Brief idea on complications and prevention of slipped disc.
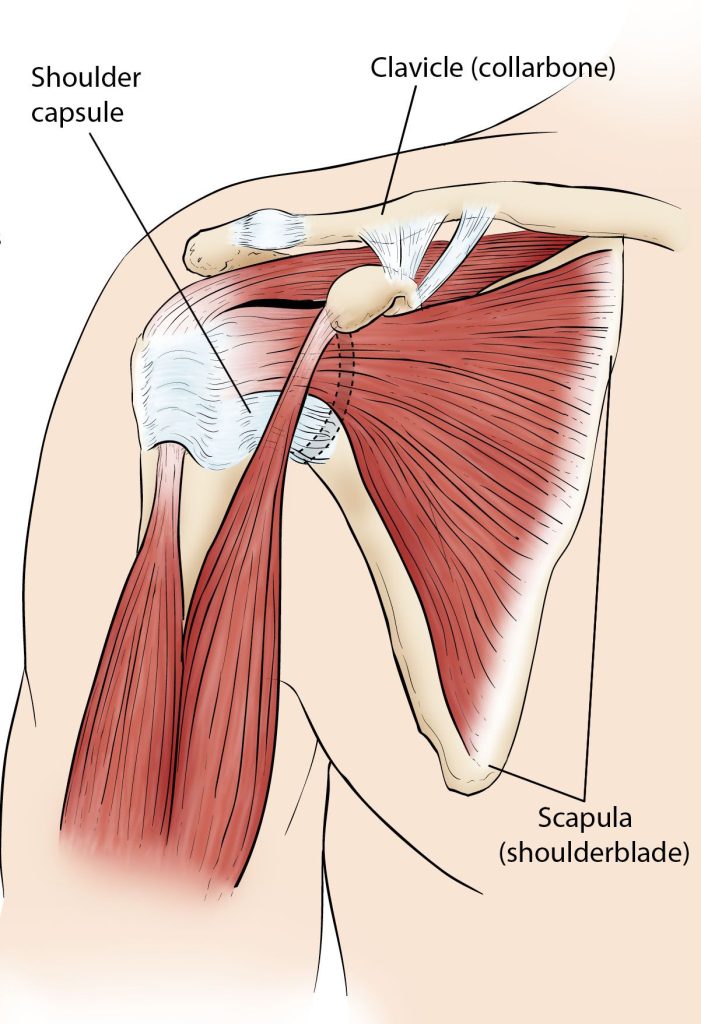
Back discomfort is frequently brought on by a herniated disc. It occurs when a spinal disk’s supple centre pops loose from its covering. This may have an impact on neighbouring nerves, resulting in limb pain, numbness, or weakness.
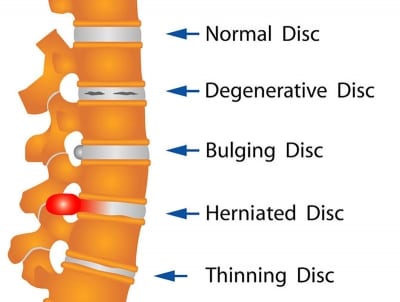
A herniated disc can cause little pain in some persons, especially if it does not push on any nerves. The problem is also known as a prolapsed disc or a slipping disc.
Herniated discs can be treated in a number of effective ways, despite the fact that they occasionally cause excruciating agony. Symptoms often subside or disappear after a few weeks, but if they continue or worsen, surgery may be necessary.
What causes slipped discs?
When the outer ring is weakened or torn, the disc slips, allowing the interior section to protrude. With ageing, this is possible. A slipped disc might also be brought on by specific movements. While you are bending or rotating to lift something, a disc could fall out of position.
A slipped disc can occur in the lower back as a result of lifting a very big, heavy object, which puts a lot of strain on the area. You can have a higher chance of developing slipped discs if your profession is physically demanding and involves a lot of lifting.
People who are overweight are more likely to experience a slipped disc because their discs must work harder to maintain the extra weight. The development of a weak immune system may also be facilitated by sedentary behaviour and weak muscles.
You are more likely to get a slipped disc as you age. This is due to the fact that as you get older, your discs start to lose part of their protective water content. They are therefore more likely to move out of place. Men experience them more frequently than women.
Symptoms of a slipped disc
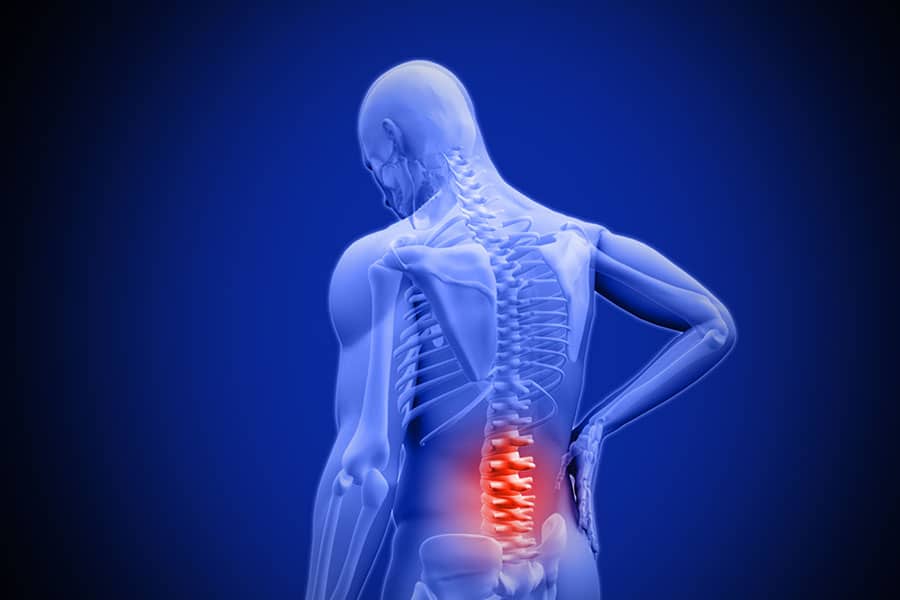
Any area of your spine, from your neck to your lower back, is susceptible to slipped discs. One of the more typical places for slipping discs is the lower back. Your spinal column is a complex web of blood vessels and nerves. The muscles and nerves nearby can experience increased pressure as a result of a slipped disc.
The following are signs of a slipped disc:
- Numbness and discomfort, usually on one side of the body
- you have discomfort in your arms or legs
- ache that gets worse at night or when performing particular motions
- ache that gets worse when you stand or sit
- short-distance walking hurts
- a mystery muscular weakness
- feeling of tingling, aching, or burning in the affected area
Various pain types might exist for different people. If your discomfort causes tingling or numbness that impairs your ability to control your muscles, consult a doctor.
How are slipped discs diagnosed?
Your doctor will examine you physically first. They’ll be searching for the cause of your discomfort and agony. To do this, it will be necessary to assess your nerve and muscle strength as well as whether you experience pain when moving or contacting the affected area. In addition, your doctor will inquire about your health history and symptoms.
When you first started experiencing symptoms and the activities that make your discomfort worse will be of interest to them. Your doctor can see your spine’s bones and muscles with the aid of imaging scans to look for any damaged areas. Imaging scan examples include:
- X-rays
- A CT scan
- MRI images
- discograms
All of these pieces of information can be put together by your doctor to pinpoint the source of your pain, weakness, or discomfort.
Complications of a slipped disc
Permanent nerve damage might result from a significant slipped disc that is left untreated. A slipped disc may, in extremely rare circumstances, prevent nerve impulses from reaching the cauda equina nerves in your lower back and legs. You could lose control of your bowels or bladder if this happens.
The condition known as saddle anaesthesia is another long-term consequence. You lose feeling in your inner thighs, the back of your legs, and the area behind your rectum as a result of the slipped disc compressing nerves in this instance.
While a slipped disc’s symptoms may get better, they might also get worse. It’s time to contact your doctor if you are unable to engage in the activities you formerly enjoyed.
How are slipped discs treated?
A slipped disc can be treated surgically or conservatively. The course of treatment is usually determined by how much pain you’re in and how much the disc has moved out of place.
Using an exercise regimen that stretches and strengthens the back and surrounding muscles, the majority of people can get relief from slipped disc discomfort. Exercises that might strengthen your back and lessen your back discomfort may be suggested by a physical therapist.
Additionally helpful are using over-the-counter painkillers, avoiding strenuous activity, and uncomfortable positions. When you have a slipped disc, it may be tempting to avoid all physical activity, but doing so can cause muscle weakening and joint stiffness. Instead, make an effort to stay as active as you can.
Instead, make an effort to stay as active as you can by stretching or engaging in low-impact sports like walking. Stronger medications may be prescribed by your doctor if the pain from a slipped disc does not go away with over-the-counter remedies. These consist of:
- drugs that relax the muscles to treat spasms
- narcotics for pain relief
- drugs for nerve pain such as gabapentin or duloxetine
If your symptoms do not go away after six weeks or if your slipped disc is impacting your ability to use your muscles, your doctor might advise surgery. Without removing the complete disc, your surgeon may only cut away the damaged or bulging area. It’s known as a microdiskectomy.
In more serious situations, your doctor can remove the disc and fuse your vertebrae together or replace it with an artificial one. Your spinal column will become more stable as a result of this treatment, a laminectomy, and a spinal fusion.
REFERENCE:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/herniated-disk
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/191979
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12768-herniated-disk
For more details, kindly visit velow.