Can Insomnia Increases the Risk of Heart Attack?
Not only is getting enough sleep crucial for your energy levels, but also for the health of your heart. Discover the link between heart health and sleep.
Sleep is not an indulgence. It is essential for health. Your body can mend itself while you sleep. Also, getting adequate restful sleep enables you to go about your day properly.
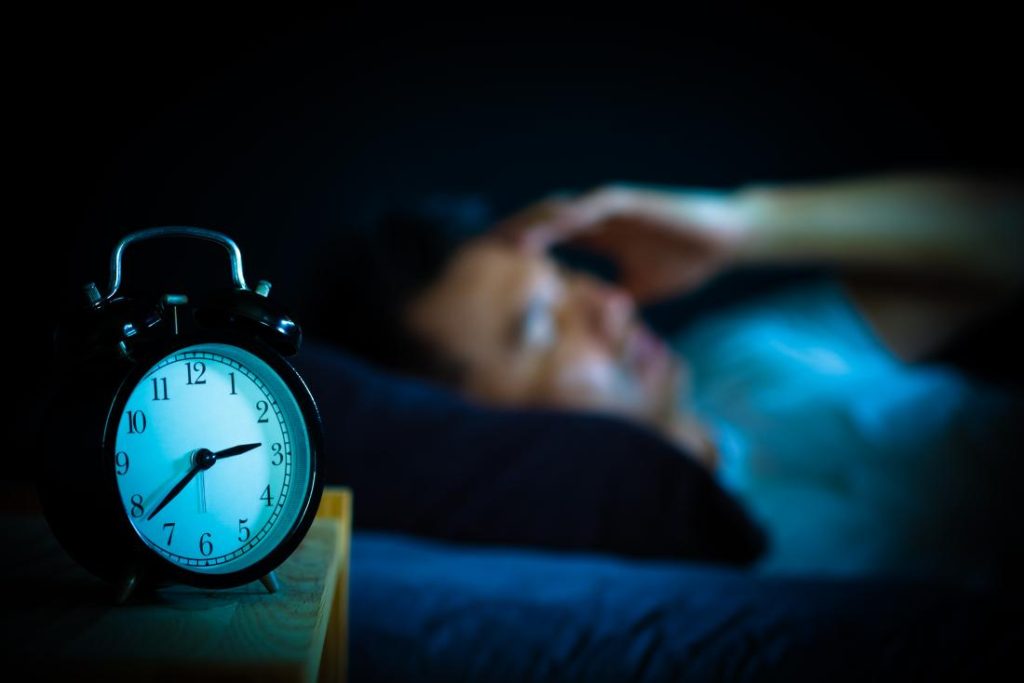

Sleep gives the body the chance to recover and replenish, and it is crucial for almost every element of physical health. Insufficient or interrupted sleep can increase the risk of cardiovascular conditions such heart disease, heart attacks, diabetes, and stroke. It can also affect blood pressure and increase the likelihood of heart attacks.
As a result, getting enough sleep can contribute to living a heart-healthy lifestyle. Also, for those with heart issues and may help prevent harm to the cardiovascular system in healthy individuals.
How much sleep do I need?
Adults typically require at least 7 hours of sleep per night. 1 The majority of American adults—more than 1 in 3—state that they don’t receive the necessary amount of sleep. 2 While this could be alright for a day or two, chronic sleep deprivation can cause serious health issues and exacerbate some already existing conditions.
Health conditions linked to lack of sleep
People who sleep for fewer than 7 hours a night are more likely to report having health issues, such as asthma attacks, heart attacks, and depression. The risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke is increased by certain of these medical conditions. These health issues consist of:
- Elevated blood pressure. Your blood pressure lowers when you are sleeping normally. Your blood pressure will be higher for a longer time if you have sleep issues. One of the major dangers for heart disease and stroke is high blood pressure. One in three individuals in America, or 75 million people, have excessive blood pressure.
- Diabetes type 2. Diabetes is a condition that can harm your blood vessels because it causes blood sugar levels to rise. According to several research, having adequate restful sleep may enhance people’s ability to control their blood sugar.
- Obesity. Unhealthy weight gain might be a result of sleep deprivation. Children and teenagers need more sleep than adults do, therefore this is particularly true for them. Lack of sleep may have an impact on the area of the brain that manages hunger.
How Sleep Deprivation Affect Heart Health?
There is strong evidence that sleep disorders, such as sleep deprivation and fragmented sleep, are harmful to heart health.
The body needs time to rest in order to heal itself. The non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep stages are characterised by a slowed heart rate, decreased blood pressure, and stable breathing. These modifications lessen the heart’s workload, allowing it to recover from the strain it experiences while awake.
Without enough sleep each night, a person doesn’t spend enough time in the deep NREM sleep stages that are good for the heart. Those who experience frequent interruptions to their sleep may experience the same issue.
Chronic sleep loss has been associated with a variety of cardiac issues, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart attacks, obesity, diabetes, and stroke.
Blood pressure during sleep
Blood pressure decreases by about 10% to 20% when you sleep normally and healthily. Research has shown that this practise, known as nocturnal dipping, is important for cardiovascular health.
Poor sleep is linked to non-dipping, which is when a person’s blood pressure doesn’t drop at night due to lack of sleep or sleep interruptions. According to studies, having high nocturnal blood pressure is associated with generalised hypertension (high blood pressure).
In fact, studies have shown that high blood pressure during the night is much more indicative of heart issues than high blood pressure during the day. Non-dipping has been linked to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. Reduced blood supply to the brain and kidney issues have also been connected to it.
Many studies have shown that sleep loss has the effect of raising daytime blood pressure, however not everyone is affected equally. In middle-aged people, the connection between sleep deprivation and high blood pressure is strongest. Individuals who have other hypertension risk factors, work long hours in stressful occupations, or have chronically poor sleep patterns are more likely to have elevated blood pressure.
Coronary Heart Disease and Sleep
The most common cause of death in the US is coronary heart disease. It is sometimes referred to as coronary artery disease and occurs when atherosclerotic atherosclerosis, or plaque buildup in the arteries, causes them to harden and narrow. The heart’s capacity to receive enough blood and oxygen is decreased as a result.
Lack of sleep has been linked to atherosclerosis, according to research. White blood cells, which are produced by the immune system and accumulate in the arteries as a result of inflammation, lead to the formation of plaque. Chronic inflammation is sparked by a lack of sleep, and this chronic inflammation makes the arteries harder and leads to plaque buildup.
It is also thought that the effects of sleep on blood pressure affect how sleep loss affects coronary heart disease. The arteries are strained by hypertension, which reduces their ability to carry blood to the heart and makes heart disease more likely.
Heart failure and sleep
Heart failure occurs when there is insufficient blood flow from the heart to provide the body with the oxygen and blood it requires to function. Strong correlations between sleep issues and heart failure were observed in an observational research including more than 400,000 persons.
People in that study had a higher chance of developing heart failure if they slept for fewer than seven hours per night. Heart failure was also more prevalent in individuals who had other signs of poor sleep, such as symptoms of insomnia, daytime sleepiness, snoring, and an evening personality. One’s risk of developing heart failure increases with the number of these symptoms of poor sleep they experience.
A Heart Attack and Sleep
When the blood supply to the heart is cut off, a heart attack—also referred to as a myocardial infarction—occurs. Due to the harm that results from the heart not receiving enough oxygen, heart attacks are sometimes fatal.
Lack of sleep increases the risk of heart attacks. According to one study, those who slept for fewer than six hours per night had a 20% increased risk of having a heart attack. NREM sleep aids the heart in slowing down and recovering, whereas REM sleep is more stressful and active. The balance of these stages can get off if you don’t get enough sleep, which raises your risk of having a heart attack.
Heart attacks may occur if sleep disturbances occur, according to some research. Frequent sleep disturbances can create cardiac stress and may result in a heart attack because both heart rate and blood pressure might suddenly jump upon awakening.
Stroke and sleep
A stroke occurs when the brain’s blood supply is interrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen and resulting in cell death. Ischemic strokes happen when an artery is blocked by a blood clot or plaque. A mini-stroke, also known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA), merely includes a momentary blockage.
Lack of sleep has been linked in studies to a higher chance of suffering a stroke. Lack of sleep raises blood pressure, and high blood pressure is thought to be the main contributor to stroke risk. Insufficient sleep may also make it simpler for blockages to happen and result in mini-strokes or strokes by promoting the building of plaque in the arteries.
Sleep and Heart Rate
The heart rate normally decreases throughout NREM sleep stages and then increases as you get ready to wake up.
A poor night’s sleep, particularly sudden awakenings, can cause a sudden increase in heart rate. According to research, those who have trouble sleeping are more prone to experience irregular heartbeats. These factors suggest that sleep deprivation and heart palpitations may be related.
Also, a research of senior citizens revealed that those who frequently experience nightmares are far more likely to report having an abnormal pulse. When a person’s sleep is disrupted by a nightmare, their heart rate may rise, and they may awaken feeling as though their heart is racing.
Chest Pain and Sleep
There are several causes of chest pain. Angina is a type of chest pain brought on by inadequate blood flow via blood arteries. Heart problems are unrelated to non-cardiac chest pain, such as heartburn or a muscle injury.
Studies have found a link between sleep deprivation and chest discomfort, and they also show that when sleep is disrupted, a fast rise in blood pressure and heart rate can result in angina.
Even non-cardiac chest pain may be related to sleep. Sleep disturbances are a common symptom of heartburn and acid reflux, which may increase the likelihood that these people will experience chest pain in the middle of the night.
Undiagnosed chest discomfort and poor sleep have also been linked in numerous studies. High incidence of symptoms like sleeplessness are present in those with persistent, unexplained chest discomfort. This connection may be related to stress and anxiety, including panic attacks, which are emotional responses that may be more frequent in persons with poor sleep, however its exact nature is unknown.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/news/20230301/insomnia-increases-risk-heart-attack-study
- https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/sleep.htm
- https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-deprivation/how-sleep-deprivation-affects-your-heart
For more details, kindly isit below.