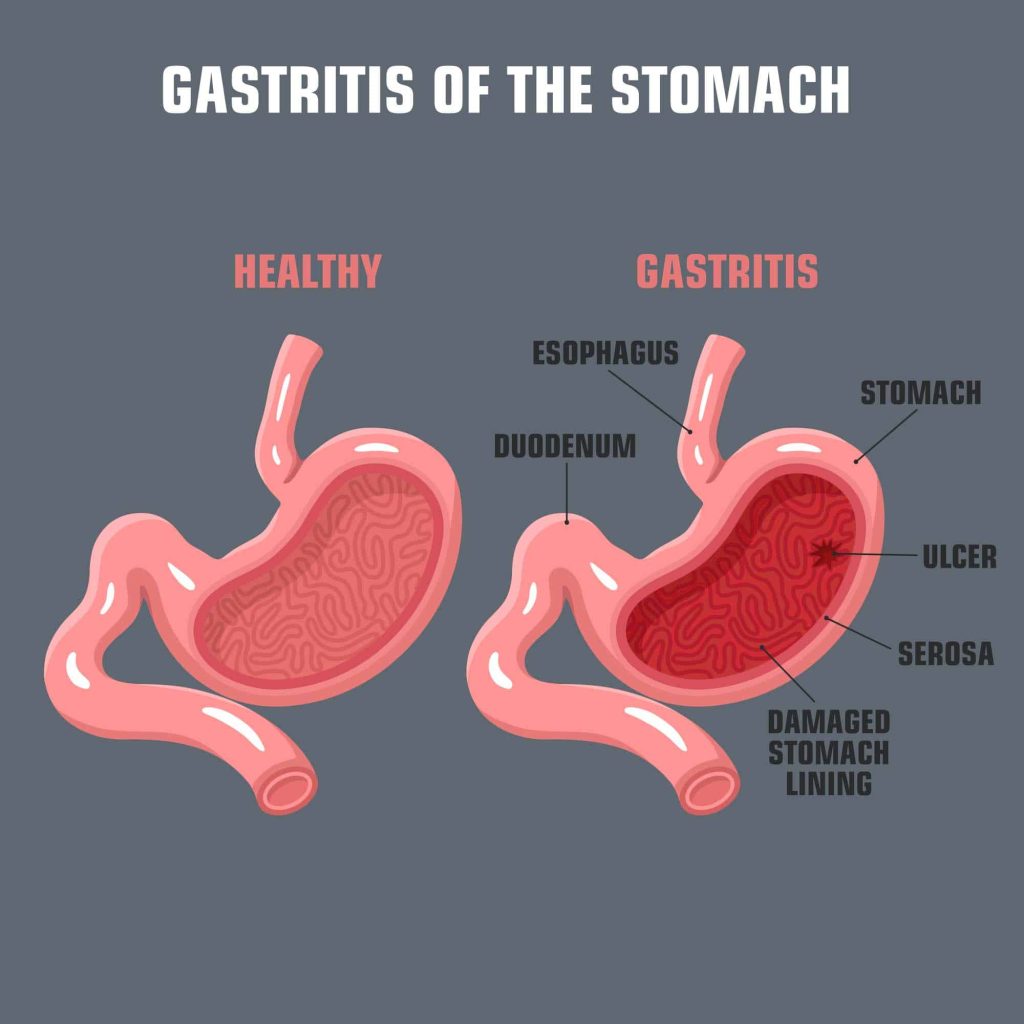
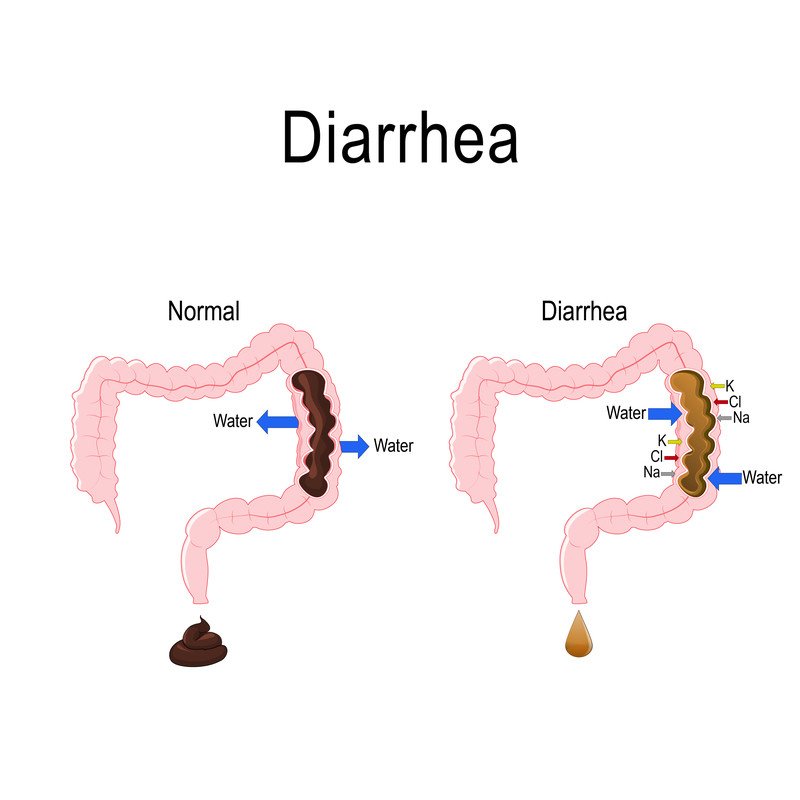
Typhoid: Important Causes and symptoms you need to know.
A bacterial infection called typhoid can cause vomiting, diarrhoea, and a high fever. The bacterium Salmonella typhimurium is to blame (S. typhi). If a doctor diagnoses it early, antibiotics can be used to treat it. Typhoid can be fatal if it persists.
Typhoid is typically spread by eating or drinking infected food or water. Additionally, carriers who are unaware that they carry the germs could spread it from one person to another. In areas where sanitation and hygiene are less effective, typhoid is more common.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are around 5,700 cases of typhoid reported in the US each year. Most persons who get diagnosed after visiting another country probably contracted it there.
What is Typhoid?
The bacterium S. typhi is what causes the infection known as typhoid. Human blood and intestines are home to the bacteria. Direct contact with the infected person’s excrement is how it travels from one person to another.
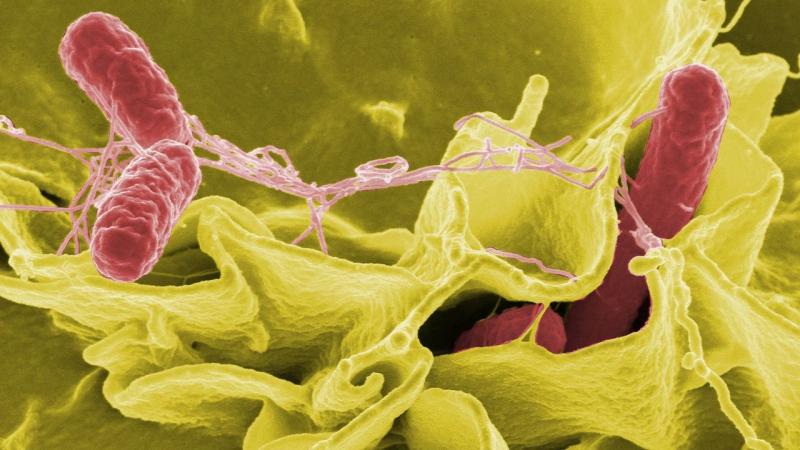
Since no animals are capable of carrying this illness, only humans may spread it. S. typhi enters through the mouth and stays in the intestine for 1-3 weeks. After that, it enters the bloodstream after passing through the gut wall.
It spreads into various tissues and organs from the bloodstream. Because S. typhi can dwell within the host’s cells and is immune system-safe, the host’s immune system is powerless to fight back. Typhoid is diagnosed by a physician looking for S. typhi in a blood, stool, urine, or bone marrow sample.
Symptoms of typhoid
Typically, 1-3 weeks after bacterial exposure, symptoms appear. Typhoid has two primary symptoms: fever and rash. The temperature associated with typhoid is extremely high, gradually rising over several days to 104°F.
Rose-colored dots make up the rash, which does not affect everyone and is most noticeable on the neck and abdomen. Additional signs can include:
- constipation
- diarrhoea
- reduced appetite
- bloating
- nausea
- weakness
- abdomen ache
- headaches
Causes of Typhoid
The bacteria S. typhi is what causes typhoid. It spreads by contaminated food, beverages, and drinking water that has faecal matter in it. If the water is contaminated, washing fruits and vegetables might transmit the disease as well.
Typhoid can affect some people even when they show no symptoms. After their symptoms have subsided, some people keep the germs in their bodies. The illness can occasionally return.
Typhoid-positive individuals may not be permitted to work with youngsters or senior citizens until subsequent negative medical tests.
Who is at risk?
In South Asia, Southeast Asia, and sub-Saharan Africa, typhoid fever is most common. Typhoid infection risk is higher for people who reside, work, or travel to areas with a high prevalence of the infection.
Typhoid fever outbreaks can still occur in places with poor sanitation and hygiene, even in nations with a low incidence of the disease. About 500 cases of typhoid fever are reported in the United States each year, and more than half of these infections were acquired abroad.
Localized outbreaks, however, typically occur in the food business, where a carrier of the virus spreads it through food. People who work in restaurants or other food-related companies may be more vulnerable, notwithstanding the rarity of this.
Treatment of Typhoid
Antibiotics are the sole effective treatment for typhoid. Cipro (ciprofloxacin) is most frequently prescribed by doctors to non-pregnant patients. In addition to these, a doctor might prescribe:
- chloramphenicol (Chloromycetin)
- ampicillin (Ampi, Omnipen, Penglobe, and Principen)
- sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (Bactrim)
Chloramphenicol should not be used during pregnancy. Typhoid patients should consume enough water to rehydrate themselves. A person may require surgery in more serious circumstances where the bowel has become perforated.
However, there is concern about the escalating antibiotic resistance of S. typhi, as there is with a number of other bacterial diseases. Multidrug-resistant typhoid strain outbreaks have occurred, such as the one that hit Pakistan in 2018 and affected individuals who were resistant to five different antibiotic classes.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/156859
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/typhoid
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/typhoid-fever/symptoms-causes/syc-20378661
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17730-typhoid-fever
For more details, kindly visit below.