What to know about cognitive functioning
Cognitive functioning has an impact on people’s memory and thought processes. A decline in a person’s mental and physical responses to their surroundings may result from impairment in this area of brain health. The way the brain functions and shows up as behavior is known as cognitive functioning or cognition.
It plays a crucial role in sustaining daily functioning and brain activity. It controls people’s thoughts, behaviors, learning, and attention to their surroundings. This article looks at dementia, mild impairment, cognitive decline, normal brain function, how the brain functions, and strategies to enhance cognitive function.
Cognitive functioning is the capacity for thought, learning, and memory. The mental process of gaining knowledge and understanding through thought and senses, paying attention, learning through memory, making decisions, planning, reasoning, speaking, and being aware of one’s surroundings is referred to as cognition in research from 2023.
One of the hardest-working organs, the brain operates automatically when it is in good working order. One aspect of a person’s brain health is cognitive function. Other factors include: Motor function: Which controls movements, balance, and how people move. The ability to perceive and react to emotions is known as emotional function. People’s feelings and reactions to touch sensations are referred to as tactile function.
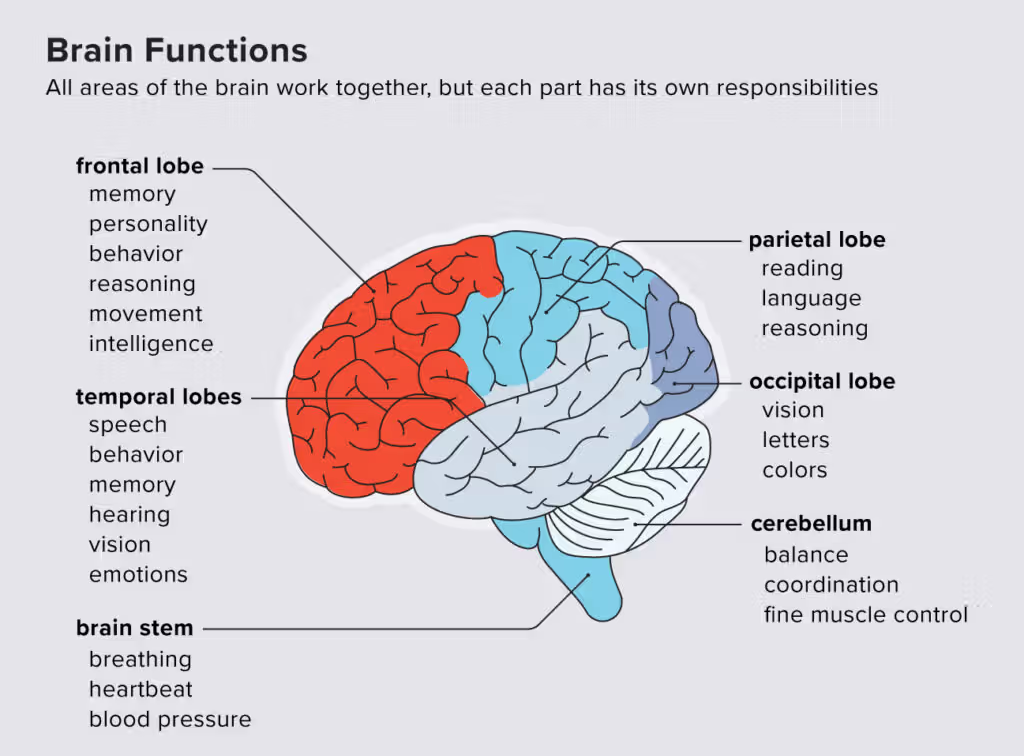
All areas of the brain work together, but each area has its responsibilities:
The upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, controls vital functions such as breathing.
The cerebellum helps with movement.
The upper part of the brain stem controls reflexes and voluntary movements.
The forebrain has a left and right hemisphere: the left helps with word formation, and the right helps with reasoning skills.
The frontal lobe helps with short-term memory storage.
The motor cortex in each frontal lobe helps plan movement.
The parietal lobe behind the frontal lobe supports reading.
The somatosensory cortex helps receive sensory information.
The occipital lobe processes images and links to memory.
The temporal lobe is responsible for receiving information through the ear.
The inner brain helps modify our response to things we perceive in our environment.
The hypothalamus governs important functions such as waking up and emotional responses.
The hippocampus sends memories to the correct hemisphere.