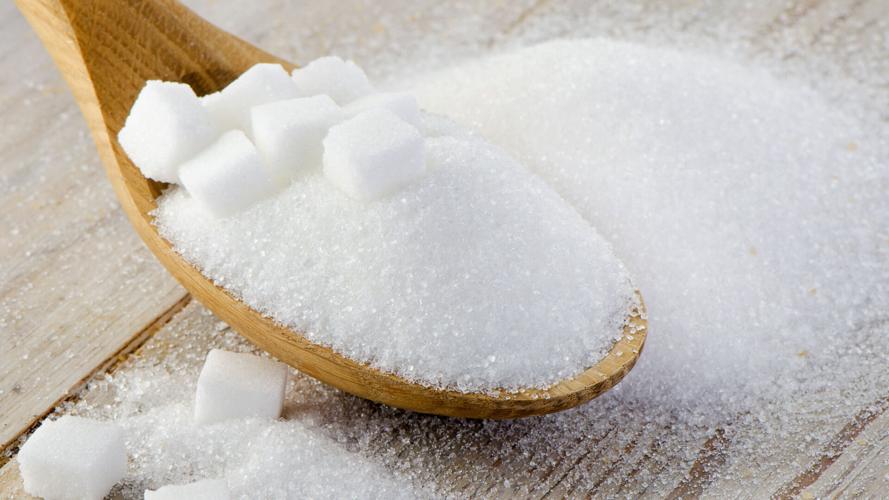
Eating Over 6 Teaspoons of Sugar increases health risk.
Although sugar is a natural component of food, it can also be added during production or cooking.
Understanding the risks of consuming too much sugar is still a work in progress for researchers.

According to a recent comprehensive analysis, sugar consumption is linked to a number of detrimental health effects, such as heart disease and other cancers. People can take action to reduce their use of added sugars and beverages with added sugar.
It’s important to provide the body with the nutrients it requires. To avoid obtaining too much or too little of any one vitamin, careful balancing is required. Although sugar is a nutritional staple, excessive sugar consumption can hurt one’s health.
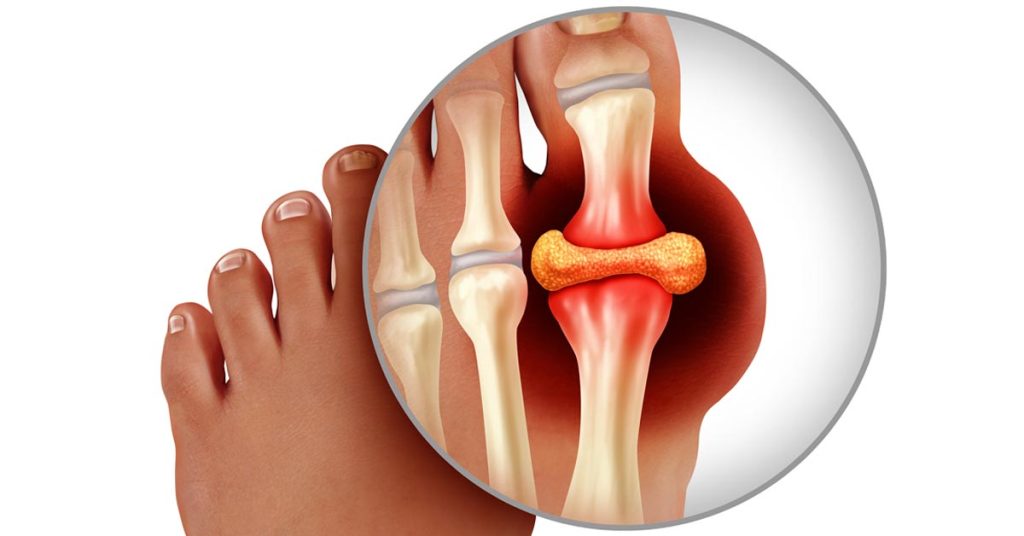
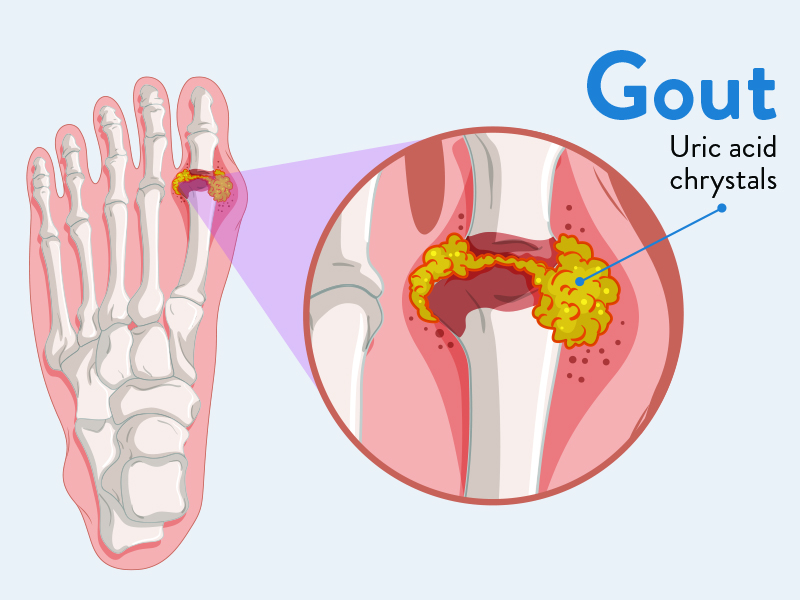
Intake of dietary sugar was linked to several unfavorable health outcomes. This including as weight gain, gout, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and specific forms of cancer. According to a recent review published in The BMJ, the quality of the evidence, nevertheless, varied.
Based on these results, the review authors advise consumers to limit their intake of added sugars to six tablespoons or less per day and to have no more than one sugar-sweetened beverage per week.
Added sugars and natural sugars
A few different forms of carbohydrates fall under the umbrella phrase “dietary sugar.” As an illustration, sugars include glucose, fructose, and lactose. People will obtain some of the sugar they need by consuming foods like fruit or milk, which naturally contain some sugar.
Any sugar that producers or consumers add to foods is referred to as added sugar. Some organisations make suggestions for restricting the use of added sugars based on this distinction.
People cannot completely cut out sugar from their diets because the body needs a certain amount, but the source is crucial. Journalist and licenced dietician Molly Kimball clarified that she was not part in the study.
“Our bodies’ main energy source, including the brain, the central nervous system, and the muscles, is glucose. Your body’s cells require glucose to survive. But since many foods, including proteins and carbohydrate-containing foods like vegetables and whole grains, can be naturally transformed by our bodies into glucose, we don’t need to include extra sugars such as sucrose or glucose into our meals.
In order to provide the best advice on sugar consumption, researchers are still examining the available data.
How dietary sugar affects health?
Over 8,500 articles total, spread across 73 meta-analyses, were considered in this comprehensive evaluation. The review’s authors sought to investigate the effects of dietary sugar consumption on health outcomes. The intake of beverages with added sugar was one particular topic of attention because it might be a substantial source of extra sugar.
The authors of the review discovered a number of negative links between eating sugar and poor health outcomes. They found the following highlights in their research:
Greater body weight was linked to greater consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages. A higher risk of gout, a higher risk of coronary heart disease, and an increased risk of all-cause mortality were all linked to increasing use of sugar-sweetened beverages.
Consuming dietary sugar was linked to an increased chance of developing specific cancers, including as pancreatic, breast, prostate, and total cancer mortality.
Consuming dietary sugar has been linked to a number of detrimental cardiovascular outcomes, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke.
They also discovered a few other detrimental links between consuming sugar and 45 different health issues, such as melancholy, oral health issues, and childhood asthma.
The evidence linking sugar consumption to cancer is currently weak, according to researchers, and this subject needs more research. The strength of the evidence supporting the correlations was also inconsistent.
Additionally not engaged in the study, Dr. Felix Spiegel, a bariatric surgeon at Memorial Hermann in Houston, Texas, made the following observations:
The review’s conclusions are strong and compelling. Consuming too much sugar significantly raises the risk of metabolic diseases like diabetes, cancer, heart disease, psychiatric disorders, and dental issues.
Study restrictions
This review did have several shortcomings. First, scientists admit that there was a chance for some publication bias. Second, the researchers were constrained by the limitations of the studies they reviewed and by the variations among the investigations. Studies, for instance, have examined sugar intake using a variety of techniques, many of which have a high potential for data collection errors. Studies also used various methods to calculate sugar intake.
Reviewers were unable to determine the amount of sugar in certain items. The authors also emphasise how crucial it is to look for multiple confounding variables before interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Because of funding conflicts, some of the analyses that were included had outcomes that should be read with caution. Last but not least, the present reviewers neglected to consider the conflicting objectives of the many studies from the meta-analyses they examined.
Decrease your sugar consumption
People can take action to reduce their intake of added sugars by consulting with medical specialists and other experts as necessary. Although every person has different needs, the findings of this study indicate that restricting added sugars may help prevent some undesirable health effects.
Dr. Spiegel provided the following recommendations for cutting back on sugar intake:
“Reading labels and checking for hidden sugar are two steps to decrease consumption. Avoiding packaged foods is also a great idea. Fruits are a great alternative that is also highly beneficial. Simple grilling or air frying should be used for meat, fish, and poultry without the addition of seasoning or glaze. Instead, use a lot of natural spices. Constantly consuming water is also beneficial. Avoiding sugary alcoholic beverages can help limit overconsumption of sugar.
The natural glucose required to maintain a healthy body will be provided by fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats. If you do consume packaged goods, check the nutritional labels and be aware of how specific foods affect your daily sugar intake, advised registered dietitian Molly Kimball, who was not involved in the study.
Takeaway
An connection between sugar consumption and 45 health outcomes, such as heart disease, diabetes, obesity, asthma, depression, several malignancies, and death, has recently been discovered by a new meta-review.
Health professionals advise limiting added sugar consumption to 6 teaspoons per day. Fresh or frozen fruit, low- or no-sugar yogurts, sugar-free sweeteners like stevia, and other foods are examples of low-sugar substitutes. Additionally, it’s crucial to pay attention to portion management.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/consuming-over-6-teaspoons-of-added-sugar-a-day-linked-to-stroke-depression-asthma
- https://www.healthline.com/health-news/eating-over-6-teaspoons-of-sugar-daily-may-raise-your-risk-of-these-45-health-conditions
- https://www.medigoo.com/news/six-teaspoons-of-added-sugar-a-day-linked-to-stroke-depression-asthma/
- https://medicaldialogues.in/mdtv/diet-nutrition/videos/eating-more-than-6-teaspoons-of-sugar-a-day-linked-to-cancer-stroke-diabetes-early-death-109787
For Diabetes medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?therapy=13