Quick peek on causes of hiccups and its prevention.
The diaphragm uncontrollably contracts, which results in hiccups. Drinking carbonated beverages, indulging in a heavy meal, inhaling too much air, or being stressed are a few common triggers for this spasm.
What are hiccups?
The muscle tissue just below your lungs, the diaphragm, contracts repeatedly and uncontrollably during hiccups.
In addition to defining the boundary between your chest and abdomen, the diaphragm controls respiration. The contraction of your diaphragm causes your lungs to take in oxygen. Your lungs exhale carbon dioxide as your diaphragm relaxes.
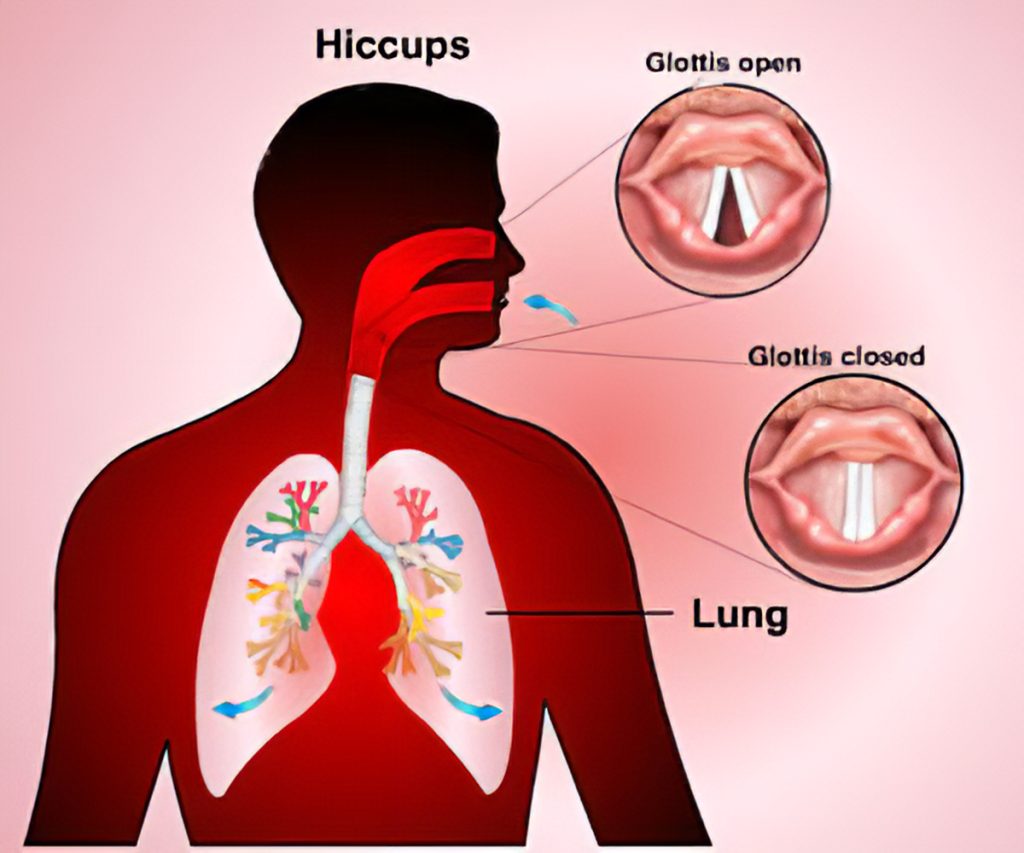
Hiccups are brought on by the diaphragm contracting irregularly. Every time the diaphragm contracts, the larynx (voice box) and vocal cords abruptly close. A quick rush of air enters the lungs as a result of this. Your body responds by gasping or chirping, which produces the hiccup-specific sound.
Hiccups can’t be predicted in advance. Prior to eliciting the unique hiccup sound, each spasm is typically preceded by a small constriction of the chest or throat.
The majority of hiccup episodes begin and terminate quickly and without apparent cause. Typically, episodes are only a few minutes long.
Causes of Hiccups
Why people experience hiccups is a mystery. Hiccups can occur for a variety of reasons, including inflamed nerves and low blood carbon dioxide levels. Important components of breathing include the vagus nerve, which connects the brain to the stomach, and the phrenic nerve, which runs from the neck to the diaphragm.
Mild hiccups (those that disappear quickly) can occur when you:
- Drink and eat too soon.
- ingest alcohol or fizzy beverages.
- Eat excessively.
- Feel anxiety, including exhilaration and terror.
- strain your neck too far.
- ingest drugs (particularly those for anxiety – benzodiazepines).
- Drink anything really hot or chilly.
- undergoing chemotherapy
- are put to sleep before an operation.
- inhale dangerous vapours.
Hiccups lasting for more than two days
Persistent hiccups are those that don’t go away after a few days. They are referred to as “intractable” if they persist for several months (long-lasting hiccups). Rarely do hiccups last for a long time. They could make you feel anxious and worn out. Hiccups that are difficult to control may be a symptom of a more serious underlying medical condition and may persist until that problem is resolved.
Among these more serious underlying problems are:
- tumours and cancer.
- Stroke.
- stomach or esophageal conditions, such as GERD (a gastrointestinal and abdominal disorder).
- the diaphragm’s pleurisy.
- Uremia.
- Pneumonia.
- Bowel ailments.
- irritated bladder and pancreatitis.
- Cancer of the liver with hepatitis
- lesions and tumours.
Additionally, hiccups might occur throughout a procedure’s recovery and after surgery. If your hiccups continue for a long time, consult a doctor.
How are hiccups diagnosed?
It’s simple to identify glitches. Simply hearing the “hic” sound will be enough for your healthcare provider.
However, your medical professional might do a physical examination to see whether an underlying condition might be the source of your hiccups. The physician may request testing including imaging tests, endoscopic tests, and blood tests if the physical examination indicates anything concerning.
How do I treat hiccups?
Some treatments could or might not be effective because the precise cause of hiccups is unknown. There is often no damage in attempting these at-home remedies because they won’t do you any harm. Home remedies consist of:
- swift water consumption.
- swallowing crushed ice, dry bread, or granulated sugar.
- tugging your tongue gently.
- Gagging (sticking a finger down your throat) (sticking a finger down your throat).
- rubbing your eyes softly.
- water is gargled.
- retaining breath.
- Taking a breath into a paper bag (do not use a plastic bag).
How are hiccups prevented?
Pre-treatment medicine can occasionally stop hiccups from occurring. For instance, taking metoclopramide before anaesthesia might stop the hiccups that can result from it. Ramosetron-containing steroids may stop chemotherapy-related hiccups.
Again, the following factors can result in minor hiccups (those that pass quickly). As a result, you might try to steer clear of the following to stop hiccups from occurring. Try to avoid:
- Drink and eat too soon.
- ingest alcohol or carbonated beverages
- Eat excessively.
- Feel anxiety, including exhilaration and terror.
- strain your neck too far.
- ingest drugs (particularly those for anxiety – benzodiazepines).
- Drink anything really hot or chilly.
- inhale dangerous vapours.
Possible complications of untreated hiccups
Hiccups that last a long time can be painful and potentially dangerous to your health. Long-lasting hiccups might interfere with your food and sleeping schedules and result in:
- sleeplessness
- exhaustion
- malnutrition
- slim down
- dehydration
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hiccups
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/181573
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hiccups/symptoms-causes/syc-20352613
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17672-hiccups
For more details, kindly visit below.