Important factors of Hepatitis C you need to know.
After contracting the hepatitis C virus, you experience hepatitis C, an inflammation of the liver. This virus is bloodborne, which means that the only way to spread or get it is through blood that has the virus in it.
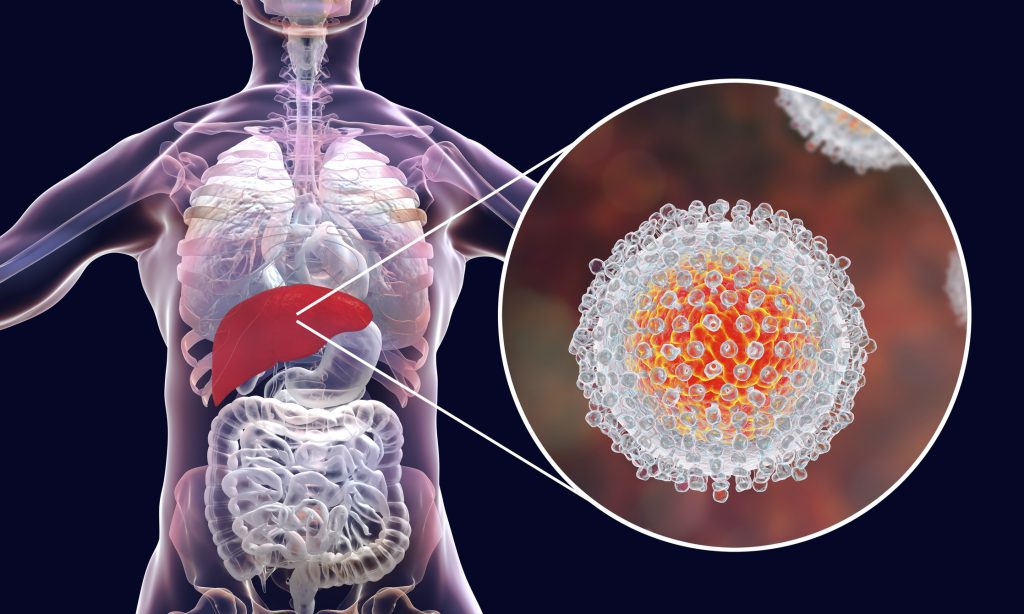
Acute or chronic hepatitis C are both possible.
- Acute hepatitis C: Many times, acute hepatitis C has no symptoms at all. Any symptoms you do have may start to show up a week or two after exposure. They may go away on their own in a matter of weeks.
- Chronic hepatitis C: On the other hand, chronic hepatitis C symptoms may emerge (and worsen) over the course of months or even years. Sometimes symptoms don’t show up until they’re quite bad.
Around 58 million people worldwide are thought to have chronic hepatitis C, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis C is one of the most prevalent hepatitis kinds in the United States, along with hepatitis A and B. A vaccination to prevent hepatitis C does not yet exist, in contrast to those for hepatitis A and B.
If untreated, hepatitis C can result in serious, sometimes fatal health issues, such as:
- cirrhosis (scarring of the liver)
- liver damage
- liver tumour
However, hepatitis C is typically curable. Rapid testing and treatment can lessen your risk of developing severe symptoms and liver failure.
Symptoms of hepatitis C
Acute
Most sufferers of acute hepatitis C don’t exhibit any symptoms. If they do, symptoms usually start to manifest two to twelve weeks following exposure. Acute hepatitis C is rarely diagnosed since there are no clear signs. As a result, physicians frequently refer to hepatitis C as the silent pandemic.
The severe symptoms resemble those of other viral illnesses quite closely. Acute hepatitis C symptoms include:
- the fever
- fatigue
- abdomen ache
- reduced appetite
- dizziness or vomiting
- dark faeces
- stool in a shade of clay
- joints hurt
- jaundice, hardly ever
These illnesses frequently only last a few weeks and are minor. You might not require medical therapy if you have acute hepatitis C. This is because your body can sometimes fight the illness on its own.
It’s possible that you won’t even be aware of having the illness if you don’t exhibit any symptoms. Even though you may not be experiencing any symptoms, you can still spread the infection to others.
Chronic
Acute hepatitis C will progress to chronic hepatitis if your body cannot rid itself of the hepatitis C virus. Of those who have hepatitis C, between 55 and 85% go on to have chronic hepatitis C.
Without treatment, the chronic type of hepatitis C won’t go away on its own, and your symptoms may worsen. There may be long-term health effects from these symptoms. They might potentially result in liver cancer and long-term liver damage.
Chronic hepatitis C symptoms include:
- chronic fatigue
- a general sense of being sick
- Aches and pains in muscles and joints
- unaccounted weight loss
- mood swings, including depressive or anxious thoughts
- difficulty paying attention or remembering things
The chronic type of the illness won’t always result in immediately noticeable symptoms, similar to acute hepatitis C. You should get tested as soon as you can if you have any of the aforementioned symptoms and think you may have been exposed to the virus.
Causes of hepatitis C
Blood-to-blood contact is how the virus is spread. In other words, if the blood of a person who has hepatitis C comes into touch with your blood, you could contract the virus. This could occur because of:
- transplantation of organs
- sharing goods like toothbrushes and razors
- sharing syringes
- childbirth (the person giving birth can spread the infection to the infant)
the exchange of blood during sexual intercourse - piercing or getting a tattoo using non-sterile tools
- If you’ve already had the virus, you could get it again.
Blood transfusions were thought to be a very plausible source of hepatitis C virus transmission before 1992. You now have a far lower probability of catching the virus through a transfusion because to medical advancements in blood screening.
You could be at an increased risk of transmission if you:
- before 1992, you had a blood transfusion
- had a transplanted organ before 1992
- received blood products or clotting factor concentrates prior to 1987
- received long-term hemodialysis treatment
- hepatitis C-positive mother gave birth to them
- had a hepatitis C-infected sexual partner
- used needles that weren’t sterile
You can avoid spreading hepatitis C by:
- kissing, embracing, or otherwise touching
- feeding your infant
- sharing meals and beverages
- sneeze and coughing
Is hepatitis C curable?
Hepatitis C infections, whether acute or chronic, are frequently fully curable. (Keep in mind, though, that you still risk getting the virus again.)
Antiviral medication-based therapy can effectively treat hepatitis C 95% of the time. When tests no longer show the virus in your blood 12 weeks after the conclusion of treatment, medical specialists will consider you to be cured.
How is hepatitis C treated?
Hepatitis C patients do not always require therapy. Your immune system might be strong enough to successfully combat the illness and eliminate the virus from your body. Medication is typically effective in treating the illness if your immune system is unable to eradicate the infection.
Hepatitis C medications
Hepatitis C can be treated with a wide range of drugs. Antivirals are the most common type of treatment, while Riboviria may also be recommended if other measures have failed.
Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), a class of medications, work to completely eradicate the hepatitis C virus from your body. It also assist in the prevention of liver damage.
Several of the brands of these medicines include:
- Zepatier
- Harvoni
- Epclusa
- Vosevi
- Mavyret
Hepatitis C has been classified into 6 distinct genotypes, or strains, by researchers.
Knowing your genotype will help your doctor or other healthcare provider decide which drug will work best for you. Your genotype may have an impact on the kind of treatments you can receive because some strains have acquired a tolerance to some drugs.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hepatitis-c
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-c/symptoms-causes/syc-20354278
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15664-hepatitis-c
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/294705
For more details, kindly visit below.