Get liberty from painful and frustating frozen shoulder.
The shoulder stiffens and loses mobility as a result of the common condition known as frozen shoulder. Additionally called sticky capsulitis.
Although these two illnesses are unrelated, the term “frozen shoulder” is sometimes used improperly to refer to arthritis. Arthritis can apply to one or more joints, whereas frozen shoulder particularly refers to the shoulder joint.
It often affects adults between the ages of 40 and 60, and women are more prone to develop it than males. About 3% of persons are thought to be affected. One or both shoulders may be impacted.
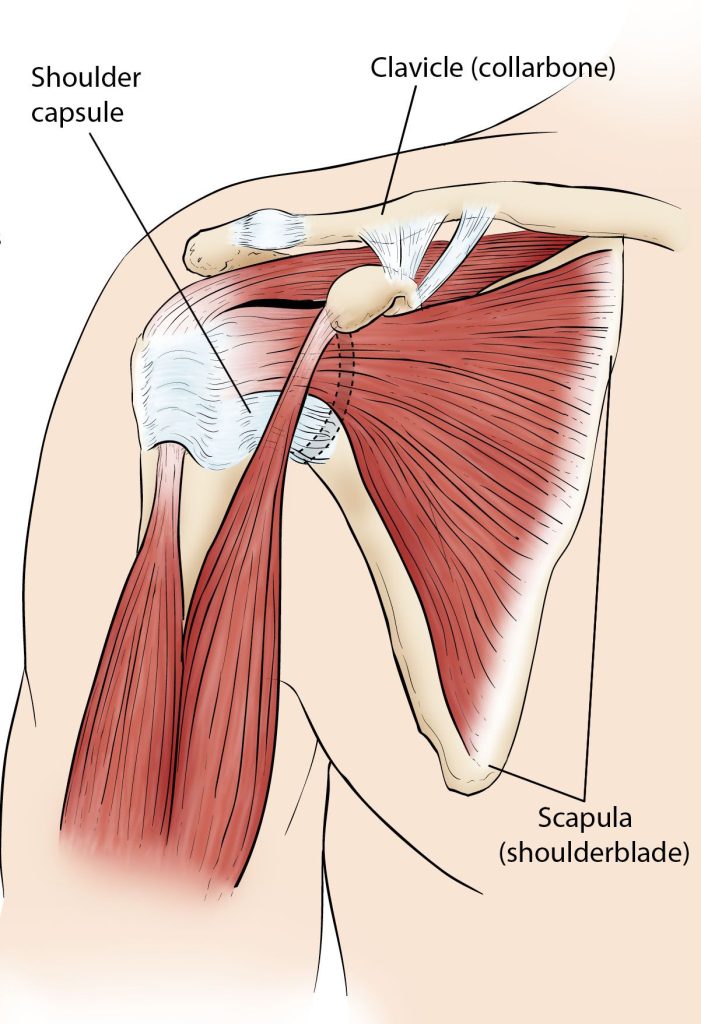
Three bones that make up your shoulder connect together in a ball and socket fashion. They are your collarbone, shoulder blade, and upper arm (humerus) (clavicle). Additionally, the tissue that surrounds your shoulder joint holds everything in place. The shoulder capsule is what we refer to as.
When a shoulder is frozen, the capsule grows to be extremely thick and rigid. Bands of scar tissue develop, and the synovial fluid needed to keep the joint lubricated is reduced. These things further restrict motion.
Symptoms of frozen shoulder
The major signs of a frozen shoulder are pain and stiffness, which make moving it challenging or impossible.
You’ll probably have a dull or aching pain in one shoulder if you have frozen shoulder. The shoulder muscles that surround the top of your arm may also be painful. Your upper arm can have the similar sensation. It might be difficult to fall asleep at night if your pain gets severe.
Typically, a frozen shoulder will go through three stages. Each has its own own timing and set of symptoms.
Freezing phase:
- Every time you move your shoulder, a pain (sometimes quite intense) develops there.
- Over time, it gradually grows worse and could hurt more at night.
- This may last for six to nine months.
- Your shoulder’s range of motion is constrained.
Frozen stage:
- Although your pain may lessen, your stiffness will only get worse.
- It gets increasingly challenging to move your shoulder and more challenging to carry out normal tasks.
- 4 to 12 months are possible during this stage.
Thawing phase:
- You begin to regain your normal range of motion.
- It could take anywhere from six months to two years to complete.
Causes of Frozen shoulders
Three bones make up the shoulder: the humerus, which is the upper arm bone, the collarbone, and the shoulder blade. A ball and socket joint is present in the shoulder. The upper arm bone’s rounded head slides into this socket.
The shoulder capsule is a band of connective tissue that encircles the joint. The joint can move freely thanks to synovial fluid.
The formation of scar tissue in the shoulder is hypothesised to cause frozen shoulder. As a result, there is less movement possible due to the capsule of the shoulder joint becoming thicker and more rigid. It could become unpleasant and stiff to move.
The actual cause is not always known and cannot always be determined. But the majority of those who have frozen shoulder have been immobile recently due to an accident or fracture. Patients with diabetes frequently experience the condition.
Who is at risk?
- Adults, typically between the ages of 40 and Adults, typically between the ages of 40 and 60.
- Gender: More prevalent in women than in men.
- Recent shoulder injury: Any operation or damage to the shoulder that necessitates immobilisation (by using a shoulder brace, sling, shoulder wrap, etc.). A rotator cuff tear and fractures of the shoulder blade, collarbone, or upper arm are two examples.
- Diabetes: Frozen shoulder affects between 10 and 20 percent of those with diabetes mellitus.
- Stroke, hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid gland), hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland), Parkinson’s disease, and heart disease are among the other illnesses and ailments. Because a stroke may impede arm and shoulder movement, it is a risk factor for frozen shoulder. The risk of having a frozen shoulder is higher in certain illnesses and circumstances is not clear.
How is frozen shoulder diagnosed?
In order to identify frozen shoulder, your doctor will:
- Review your medical history and talk about your symptoms.
- Examine your shoulders and arms physically:
- Your shoulder will be moved in all directions by the doctor to determine its range of motion and whether it hurts when you move it. Finding your “passive range of motion” involves an examination in which your doctor moves your arm rather than you.
- In order to determine your “active range of motion,” the doctor will also watch you move your shoulder. The two motions are contrasted. The range of motion for those who have frozen shoulders is constrained, both actively and passively.
- In order to confirm that another shoulder issue, like arthritis, is not the source of the symptoms, normal shoulder X-rays are also taken. In most cases, frozen shoulder can be diagnosed without the use of sophisticated imaging techniques like ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They might be examined to rule out other issues, like a torn rotator cuff.
Treatments for frozen shoulder
Until the early phase has passed, treatment typically consists of pain management techniques. If the issue continues, rehabilitation and surgery can be required to restore motion if it doesn’t happen naturally.
Several straightforward remedies are:
- Compresses, both hot and cold. These aid in reducing swelling and pain.
- Medications that lessen swelling and pain. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), which include acetaminophen (Tylenol®) and ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®). Your doctor might also recommend more painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications. Injections of steroids may be used to treat more severe pain and edoema. Direct injection of a corticosteroid, such as cortisone, into the shoulder joint.
- Physical treatment. Exercises for stretching and range of motion given by a physical therapist.
- Exercise regime at home. Maintain your home workout routine.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Using a tiny battery-powered device to block nerve impulses and so lessen pain.
After roughly a year of testing, if these straightforward treatments haven’t reduced discomfort and shoulder stiffness, alternative techniques may be explored. These comprise:
- Anesthesia-induced manipulation: During this procedure, your doctor will make your shoulder move by forcibly sedated you. As a result, the joint capsule will either stretch or rip, releasing the tension. The range of motion will consequently grow.
- During a shoulder arthroscopy, your doctor will make incisions through your joint capsule’s tight spots (capsular release). Your shoulder is sliced in small places, and tiny pencil-sized instruments are implanted.
For better outcomes, these two techniques are frequently combined.
Can frozen shoulder be prevented?
Physical therapy should be started as soon as possible following any shoulder injury that causes painful or problematic shoulder movement in order to prevent or at least reduce the likelihood of developing a frozen shoulder. An exercise regimen can be created by your physical therapist or orthopaedic physician to suit your individual requirements.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/frozen-shoulder
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/166186
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/frozen-shoulder/symptoms-causes/syc-20372684
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/what-is-a-frozen-shoulder
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15359-frozen-shoulder
For more details, kindly visit below.