What are the best ways to prevent Pneumonia?
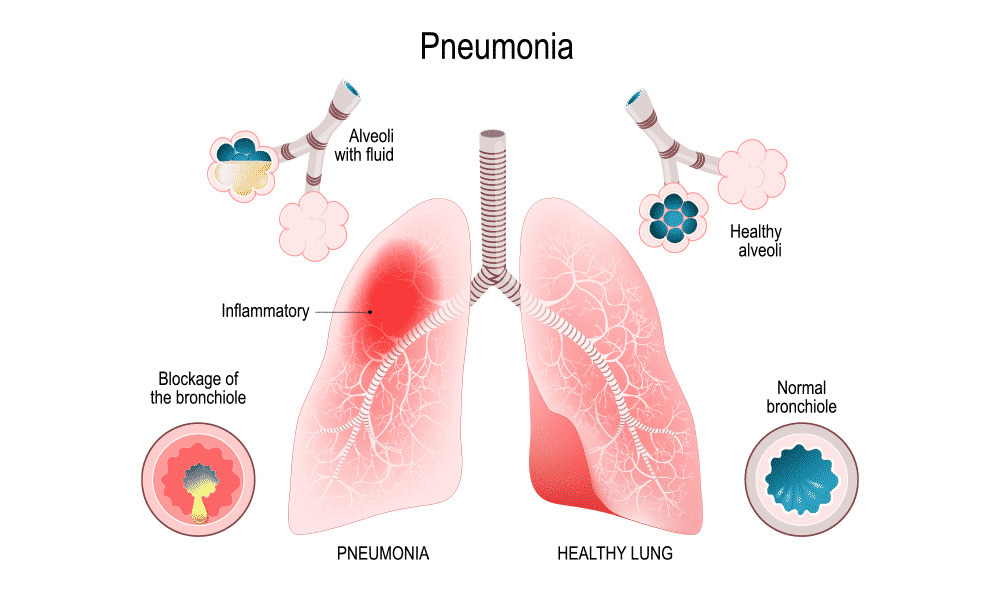
A buildup of fluid or mucus can lead to pneumonia, a lung infection. Your alveoli, which are tiny air sacs that transport oxygen from the air you breathe into your blood, are less effective as a result of these buildups.
Although pneumonia is not communicable, it can be brought on by a variety of factors, some of which may be contagious. These consist of:
- viruses
- bacteria
- fungus
- chronic lung conditions
- asthma
- smoking
- utilising a ventilator
- more upper respiratory illnesses
When you breathe in food, stomach acid, or saliva into your lungs, you can have a specific type of pneumonia called aspiration pneumonia.
Because of procedures that interfere with normal breathing, such as the requirement for a “breathing tube” (also known as an endotracheal tube), inactivity, or taking specific medications, being in the hospital can increase a patient’s risk of developing pneumonia.
Ways to prevent risk of Pneumonia
Vaccination for pneumococcal conjugation
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccination (PCV13) offers defence against 13 different bacterial species that can lead to life-threatening illnesses in both children and adults.
PCV13 is one of the routine vaccinations given to infants, and it is given by a paediatrician. Beginning when they are 2 months old, it is administered to infants in a series of three or four doses. Babies receive their final dose by the age of 15 months.
PCV13 is administered as a one-time injection to persons 65 years of age and older. Your physician might advise revaccination in five to ten years. This vaccination should also be given to people of any age who have risk factors, such as a compromised immune system.
Vaccination for pneumococcal polysaccharides
One dose of the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) provides protection against 23 different bacterial species.
It is not suggested for kids. Adults over 65 who have already gotten the PCV13 immunisation are given the PPSV23 vaccine. Usually, it’s presented a year later.
This vaccination should also be given to people aged 19 to 64 who smoke or have health issues that raise their risk of pneumonia. Most people who receive PPSV23 at age 65 don’t need to get it again later.
Clean your hands.
Though pneumonia itself is not contagious, it can be brought on by a number of infectious agents, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The easiest approach to prevent introducing these organisms into your respiratory system is by regularly washing your hands.
- Make careful to thoroughly wash your hands by utilising the following procedures:
- Use clean, preferably running water, to wet your hands.
- Use enough soap to completely cover your hands’ and wrists’ surfaces.
- Your hands should be fully and quickly lathered. Make sure to scrub your hands, wrists, fingernails, and all other exposed surfaces.
- Spend no less than 20 seconds cleaning your hands and wrists.
- Put your hands and wrists in clean, preferably running, water to rinse them.
- Use a fresh towel to dry your hands and wrists, or let them air dry.
- To stop the faucet, use a towel.
You can also wash your hands with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer if you don’t have access to soap and water.
Avoid being around sick individuals.
The majority of respiratory illnesses are transferred by minuscule airborne or surface-contact particles. Avoiding contact with sick persons is a crucial step in avoiding pneumonia and other respiratory infections.
If you must be among ill individuals or are in a busy environment, make sure to:
- regular hand washing
- Wear a mask over your mouth and nose to avoid the flu dependable source, chilly, and COVID-19 dependable source
- urging people to hide their sneezes and coughs
- Do not exchange personal things
Make healthy choices.
Your body’s capacity to fend off infections that can result in pneumonia is strongly influenced by how you take care of your body and the world around you.
The following activities can help you fortify your immune system and lungs:
- having enough sleep
- maintaining a healthy diet
- exercising consistently
- eschewing smoking
- lowering your exposure to toxic substances or pollutants
- maintaining a current immunisation schedule
Prevent pneumonia from developing from a cold
Ask your doctor what preventative measures you may take if you already have a cold to keep it from developing into pneumonia.
Some recommendations are:
- ensuring adequate sleep when recuperating from a cold or other illness
- consuming a lot of water to relieve congestion
- supplementing with zinc and vitamin C to strengthen your immune system
What happens if I get pneumonia?
The type of pneumonia you have and its severity will determine how it is treated. One portion of your lungs may only be affected by pneumonia, or it may spread to both of your lungs’ interior spaces.
Antibiotics may be administered to you if a bacterial infection caused your pneumonia or if the fluids that accumulate after aspiration get infected. Antifungal drugs can also be used to treat fungus-related pneumonia.
Antibiotics and Antifungals won’t help if the virus that is causing your pneumonia is caused by them. Antiviral medication may be used to treat various viruses, such as the flu. Otherwise, the best way to treat viral pneumonia is with supportive care, possibly even in a hospital.
Regardless of the cause, severe cases of pneumonia may necessitate the use of more intensive therapies, such as supplemental oxygen, breathing treatments, or even mechanical ventilation.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/influenza-seasonal
- https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/preventing-pneumonia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-prevent-pneumonia
- https://apic.org/monthly_alerts/top-9-ways-to-reduce-the-risk-of-pneumonia-if-you-or-a-loved-one-is-hospitalized/
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/can-you-prevent-pneumonia
For more details, kindly visit below.