Top causes, signs, and symptoms of Gallstone.
Gallstones are bile substance clumps that harden inside of your gallbladder. They come in sizes ranging from that of a sand grain to that of a ping pong ball. The majority of them aren’t harmful, but if they escape and enter your bile ducts, they may do some damage. Cholelithiasis is the medical term for the presence of gallstones.
What are gallstones?
Your gallbladder, a tiny, pear-shaped organ where your body stores bile, is where gallstones develop. They are concentrated bile components in the shape of pebbles. Cholesterol, bilirubin, bile salts, and lecithin are all components of bile fluid. The typical components of gallstones are cholesterol or bilirubin, which accumulate at the base of your gallbladder and harden into “stones” over time.
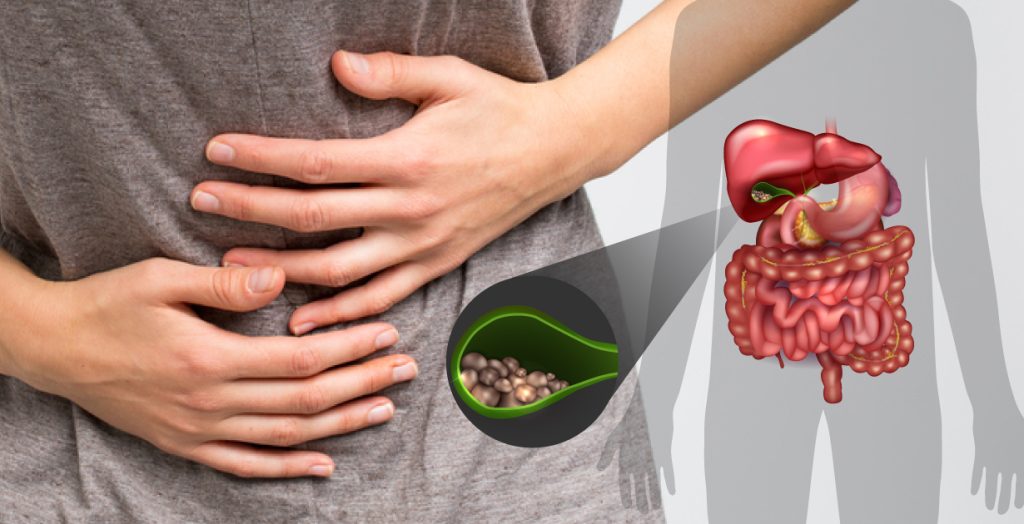
Gallstones can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. As the bile keeps washing over them and they continue to gather new materials, they eventually develop. The smaller stones are actually more prone to create problems. Smaller stones can move, whereas larger ones have a tendency to remain stationary. Traveling gallstones may become obstructed and lodged somewhere.
How does having gallstones affect you?
Your biliary system includes your gallbladder. It is a part of a system of organs that exchange bile with one another. The bile ducts, a network of pipes, connect these organs. The bile ducts carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and then from the gallbladder to the small intestine. Additionally, your pancreas delivers its own digesting juices through the bile ducts.
The passage of bile into or out of your gallbladder might be obstructed by a gallstone that moves near its mouth. A gallstone that escapes from your gallbladder and enters your bile ducts may stop bile from flowing through them. Bile will back up into the adjacent organs as a result of this. Your organs and bile ducts experience pressure, pain, and inflammation when bile backs up.
Signs and symptoms of gallstones
The upper right abdomen or the middle of your stomach may hurt as a result of gallstones. Occasionally, eating fried or high-fat foods may cause you to have gallbladder pain, although this can happen at nearly any time.
Gallstone-related pain often only lasts a few hours, but it can be very painful. The symptoms of gallstones may worsen and eventually include the following:
- elevated temperature
- quick heartbeat
- the skin and eye whites are becoming yellow (jaundice)
- rough skin
- diarrhoea
- chills
- confusion
- a decrease in appetite
These signs could indicate a gallbladder infection or an inflammation of the pancreas, liver, or gallbladder. No matter what, if you’re experiencing one or more of these problems, it’s essential to visit a doctor or head to the emergency room. Gallstone symptoms can resemble the symptoms of other deadly conditions including appendicitis and pancreatitis.
Asymptomatic gallstones
Gallstones don’t hurt by themselves. Instead, pain happens when gallstones obstruct bile flow from the gallbladder.
The American College of Gastroenterology estimates that “silent gallstones” affect roughly 80% of persons with gallstones. This indicates that they are symptom- and pain-free. In certain situations, your doctor might find the gallstones during abdominal surgery or using X-rays.
Causes of Gallstone
It is believed that a bile chemical imbalance within the gallbladder is the real cause of gallstones. Although scientists are still unsure of the precise explanation for the imbalance, there are a few potential causes:
Cholesterol buildup in bile
Yellow cholesterol stones might develop if your bile contains an excessive amount of cholesterol. If your liver produces more cholesterol than your bile can break down, these hard stones may form.
Excessive bilirubin levels
A substance called bilirubin is created as part of the regular breakdown of red blood cells. Following creation, it moves through the liver before being subsequently eliminated from the body.
Your liver may overproduce bilirubin under certain circumstances, such as liver disease and some blood diseases. When your gallbladder is unable to break down the extra bilirubin, pigment gallstones develop. They are typically black or dark brown in colour.
Bile that is concentrated because the gallbladder is packed
For your gallbladder to work effectively, it must be able to release its bile. Insufficient bile excretion can result in too concentrated bile, which can lead to the formation of stones.
Risk factors for gallstones
While certain gallstone risk factors can be influenced by food, others are less so. Age, race, sexual orientation, and family history are examples of uncontrollable risk variables.
Risk factors for lifestyle
- living while overweight
- a low-fiber, high-fat, or high-cholesterol diet
- shedding pounds quickly
- having type 2 diabetes nowadays
Genes as risk elements
- a female birth gender
- being of Mexican or Native American ancestry
- having gallstones running in one’s family
- being at least 60 years old
Medical danger signs
- experiencing cirrhosis
- having a baby
- taking certain drugs to reduce cholesterol
- taking prescription drugs high in oestrogen (like certain birth controls)
Despite the fact that some drugs may raise your risk of developing gallstones, don’t stop taking them without first speaking with your doctor.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gallstones
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7313-gallstones
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/symptoms-causes
For more details, kindly visit below.