Important variation between Genital herpes and Oral herpes.
What is herpes simplex?
Genital and oral herpes are viral infections brought on by the herpes simplex virus, generally known as HSV. Many people have HSV that is asymptomatic, which means they have the virus but have never experienced a herpes outbreak or active episode.
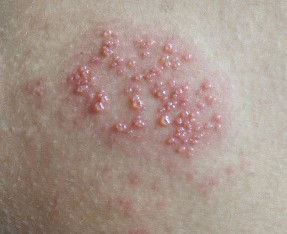
Others may occasionally get sores or blisters that are tiny and filled with fluid. Although they can emerge on your hands, fingers, or other regions of your body, these blisters most frequently develop on your genitalia, mouth, and lips.
HSV can be spread through sexual contact, but there are other ways to spread the virus. Herpes is stigmatised a lot, yet it’s actually quite common and nothing to be ashamed of.
The World Health Organization has provided estimates that show:
- In 2016, over 67% of people under 50 worldwide had oral or genital HSV-1.
- In 2016, approximately 13% of individuals aged 15 to 49 had HSV-2.
According to other studies, by the time adults are in their 50s, almost 90% of them carry HSV-1 antibodies. Herpes still has no known cure, however antivirals and natural therapies might lessen the intensity of symptoms. Less frequent herpes outbreaks may also result from antiviral therapy.
The herpes simplex virus comes in two primary varieties: HSV-1(Genital herpes) and HSV-2(Oral herpes).
Genital Herpes
A typical sexually transmitted infection is genital herpes (STI). Genital herpes is brought on by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). During sexual activity, skin-to-skin contact can frequently spread genital herpes.
Some virus-infected individuals may not even exhibit any symptoms or may have extremely minor ones. They still have the ability to spread the infection. Others experience discomfort, itchiness, and ulcers in their mouth, anus, or genitalia.
Herpes genitalis cannot be cured. Symptoms frequently return after the initial outbreak. Drugs can reduce symptoms. It also lessens the chance of spreading infection. A genital herpes infection can be stopped from spreading with the aid of condoms.
Oral Herpes
Herpes simplex virus type 1 frequently causes the infection known as oral herpes (HSV-1). Oral herpes symptoms most frequently manifest as “fever blisters” and “cold sores,” respectively, on or near the lips. However, oral herpes is not always restricted to one region.
Some people may experience symptoms that manifest between the top lip, on the nose or inside it, or on the chin or cheek. Herpes is referred to as oral-facial herpes in these cases. Most likely, you have witnessed an oral herpes outbreak previously.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Oral herpes
The worst stage of oral herpes is typically the initial (primary) infection. It may result in severe flu-like symptoms, such as headache and enlarged lymph nodes. Some individuals, however, have no symptoms at all. Sores on, around, and in the mouth can develop during the early infection.
Recurring infections typically have considerably milder symptoms, and the sores almost always appear on the lips’ outer margins. Some people never experience another infection after the initial one. The most typical warning signs and symptoms of recurrent oral herpes simplex infection are listed below.
- The location where the infection will first manifest itself may experience initial redness, swelling, heat/pain, or itching.
- Blisters that hurt and are packed with fluid might develop on the lips or under the nose. The fluid and blisters are very contagious.
- The blisters will start to bleed and scab over.
- The sores will start to crust up and heal after four to six days.
An oral herpes outbreak might mimic other diseases or health issues in terms of its signs and symptoms. For a precise diagnosis, always speak with your doctor.
Symptoms of Genital herpes
Most HSV carriers are unaware of their infection. They could have no symptoms at all or just very minor ones.
Within two to twelve days of viral exposure, symptoms appear. They may consist of:
- Itching or discomfort at the genitalia
- Blisters or little pimples near the genitals, anus, or mouth
- Discouraging ulcers that develop when blisters break and leak or bleed
- As the ulcers heal, scabs appear.
- unpleasant urination
- discharge from the urethra, the tube that allows the body to excrete pee
- Expulsion from the vagina
You might frequently have flu-like symptoms during the initial outbreak, such as:
- Fever
- Headache
- Body pains
- Groin lymph nodes that are swollen
What causes herpes simplex?
HSV-1
HSV-1, or oral herpes, can be contracted or transmitted through close contact with a herpes sore, saliva, or other bodily secretions when an episode is in progress. Someone who comes into contact with the infection site directly from you could catch the virus if you’re shedding it.
Direct contact examples include:
- kissing
- verbal sex
- supplementary skin-to-skin contact
In other words, you might catch the virus if you contact your partner’s cold sore and then quickly touch your own face or genitalia. Many youngsters get the virus from an adult who has a cold sore after being kissed or handled on the face.
In principle, the virus can spread through sharing razors, drinkware, and eating utensils, but this is extremely unlikely because, according to earlier estimations, the virus can only survive outside your body for a short period of time (a few hours to a few days).
HSV-2
Similar to HSV-1, HSV-2, often known as genital herpes, can be contracted or transmitted through direct contact with a herpes sore, saliva, or other bodily secretions while an episode is in progress. Additionally, HSV-2 can spread during viral shedding.
Direct communication may involve:
- kissing
- verbal sex
- while having a sexual encounter, sharing sex toys
- invasive sex
- at the infection site, more skin-to-skin contact
Remember that both kinds of the virus can produce oral or genital episodes, despite the fact that many people associate HSV-1 with oral herpes and HSV-2 with genital herpes.
When to see a doctor
It can be challenging to determine whether to seek medical attention for a diagnosis and treatment because a person with herpes may not exhibit any symptoms.
As soon as someone notices sores on or around their genitalia, Planned Parenthood advises that individual to see a doctor. Syphilis is one STI that can have similar symptoms but calls for a different course of action. The American Sexual Health Association also advises getting a culture of any lesion or cold sore one detects before visiting a doctor.
Before visiting a doctor, people might choose to perform an at-home STI test. At-home tests should not, however, be used in place of expert diagnosis and care.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/herpes-hsv1-and-hsv2/oral-herpes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/genital-herpes/symptoms-causes/syc-20356161
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/151739
- https://www.healthline.com/health/herpes-simplex
For more details, kindly visit below.