Pregnancy: Low fiber may cause neurodevelopmental delays.
Low fiber intake during pregnancy may increase the risk of neurodevelopmental impairments in offspring, according to a recent study.
An essential part of a nutritious, well-balanced diet, particularly while pregnant, is fiber. With the right advice from nutritionists, pregnant women can increase their fiber consumption as necessary.
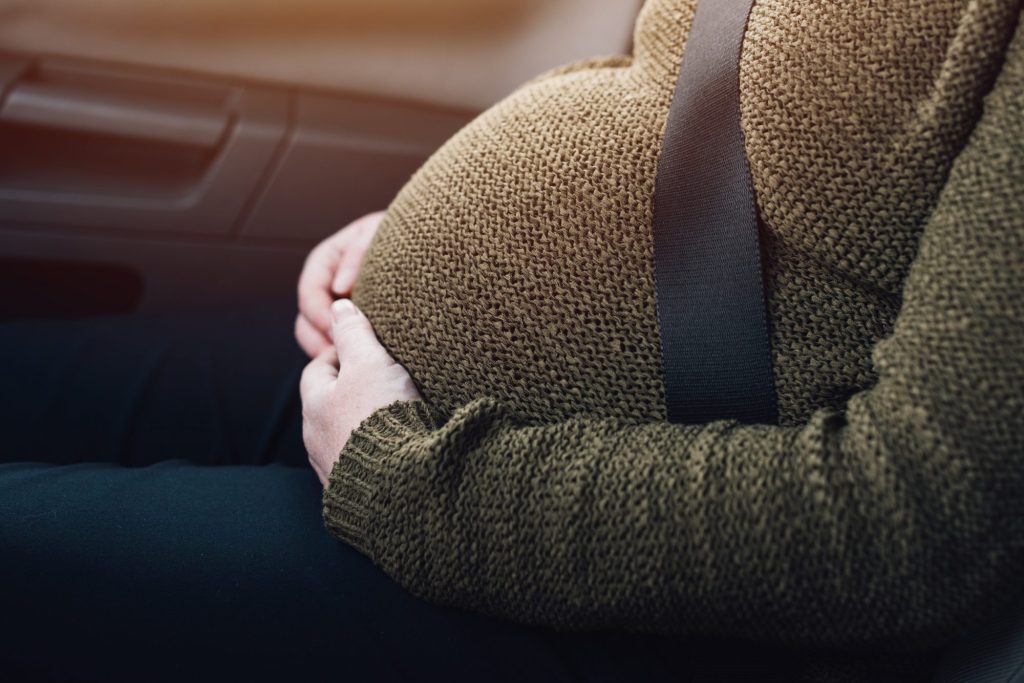

The complex period of pregnancy can have an impact on a variety of health consequences.
Researchers are still trying to figure out how behaviors and the environment during pregnancy affect the offspring’s later years.
The baby’s health and growth can be impacted by nutrition throughout pregnancy, but researchers are still trying to determine how various dietary details will affect the baby’s development.
Fiber intake during pregnancy was the subject of a recent study published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
According to the study’s findings, consuming less fiber during pregnancy increases the likelihood of neurodevelopmental impairments in the progeny.
Low fibre during pregnancy slows brain development
Researchers for the study observed that earlier research on animals had connected a reduced fiber diet during pregnancy to delayed brain development in children.
The data from 76,207 mother-infant pairs were evaluated by the researchers using information from the Japan Environment and Children’s Study.
They examined participants’ fiber consumption while pregnant and divided them into one of five groups according to how much fiber they consumed.
They then evaluated three-year-olds for developmental impairments. Parents or other primary carers were asked to complete questionnaires that measured children’s communication, fine and gross motor abilities, problem-solving, and personal-social skills to achieve this. With a lower score, there was more developmental delay.
In contrast to the group of moms who consumed the most total dietary fiber, the researchers discovered that those with the lowest fiber intake had the highest linked risk of having children with neurodevelopmental delays.
They discovered four crucial regions linked to slowed newborn brain development as a result of inadequate fibre intake:
- communication
- problem-solving
- personal-social
- small-motor abilities
The group with the lowest consumption of dietary fibre still carried significant risks for developmental delays, even when taking folic acid intake into consideration.
According to research author Kunio Miyake, Ph.D., of the University of Yamanashi, “most pregnant women in Japan consume far less dietary fiber than what is recommended intake; thus, this maternal nutritional imbalance during pregnancy may adversely affect the neurodevelopment of their offspring.”
Therefore, providing nutritional advice to expectant moms is essential to lowering the likelihood that their offspring would experience future health issues.
The authors of the study hypothesize that the results are due to the interaction of fiber with the brain’s microbiome and the gut microbiota.
“Dietary fiber is known to affect the regulation of gut microbiota and the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs),” Dr. Miyake said.
Recommendations for fibre during pregnancy
Fibre is a crucial part of a balanced diet and is especially necessary during pregnancy. Dr. Brian Power, Ph.D., an author of a non-study and nutritionist at Atlantic Technological University in Sligo, Ireland, explained to us:
Numerous studies show that increasing dietary fiber intake during pregnancy benefits many women by lowering the risk of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and uncontrollable weight gain.
The current USDA recommendation is for people to consume 14 grammes of fibre for every 1,000 calories they consume.
Therefore, with 2,000 calories per day, consumers should have roughly 28 grammes of fibre daily. A “low residue diet” or “low fibre diet” typically contains 10 to 15 grammes of fibre per day.
Only 8.4% of study participants exceeded the recommended daily intake of 18 grammes of fibre in Japan, where the recommendations range somewhat. The study’s findings may potentially indicate a risk from consuming too much fibre after accounting for folic acid.
It’s crucial to have open lines of communication with your medical team during your pregnancy in order to identify any potential nutritional deficits and how to make up for them.
How to increase your intake of fiber?
Your doctor might advise boosting your intake by eating more fiber-rich foods or taking supplements if your diet is lacking in the substance. High-fiber dietary examples come in the form of:
- whole-grain cereal with kernels
- artichokes
- beans
- a few fruits (such as raspberries, blackberries, and apples)
Dr. Al-Shaer stated, “Increasing fibre can be done simply by integrating more whole meals throughout the day, such as vegetables, legumes, nuts [and] seeds, and fruit.
“Many fruits, such as berries or bananas, are excellent sources of fibre, and all nuts and seeds are high in fibre. Try to fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables at each meal, which is a generally good rule of thumb I suggest to my patients. Except for potatoes, corn and peas, practically all vegetables are non-starchy. We can get enough fibre this way throughout the day. And a simple method to enhance our fibre intake is to sprinkle sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, flax seeds, or beans on salads or breakfast bowls,” according to registered dietician Abrar Al-Shaer, PhD.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/low-fiber-pregnancy-delayed-brain-growth
- https://www.awomansview.com/resources/low-fiber-diet-during-pregnancy-may-harm-babys-brain/
- https://www.psypost.org/2023/08/low-fiber-intake-during-pregnancy-may-delay-development-in-infants-brains-167472
For Pregnancy related medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?cPath=24