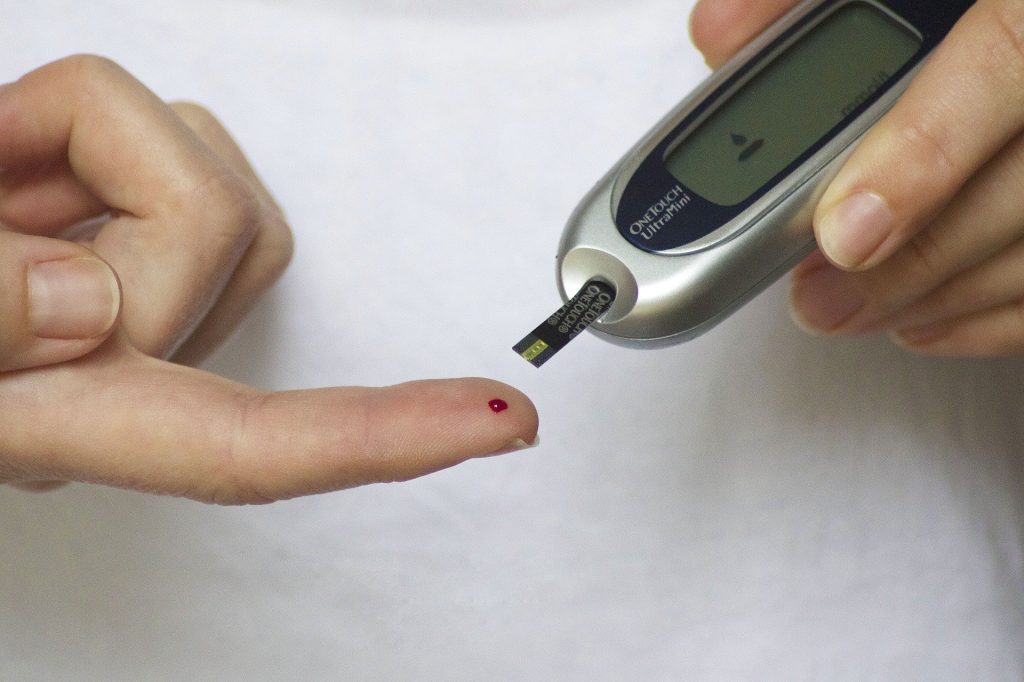
Once-weekly insulin vs daily injection: Which is better?
The effectiveness of once-weekly and once-daily insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes was compared by researchers.
They discovered that the once-weekly medication icodec reduced blood sugar levels more successfully than the conventional once-daily injections.
Further research is required, according to experts, to validate the findings. A novel, once-weekly insulin regimen may revolutionize care for type 2 diabetics, finds a recent study.
In a Phase 3 experiment, researchers compared the effectiveness and safety of once-weekly insulin termed “icodec” with the conventional once-daily injection degludec in adults with type 2 diabetes.
A long-acting insulin medication called Degludec aids in controlling blood sugar levels.
After 26 weeks, they discovered that once-weekly icodec therapy reduced blood sugar levels more than once-daily degludec. The research was released in JAMA.
Icodec may have similar glucose-lowering effects to daily insulin injections, according to a recent study.
Adherence issues with daily insulin injections
In the US, there are more than 37 million diabetics. These persons have type 2 diabetes in 90–95% of cases.
The hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas, enables cells to utilise glucose as fuel. When cells no longer react to insulin as they should, type 2 diabetes develops and elevated blood sugar levels follow.
The eyes, kidneys, and heart are just a few of the organs that elevated blood sugar can harm over time. Therefore, either lifestyle changes or the use of drugs that do not lower blood sugar with insulin is required for treatment.
When non-insulin treatments are ineffective, it is currently recommended by guidelines that persons with type 2 diabetes take insulin-based therapies to reduce blood sugar levels.
Currently, type 2 diabetes medications based on insulin necessitate daily injections. However, patients may find it difficult to administer daily injections, which lowers adherence rates.
According to research, weekly injections increase adherence. According to one study, individuals who receive insulin treatments once per week follow their treatment plans for an average of 333 days as opposed to 269 days for patients who receive daily injections.
Insulin therapy non-compliance might have serious repercussions. According to research, persons with diabetes who do not stick to their insulin medication have a higher risk of dying and being admitted to the hospital.
Thus, raising adherence rates is essential to enhancing diabetes patients’ quality of life and health outcomes.
Which is more effective? Once-weekly vs. daily insulin injection.
The researchers gathered 588 participants for the study, with an average age of 58, from 11 nations, including the USA, Argentina, and China.
Over a third of the participants were women, and every participant was on non-insulin glucose-lowering medication.
They were thereafter randomly assigned to receive one of the following treatment plans for a total of 26 weeks during the study:
- once every week icodec
- monthly placebo
- every day degludec
- a single-dose placebo
In the end, the scientists discovered that icodec more effectively lowered haemoglobin A1c (HBA1c) levels than degludec.
A measurement of the average blood sugar levels over the previous three months is called HBA1c. Those with diabetes are advised to maintain levels of 6.5% or lower. People without diabetes typically have HBA1c values of less than 5.7%.
Participants in the icodec group had HBA1c values that dropped from an average of 8.6% to 7% after 26 weeks. HBA1c values in the degludec group decreased from an average of 8.5% to 7.2% over this time.
The study’s authors found no discernible differences in participants’ fasting blood sugar levels or body weight between those taking icodec and those taking degludec.
We enquired about the potential causes of icodec’s superior results in lowering HBA1c readings from Dr. Absalon Gutierrez, associate professor of endocrinology at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston who was not engaged in the study.
Although we can’t be certain, it probably has to do with the patient’s compliance with the drug. According to how the trial was set up, it was significantly simpler to forget to administer the degludec injections than the icodec injections. According to Dr. Gutierrez, this is most likely the case in real life as well.
Side effects of icodec weekly insulin
The researchers also reported that from the beginning of the study until week 31, 5.8% of those using Degludec and 8.9% of those taking icodec suffered hypoglycemia. This is characterized by blood sugar levels that are below the normal range.
Additionally, during the duration of the experiment, 167 patients receiving degludec and 177 patients getting icodec both had adverse effects. According to the researchers, 46 and 60 incidents, respectively, were in the degludec group and the icodec group. This may have been caused by the use of insulin.
However, they pointed out that the majority of the incidents were minor, and that these included COVID-19, influenza, and diabetic retinopathy, an eye disorder that can impair vision in people with diabetes.
What are the research’s constraints?
The study’s shortcomings were listed by the researchers in their paper. They pointed out that because the trial only lasted 26 weeks, longer-term consequences are still undetermined.
They also stated that they did not gather information on patient-reported outcomes or data from continuous glucose monitoring.
Dr. Gutierrez stated: “Icodec exhibited higher hypoglycemia even though it worked somewhat better in decreasing HBA1c. Given that it can’t be titrated as regularly, this is to be expected. Additionally, the degludec titrations were not ideal according to the study’s design.
Dr. Lushun Wang, Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon and Medical Director of Arete Orthopaedic Clinic in Singapore and a non-participant in the study, was also interviewed by us:
“The trials’ duration can be extended further in order to guarantee dependable long-term efficacy and safety. To comprehend Icodec more fully, rigorous and in-depth testing should be conducted.
Data from continuous glucose monitoring may ensure a more thorough understanding of blood glucose control and its impact on the quality of life of the patient. In addition, the trial’s design used more Icodec injections than would be necessary for a daily regimen, which does not adequately reflect real-world use or any potential advantages for treatment adherence.
Effects of once weekly injection on diabetes
The researchers observed that by lowering the number of injections from at least 365 to 52 annually, icodec may increase treatment adherence and convenience for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
They went on to say that the “small absolute risk of hypoglycemia” should be outweighed by the ease and little additional glycemic advantage of once-weekly dosing.
Icodec’s practical design enables daily injections to be replaced with this once-weekly alternative, according to Dr. Wang. Its main benefit is from its capacity to deliver an insulin release that is steady and continuous over the course of a week. Hence minimizing swings in blood glucose levels. The improved HbA1c reduction seen in the studies is evidence that Icodec’s ability can result in better overall blood glucose control.
Dr. Guitierrez concurred that icodec insulin would be a viable choice for patients who struggle to take once-daily basal insulin as prescribed. To better understand the risk of hypoglycemia associated with using icodec in comparison to once-daily insulin injections, he pointed out that more research is required.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/type-2-diabetes-once-weekly-insulin-icodec-vs-daily-injection-efficacy
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(23)00520-2/fulltext
- https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/44/7/1586/138808/Switching-to-Once-Weekly-Insulin-Icodec-Versus
For Diabetes medications that have been suggested by doctors worldwide are available here https://mygenericpharmacy.com/index.php?therapy=13