Significance of Malignant tissue Tumor and its treatment.
What is malignant soft tissue tumor?
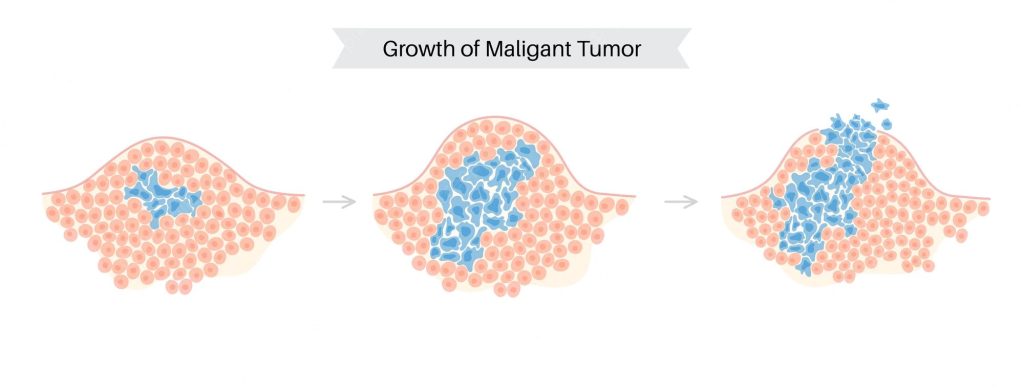
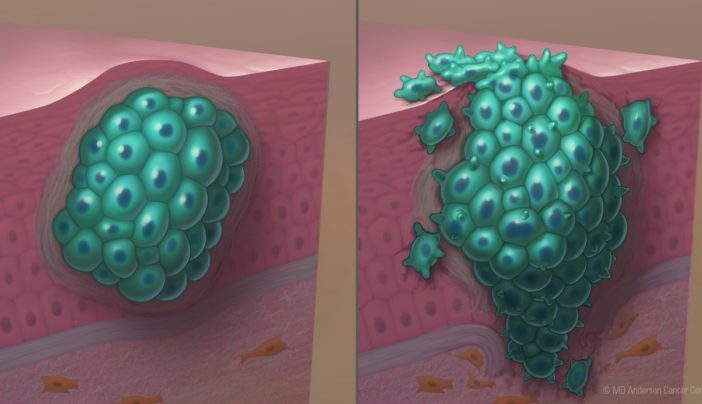
Malignant soft tissue tumours are uncommon and make up just 1% of all malignancies. These malignant tumours, sometimes referred to as sarcomas, develop in soft connective tissues. Your body’s connecting structures are formed and supported by soft connective tissues as well as bones. Soft tissues consist of:
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Cartilage
- Fat
- vascular system
- lymph nodes
Any area of your body might develop malignant soft tissue tumours, although 60% start in the arms and legs. 10% appear in the head and neck, while about 30% start in the torso or abdomen.
Who gets malignant soft tissue tumors?
Malignant soft tissue tumours can develop at practically any age, however they are most prevalent in people between the ages of 50 and 70.
These tumours come in over 50 different varieties. These tumours are typically categorised according to how they developed. Adults are most frequently affected by the following types:
- Desmoplastic tumours with tiny spherical cells.
- Stromal tumour of the stomach.
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Liposarcoma.
- malignant tumour of the peripheral nerve sheath.
- synthetic sarcoma.
- pleomorphic sarcoma that is not distinguished
- Angiosarcoma.
- The Kaposi sarcoma.
What are The Symptoms of Malignant Tumors?
It’s possible that you won’t detect a tumour until it’s too late. Their limbs and legs seem lumpy and unpainful at first, but they can get bigger before becoming painful!
Fatigue, weight loss, and pain are a few of the malignant tumours’ most prevalent symptoms. Malignant tumours can also alter the way the body looks by leaving lumps or bumps on the skin. For treatment, it’s critical to consult a doctor as soon as you have any of these symptoms.
Causes of Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumours can have a wide variety of causes, however it might be difficult to pinpoint a certain tumor’s exact origin. There are, however, a few risk factors that are linked to a higher chance of having a malignant tumour. These include a family history of cancer, exposure to specific chemicals and radiation, and specific chronic health issues.
Even though the precise aetiology of a malignant tumour may not yet be established, awareness-building efforts and the promotion of early detection and treatment can be aided by knowing the possible risk factors. Other typical causes include:
- additional body weight
- excessive alcohol use
- unsound nutrition
- active inactivity
Malignant soft tissue tumors diagnosis
Malignant soft tissue tumours require a number of processes to be diagnosed. Normally, a detailed medical history and physical examination are the first steps taken by healthcare professionals. They might also pass specific exams. Doctors can learn more about the tumour thanks to test results.
These tests could consist of:
- An X-ray scans the body to look for unusual growths.
- Using computers, computed tomography (CT) creates cross-sectional images of the inside of your body from a number of X-ray images. This examination is frequently performed to identify cancers in the chest, abdomen, or rear of the abdomen.
- Using a powerful magnet, radio waves, and a computer, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) produces detailed images of your body. If an X-ray is abnormal, you might order this to get sharper pictures.
- Using a particular glucose tracer concentrated in cancer cells, a PET scan can detect the presence of a fast expanding tumour by displaying regions of your body where the level of glucose is higher than normal.
- Ultrasound: This examination uses sound waves and their echoes to create images of various body parts.
- A portion of tissue from the afflicted area is removed during a biopsy so that it may be examined under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
Medical treatments
- Chemotherapy: Patients are administered medications intravenously or orally. In order to reduce tumours that will be removed during surgery or to eradicate any cancer cells that may still be present after surgery, chemotherapy may be utilised as the primary treatment.
- Radiation: Radiation may be used either before or after surgery to reduce tumour size and eradicate any cancer cells that may have survived.
- Targeted therapy: In order to alter how cancer cells survive and proliferate, targeted therapy targets particular components of cancer cells, such as genes and proteins.
Surgical procedures
Malignant soft tissue tumours are frequently treated with surgery in an effort to reduce the likelihood that the tumour may come back or spread. In order to remove the tumour completely and preserve as much healthy tissue as possible, surgeons must ensure that no cancer cells are left behind.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.metropolisindia.com/blog/preventive-healthcare/what-are-the-causes-and-treatments-of-malignant-tumors/
- https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/malignant
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17203-malignant-soft-tissue-tumors
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/249141
For more details, kindly visit below.