Can antibiotics help in reducing endometriosis symptoms?
Researchers discovered that compared to less than 10% of individuals without the ailment, approximately two-thirds of patients with endometriosis have higher levels of a particular bacterium around their uterus.
The researchers observed that the levels of the bacteria and the development of endometriosis-related lesions were decreased after administering antibiotics to endometriosis-affected mice.
To determine whether the results apply to people, however, more research is required.
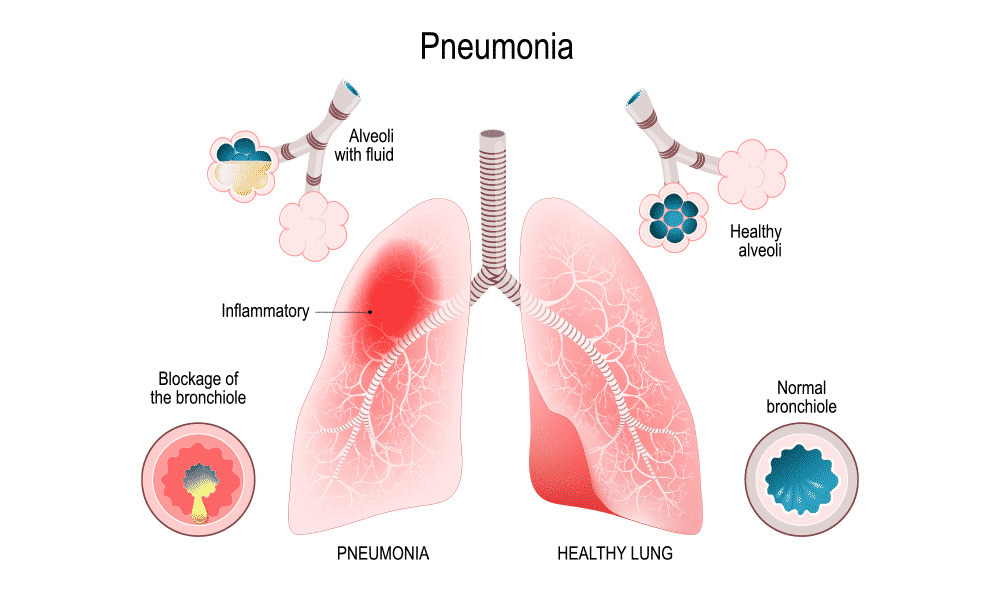
In the disorder known as endometriosis, uterine lining-like cells proliferate outside of the uterus. Along with symptoms like discomfort and nausea, this can result in the production of scar tissue and inflammation in the pelvic area as well as different organs.
In the entire world, endometriosis affects about 10% of people of reproductive age who were born female. There is presently no cure for the illness, though various therapies can assist control it. Additionally, there is no method to avoid the illness.
Millions of people worldwide could have their health and quality of life improved as a result of further endometriosis research.
Recently, scientists discovered that treating mice with a particular bacterium may lessen lesions related to endometriosis. Science Translational Medicine included the findings in one of its issues.
Not a part of the study, Dr. Marc Winter, medical director of Hoag’s minimally invasive surgical gynaecology, told us:
Fusobacterium, a type of bacteria, is implicated in this study from Japan as a potential agent encouraging the development of inflammatory cells that cause inflammation, scar tissue, and pain related to endometriosis. This finding may prompt the addition of particular antibiotics as an essential component of endometriosis therapy.
Fusobacterium in endometriosis
Starting with fibroblasts from four patients with endometriosis and four individuals without, the researchers performed a genomic study. Cells known as fibroblasts help repair wounds and create connective tissues.
They discovered that individuals with endometriosis had much higher levels of the transgelin (TAGLN) gene. It also codes for a protein known as transgelin, which is involved in cell reproduction and is crucial for the growth of the illness.
The expression of TAGLN, which may result from a bacterial infection, can be upregulated by inflammation. According to prior studies, patients with endometriosis have much higher levels of some bacterial genera than healthy people.
The researchers next evaluated the frequency of a bacterium known as Fusobacterium within and outside of the uteruses of 79 people with and 76 people without endometriosis to examine how the presence of these bacteria in the uterine effects endometriosis.
Fusobacterium was found in higher concentrations in the uterine endometrial tissue of 64.3% and the endometrial tissue that had grown outside the uterus of 52.4% of patients with endometriosis. Only 7.1% of those without the disease had higher concentrations of the bacteria in their uteri.
The scientists then looked into whether Fusobacterium encouraged endometriosis in nine mice models of the disease. They discovered that Fusobacterim-exposed animals had higher uterine lesions than control mice.
In contrast, animals without Fusobacterium did not produce as many uterine lesions. This discrepancy persisted even after oestrogen stimulation, which medical professionals believe may induce tissue resembling uterine lining to develop outside of the uterus.
Treatment with antibiotics lessened symptoms
The final goal of the study was to see whether antibiotics could eliminate Fusobacterium in mice and lessen endometriosis symptoms.
To do this, scientists treated endometriosis-affected mice models with metronidazole and chloramphenicol for a total of five days. After a week, they discovered that the mice no longer had Fusobacterium and that transgelin expression had decreased close to the uterus.
They added that animals given antibiotics had less and smaller endometrial lesions than mice not given antibiotics.
According to the researchers’ findings, both antibiotics might be effective in treating endometriosis. However, they pointed out that it is uncertain why Fusobacterium infects some people.
Endometriosis bacteria are unknown.
We discussed the limits of the study with Dr. Karnika Kapoor, a family doctor from Medical Offices of Manhattan who was not engaged in it.
Since mice don’t have a menstrual cycle and don’t naturally develop endometriosis, the mouse model employed in this study has some inherent limitations, according to the researcher.
She said that there is insufficient evidence in the study to support the theory that endometriosis is promoted by Fusobacterium near the uterus after retrograde menstruation, which occurs when the period flows upward via the fallopian tubes and is thought by some researchers to be a possible cause of the disorder.
The authors were careful to make it clear that their analysis could not establish causation, Dr. Stringfellow did observe. This is an important distinction.
“More research is required to prove that Fusobacterium is a causal agent. To ascertain whether other microbial species might have a harmful function, more investigation is also required, he added.
Treatment with antibiotics can slow the spread of endometriosis.
These two studies provide evidence that antibiotic therapy can slow the spread of endometriosis and stop the early development of endometriotic lesions.
The bacterial ecosystem in the mice given antibiotic treatment was also examined by the researchers. Mice with endometriosis who were not given antibiotics had a greater variety of bacteria in their guts.
The mice that received antibiotic treatment had the least bacterial variety.
For endometriosis, metronidazole might be more efficient.
The effectiveness of metronidazole and neomycin as a stand-alone endometriosis treatment was also investigated by the researchers. Lesions on the mice receiving metronidazole were less severe than those on the mice receiving neomycin.
Additionally, the lesions in the mice receiving metronidazole exhibited fewer inflammatory components.
Finally, mice with endometriosis treated with metronidazole were fed endometriotic mouse faeces. Endometriotic lesions developed and resembled those from endometriosis animals given aspartame in their drinking water in terms of mass and volume.
This shows that the bacterial population in the gut can affect how endometriosis develops and spreads.
Future treatments for endometriosis
Dr. Kapoor discussed the limitations of the available endometriosis treatments today.
The current endometriosis treatment options rely on hormone medication, which prevents women from becoming pregnant while receiving care. The removal of endometrial lesions raises concerns since there is a high recurrence rate, which is an option for people with recurring pelvic pain, she said.
“This research appears to point to a possible Fusobacterium-related mechanism of endometriosis, and that antibiotic elimination is a treatment possibility. If antibiotic therapies for endometriosis are found to be beneficial in subsequent research, we could be able to use them in our clinical practise. Karnika Kapoor, M.D.
Dr. Winter concurred that the discoveries might result in fresh therapeutic approaches. “The function of Fusobacterium in promoting endometriosis may result in a completely new strategy for treating it. Further research is required to understand the contribution of Fusobacterium to the development of endometriosis, according to him.
He said, “The use of a widely prescribed antibiotic metronidazole may be a key in improving the efficacy of endometriosis treatment.”
Further research is required.
If similar effects also occur in humans, more research is needed to confirm this. There may be new endometriosis treatments developed if gut bacteria can affect the onset and course of endometriosis in humans.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/why-some-antibiotics-may-help-reduce-endometriosis-symptoms
- https://www.news-medical.net/news/20230614/Antibiotic-targeting-Fusobacterium-reduces-the-formation-of-lesions-associated-with-endometriosis.aspx
- https://medicalnewsbulletin.com/can-antibiotics-be-used-as-an-endometriosis-treatment/
For Antibiotic medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?therapy=4