be decreased blood oxygen levels.
More than 4,500 middle-aged and elderly persons conducted medical check-ins and sleep tests, and the researchers analyzed the data from these participants.
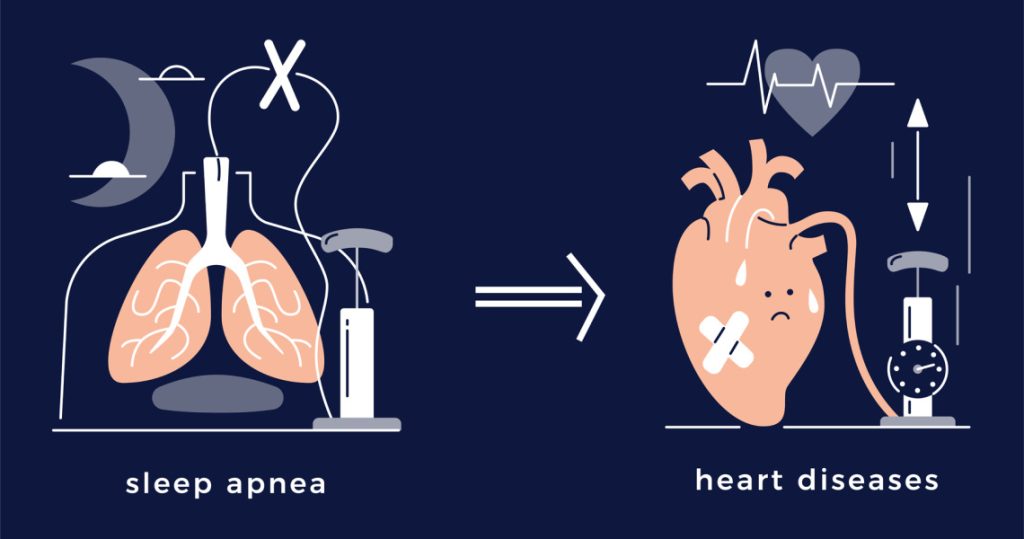
According to their theories, the source of this connection may be a significant drop in blood oxygen levels during sleep. This results in severe airway blockage.
When the upper airway becomes clogged while you’re sleeping, you develop obstructive sleep apnea. The airflow of the person is reduced or stopped as a result.
One’s likelihood of getting obstructive sleep apnea is affected by a number of things, such as:
- obesity
- extensive tonsils
- undergoing alterations in hormone levels.
The most prevalent form of sleep-disordered breathing is obstructive sleep apnea. According to a study from 2020, one-seventh of adults worldwide are expected to develop sleep apnea.
Previous studies have shown that obstructive sleep apnea is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
“Sleep problems, including sleep apnea, significantly contribute to cardiovascular morbidity, as well as all-cause mortality,” Dr. Marishka Brown, head of the National Centre on Sleep Disorder Research (NCSDR), told specialists.
The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and elevated cardiovascular risk is now the focus of a new investigation. It implies that low blood oxygen levels may be the reason of the connection.
Additional to the standard sleep apnea measurements
The Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) measures how many apneas or hypopneas a person has per hour of sleep. Apneas occur when breathing ceases or is diminished. The degree of obstructive sleep apnea can be determined using this traditional method.
According to Dr. Brown, “They use that for pretty much everything as far as this disorder, but what the research has been finding and really what this paper as well as strongly supporting is that there are other measures besides the use of the AHI as the primary diagnostic or prognostic for people with apnea.”
In the investigation, Dr. Brown was not involved. However, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), a division of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which provided partial funding for this study, is home to the NCSDR.
In their publication describing the findings, researchers emphasize that the AHI does not offer data on the severity and duration of “ventilatory deficit, oxygen desaturation, and arousals.”
Different obstructive sleep apnea symptoms
To explain why certain persons with the disorder are more prone than others to develop cardiovascular disease or pass away, the researchers in this study detailed various physiological aspects of obstructive sleep apnea.
As Dr. Brown noted, “Recent research, especially over the past few years, has shown that patients with obstructive sleep apnea are quite heterogeneous, meaning that not all people who experience sleep apnea have the disorder for the same reason.”
To support personalized therapy, she said, “Trying to identify the mechanisms underlying obstructive sleep apnea for an individual is quite an imperative.”
The study looked at several physiological aspects of obstructive sleep apnea, including:
- Hypoxic burden: During sleep, there is a decrease in blood oxygen levels, or hypoxic load.
- Ventilatory burden: Breathing pauses brought on by airway blockage
- Nighttime arousals: Arousals during the night, which occur when someone is startled awake by disrupted breathing.
“I think what they’re getting at here with these three different types of burdens from a conceptual standpoint, I can see how disruptions to sleep and in these forms might have different effects on your cardiovascular health,” said Dr. Yu-Ming Ni, a cardiologist, and lipidologist at the MemorialCare Heart and Vascular Institute at Orange Coast Medical Centre in Fountain Valley, California. He wasn’t a part of the investigation.
Effects on elderly and middle-aged people
More than 4,500 middle-aged and older adults who took part in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study (MrOS) provided data that the researchers analysed.
The NHLBI funded the MESA, which was created to research the features of preclinical cardiovascular disease. Researchers collected information from 1,973 men and women who took part in MESA for their investigation of the relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular risk. The individuals were followed for approximately 7 years, and the average participant age was 67.
2,627 men’s records from the MrOS study were used by the researchers. The subjects were followed for roughly 9 to 12 years, with an average age of 76. The MrOS project, which was supported by the NIH, sought to determine the risk factors for osteoporosis and bone fracture in older men.
Both research required participants to submit medical check-ups and thorough sleep evaluations. Participants were observed by researchers through 2018. A primary cardiovascular incident was experienced by about 110 MESA individuals and 382 MrOS participants, respectively.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-might-obstructive-sleep-apnea-heighten-cardiovascular-risk
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2546461/
- https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-apnea/sleep-apnea-linked-heart-disease
For Sleep Apnea medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?therapy=28