Can Weed/Marijuana results in Erectile dysfunction?
Marijuana is presently legal in 37 states, three territories, and the District of Columbia as a result of numerous marijuana initiatives, with 19 states permitting recreational use.
In 2018, more than 11 million Americans consumed marijuana, according to data from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). In conclusion, marijuana usage, whether for therapeutic or recreational purposes, is very widespread.
Pain management is a common use of medical marijuana in the US. Although marijuana doesn’t have the potency to significantly lessen really severe pain, it does work quite well to alleviate the chronic pain that afflict millions of Americans each year, according to reputable sources like Harvard Medical School.
Similar to the majority of recreational substances, marijuana can have both advantages and disadvantages. The immediate effects of marijuana include pain alleviation, changed perceptions, emotional changes, and some degree of mental and functioning impairment.
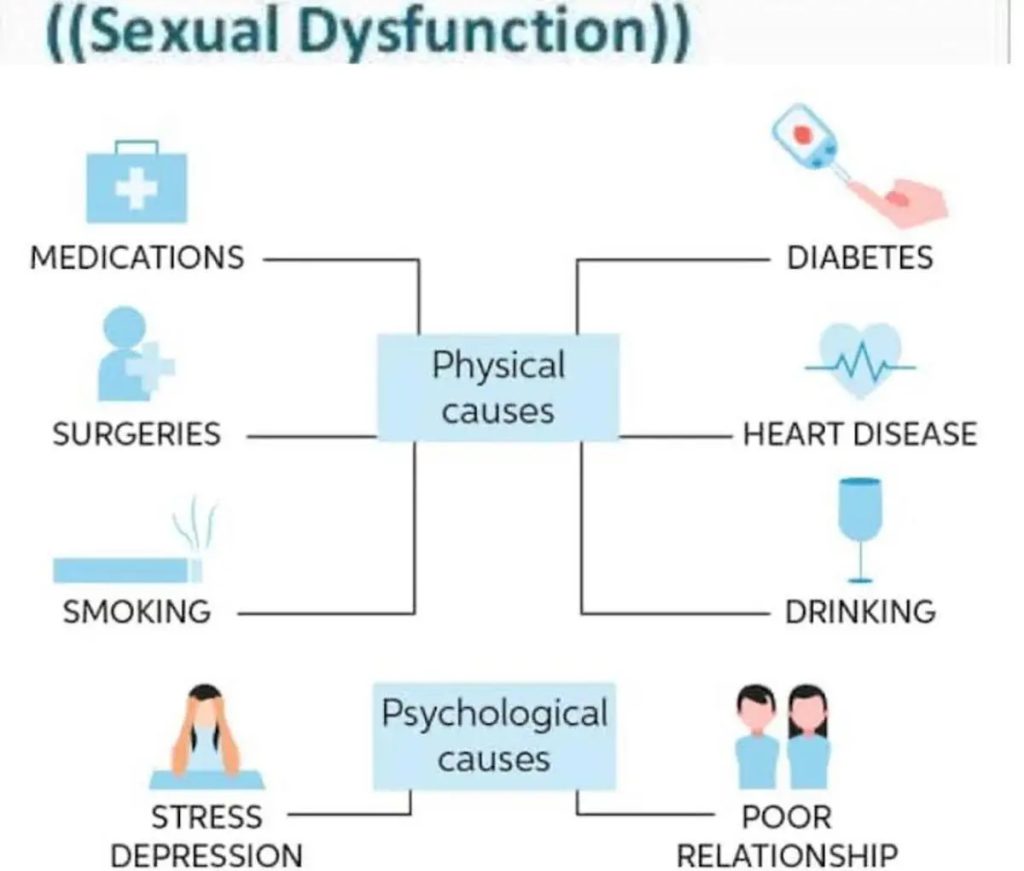
The majority of these are brought on by delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main psychoactive component of marijuana. Additionally, marijuana has certain negative impacts on the sex life, such as a higher chance of erectile problems (ED). The scientific evidence for this connection is, however, contradictory, with some studies pointing to a reduction in sexual performance caused by marijuana and others pointing to an increase.
Marijuana and ED
Although a few small studies have suggested that using marijuana for recreational purposes may cause ED, the authors of a 2018 meta-analysis came to the conclusion that there is not enough data to prove a connection. However, it is easy to pinpoint which THC side effects might be to blame for the malfunction. A person may have a larger danger if they combine marijuana and tobacco.

Smoking cigarettes increases the chance of having ED because it inhibits blood flow to the veins and arteries. Similar risks may be associated with marijuana use, particularly when combined with tobacco. The smooth muscle of the penis has cannabinoid receptors. Because of this, it is theoretically feasible that THC will affect penile function, which may result in ED. There isn’t enough evidence, though.
Cannabis use can result in feelings of exhilaration, followed by tiredness and a reduced reaction time, according to NIDA. Less sex cravings may result from these results.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), marijuana use may also have an impact on the circulatory system, raising blood pressure and heart rate. Both of these consequences increase a person’s risk for ED and are more likely to be felt by marijuana smokers.
There is some evidence that regular cannabis usage may make it more difficult for males to experience orgasms or to have them when they want them. There was, however, no discernible difference in the risk for ED between a group that used cannabis and a control group according to at least one study.
Effects of Cannabis
THC enters the circulation through the lungs when marijuana is smoked. It travels through the bloodstream to the brain and other bodily organs.
The reward and pleasure centres of the brain are impacted by THC. Dopamine influences mood and experience by signalling the body to release more than usual. This is the reason why using the medication results in a “high.”
Other immediate impacts of marijuana use could be:
- sensory perception altered
- followed by euphoria, sleepiness, and relaxation
- alterations in coordination and balance
- higher heart rate
- issues with memory and learning
- anxiety
Long-term impacts that could occur include:
- mental illness issues
- respiratory infections that recur frequently and a persistent cough
- loss of memory
Does weed cause infertility?
Current scientific research is contradictory and inconclusive. Cannabis doesn’t seem to have an impact on live births or actual pregnancies, despite the fact that we have shown harmful impacts of the drug in lab trials.
THC in particular, according to laboratory research, may have an impact on sperm quantity, activity, and quality. In a similar vein, laboratory and animal research indicate that cannabis may alter testosterone levels. Again, no human subjects have been used to replicate these results, thus more study is required.
Some specialists believe that cannabis’ impact on hormones and sperm may make matters worse for persons who are already dealing with fertility problems. They advise abstaining from cannabis when trying to conceive.
Marijuana and Medication
The use of marijuana and its components for medical purposes has recently drawn a lot of interest. Cannabidiol (CBD) was approved by the FDA in June 2018 for treating epilepsy that is brought on by Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, two severe and uncommon diseases.
Marijuana contains certain substances that have therapeutic potential for a number of other ailments. Before these treatments can be approved, however, there is still a lot more research to be done. Many Americans consume marijuana or its derivatives in the expectation that it would improve their health, even in states where it is still illegal to do so. Most dangers associated with doing so are unclear.
Like other drugs, marijuana may interfere with various prescription medications and complementary therapies, such as:
- Blood thinners: Warfarin, various herbs, and supplements, as well as marijuana, may all have stronger blood-thinning effects.
- Alcohol: The psychoactive and depressive effects of marijuana may be enhanced.
- Theophylline: Marijuana may mitigate this medication’s side effects when used to treat asthma and other respiratory conditions. Marijuana may intensify the central nervous system depressing effects of benzodiazepines and barbiturates.
- Psychiatric medications: Medical marijuana may alter the effects of psychiatric drugs.
- Antiretroviral therapy: Marijuana may reduce the effectiveness of several antiretroviral medications.
Further study is required since there might be other medication interactions. Anyone worried about the effects of using cannabis or its derivatives for medical or recreational purposes should consult a healthcare provider. A doctor can provide you more specific information regarding potential side effects and drug interactions.
Conclusion:
To link marijuana consumption with ED, more data is needed. However, certain of the medication’s negative effects, like cardiovascular issues, may raise your risk of developing ED.
One review’s authors found no conclusive evidence of a connection between cannabis consumption and ED. They did find that drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes raised the risk of ED, but exercise appeared to lower it.
Anyone worried about ED might benefit from increasing their exercise routine and abstaining from alcohol and smoke. Marijuana should only be used in compliance with local regulations and when under a doctor’s supervision.
RERERENCES:
- https://www.issm.info/sexual-health-qa/can-marijuana-affect-a-man-s-sexual-function
- https://www.forhims.com/blog/marijuana-and-erectile-dysfunction-need-to-know
- https://www.goodrx.com/well-being/substance-use/can-weed-cause-ed-or-infertility
- https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction/is-smoking-weed-good-or-bad-for-ed
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317104