What is the primary role of calcium in a human body?
What is Calcium?

Calcium is a kind of mineral that a human body consumes through the intake of food. It is one of the most bountiful minerals that is necessary for all living organisms. More than 99% of calcium of a human body is found in teeths and bones and the remaining is found in extracellular serum calcium. This mineral is distributed among departments of various tissues in a human body. Several other vitamins may also be required to maintain or increase the absorption rate of calcium in the body.
The Primary role of calcium inside the body is to improve or maintain healthy teeth and bones. Your body uses calcium to maintain bones and teeth for ages. Healthy amount of calcium in the body could prevent bone disease such as Osteoporosis for the lifetime.
Calcium also plays an important role for releasing hormones and other chemicals, cardiovascular functions, muscle movements, etc. It is a cofactor for many enzymes and plays an important role for enzymes working efficiently.
Benefits of Calcium intake
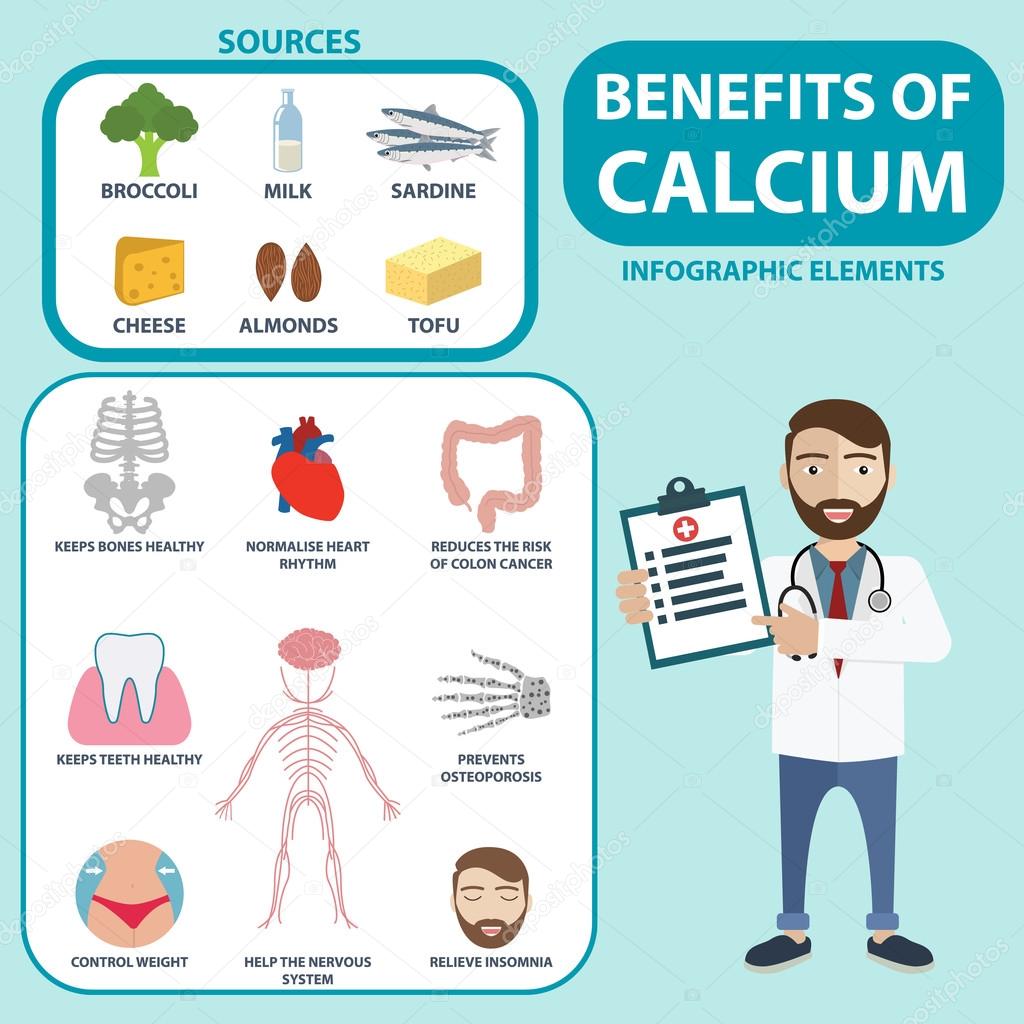
Calcium consist of various health maintenance benefits to make sure several parts, organs, and function of your body get least affected due to aging that include
- prevention and maintenance of healthy bones.
- maintains the action of heart muscles and heartbeat.
- plays an important role in blood clotting.
- reduces risk of a non-cancerous tumor called colorectal adenomas.
- lower blood pressure in younger people and in pregnant conditions.
- improves cholesterol level in the body.
- releases hormones and other chemicals.
- helps nervous signals for communication within the body.
Ways to get enough calcium
Eating a range of healthful meals from all the different food categories is the greatest approach to ensure that you get enough calcium every day. To assist the body absorb and use calcium from meals, it’s critical to get adequate vitamin D each day from foods like fortified milk or from exposure to the sun.
Here are some simple tips for choosing calcium-rich foods:
- Calcium content is higher in dairy products. Milk, yoghurt, and cheese are dairy products. Milk has 300 mg of calcium in a cup (8 ounces). The amount of calcium in skim, low-fat, and whole milk is the same.
- Vegetables that are dark green and have leaves are rich in calcium. All three vegetables—broccoli, kale, and collards—are excellent calcium sources, especially when consumed raw or just heated. (Vegetables lose a lot of their mineral content when they are boiled.)
- About 200 mg of calcium can be found in a serving of canned salmon or sardines. It is located in the fish’s soft bones.
- Calcium can be added to the diet through foods like cereal, pasta, bread, and other grain-based foods. Look for cereals that have been fortified with calcium and other minerals.
- In addition to cereal, calcium may also occasionally be added to tofu, soy and rice beverages, and fruit juices. To determine whether a food item contains additional calcium, read the product label.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.helpguide.org/articles/healthy-eating/calcium-and-bone-health.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002412.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4337919/
- https://www.abplive.com/lifestyle/health/calcium-for-bone-health-food-source-symptoms-of-deficiency-2008884
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213453016000021
For more details, kindly visit below: