Candidiasis: The most dangerous fungal infection possible?
On your skin, various bacterial and fungal species can be found. The majority of them are not harmful. Most of them are necessary for your body to function normally. However, some can spread illnesses if they start to grow out of control.
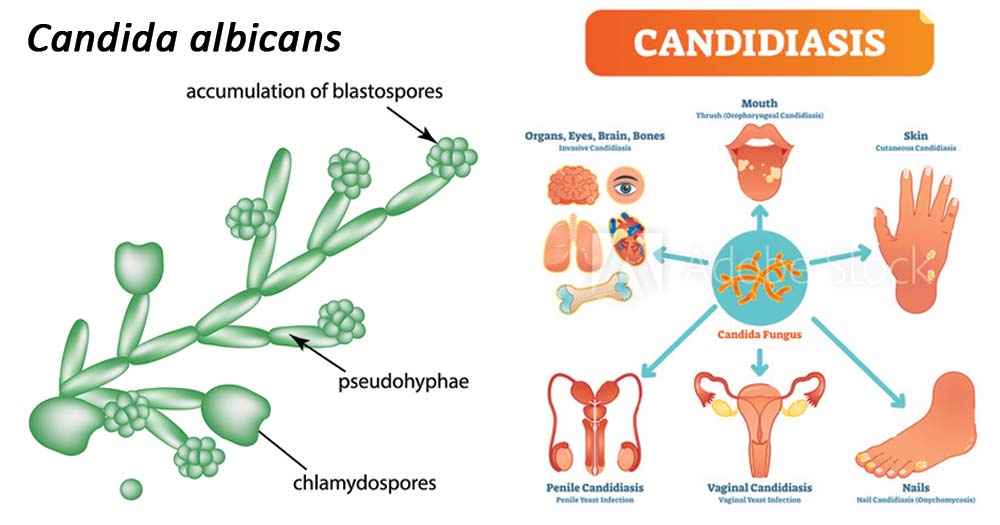
One of these potentially hazardous species is the Candida fungus. An infection may happen if there is an overgrowth of Candida on the skin. The term “candidiasis of the skin” or “cutaneous candidiasis” refers to this condition.
A red, itchy rash frequently develops as a result of cutaneous candidiasis, most frequently in the folds of the skin. Other body parts may also become affected by this rash. Even though the symptoms can be annoying, they are typically treatable with better hygiene with antifungal creams or powders.
Symptoms of candidiasis of the skin
A rash is the primary sign of cutaneous candidiasis. The rash frequently produces redness and excruciating itching. In some instances, the infection might result in painful, cracked skin. Additionally possible skin conditions include pustules and blisters.
Although the rash can appear anywhere on the body, it most frequently appears in skin folds. This covers regions under the breasts, between the fingers, in the groyne, and between the armpits. Additionally, candida can result in infections in the corners of the mouth, nails, and nail edges.
Other medical diseases that resemble skin candidiasis include:
- ringworm
- hives
- herpes
- skin problems associated with diabetes
- Dermatitis from touch
- Dermatitis seborrheica
- Eczema
- psoriasis
What causes candidiasis of the skin?
Skin infections with Candida lead to the development of candidiasis. On the skin, Candida fungus normally exist in modest numbers. But when this kind of fungus starts to grow out of control, it might result in an infection. This might happen as a result of
- a warm climate
- slender clothing
- bad hygiene
- irregular underwear changes
- obesity
- using medicines to eradicate safe microorganisms keeps Candida under control.
- using corticosteroids or other drugs that have an impact on the immune system
- a compromised immune system brought on by diabetes, pregnancy, or another health issue
- inadequate skin drying after being damp or wet
Candida fungi flourish and spread in warm, humid environments. This explains why the illness frequently affects regions with skin wrinkles.
Skin candidiasis typically isn’t contagious. However, those with compromised immune systems run the risk of contracting the disease after coming in contact with an infected person’s skin. A serious infection brought on by candidiasis is also more likely to occur in people with weakened immune systems.
Types of Candiasis and treatment
- Cutaneous candidiasis – A variety of topical antifungal medications can be used to treat the majority of localised cutaneous candidiasis infections (eg, clotrimazole, econazole, ciclopirox, miconazole, ketoconazole, nystatin)
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis: Oral azoles are typically used to treat this illness.
- Oropharyngeal candidiasis – Treatment options for oropharyngeal candidiasis include systemic oral azoles or topical antifungal medications.
- Esophageal candidiasis – Treatment for esophageal candidiasis involves fluconazole systemic therapy.
- VVC – Fluconazole can be taken orally or applied topically to treat fungus.
- Candida cystitis – Fluconazole should be used to treat Candida cystitis in non-catheterized patients; in catheterized patients, the Foley catheter should be changed or removed; and if the candiduria still occurs after the catheter change, fluconazole can be used to treat the patient.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/skin/cutaneous-candidiasis
- https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/index.html
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/guide/what-is-candidiasis-yeast-infection
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213853-overview
- https://www.britannica.com/science/candidiasis
For more details, kindly visit below.