How dangerous is a Benign tumor and its types?
What is Benign tumor?
Noncancerous growths in the body are known as benign tumours. They have distinct borders, modest growth, and can appear anywhere on the body. They don’t spread to other bodily parts like malignant tumours do.
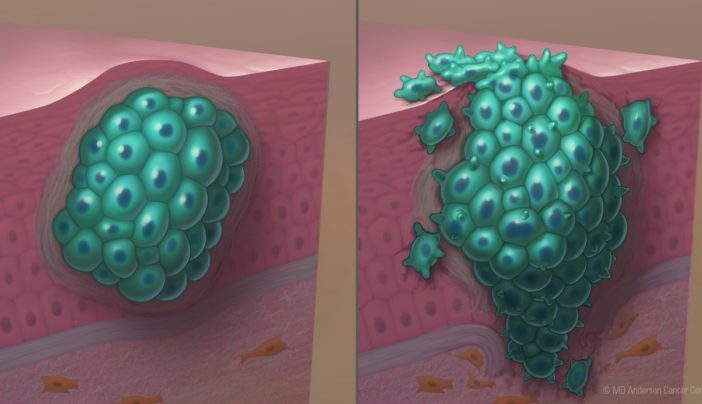
You could presume it is a cancerous tumour right away if you find a lump or mass in your body that can be felt from the outside. For instance, women who self-examine their breasts and discover lumps are frequently worried. The majority of breast tumours are benign, nevertheless. In actuality, the majority of growths on the body are benign.
Over 90% of breast tissue changes are benign, and benign growths are highly prevalent. Similar to other cancers, benign bone tumours are more common than malignant bone tumours.
Types of Benign Tumor.
Numerous benign tumours can form in various locations throughout the body.
Whereas benign tumours grow determines their classification. For instance, lipomas develop from fat cells while myomas do so from muscle. Below are some examples of several benign tumours:
Adenomas
A thin layer of tissue called epithelial tissue, which covers glands, organs, and other internal systems, is where adenomas develop. The development of colonic polyps and liver tumours are two examples. The thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands can all develop adenomas.
These tumours may progress to cancer. In fact, one in ten colon adenomas progress to cancer.
Lipomas
The most frequent kind of benign tumour, lipomas develop from fat cells. A lipoma will appear once every 1,000 people in their lifetime. They frequently appear on the neck, back, shoulders, and arms. They can be somewhat manipulated under the skin and are typically spherical and velvety.
Treatment for lipomas might not be necessary unless they are painful or developing quickly. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, they also seldom get cancer. Lipomas can develop at any age, however they are most prevalent in persons between the ages of 40 and 60.
Myomas
Myomas can develop in blood vessel walls or from muscle. They can also develop in smooth muscle, such as that which lines the uterus, the stomach, or the gastrointestinal tract. It is also referred to as a uterine fibroid if the myoma forms in the uterus.
Fibroids
Fibroids, also known as fibromas, can develop in any organ, tendon, or ligament’s connective tissue. They are called uterine fibroids in the uterus, where they are most prevalent. (Uterine myomas and leiomyomas are other names for uterine fibroids.)
The symptoms of uterine fibroids include severe vaginal bleeding, back or pelvic pain, and stomach pressure. Although they are rarely malignant, surgery for fibroid may be required to treat the symptoms.
Nevi
Moles are another name for nevi. These are typical, non-cancerous skin growths that can be tan, brown, pink, or even black in appearance.
Dyplastic nevi, for example, have a higher risk of turning into skin cancer. In order to detect these changes, routine skin exams are required.
Skin tags and other benign skin neoplasms are examples of skin growths. These atypical growths should be monitored for cancerous developments, just as moles.
Hemangiomas
Benign tumours called hemangiomas develop from blood vessels. The skin or internal organs like the liver or intestines may accumulate blood vessel cells. You might notice a red or bluish mark on the skin when it occurs. On the head, neck, or trunk, these are frequently seen. These typically disappear on their own and are seen as birthmarks by some people.
Hemangiomas that are close to the eyes or ears might impair hearing or vision. Furthermore, they may bleed or get ulcers. Some people need medical attention or laser therapy. In some situations, surgery can be required.
Meningiomas
Meningiomas are benign tumours that grow in the membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord, or the meninges. These tumours might not present any symptoms, but they may do so if they enlarge significantly or put pressure on the brain or spinal column. These signs include a headache, a seizure, side weakness, and eyesight issues.
These tumours can sporadically develop cancer. According to research, 1–3% of meningiomas develop into cancerous brain tumours.
Neuromas
Benign brain tumours called neuromas develop inside of nerves. Almost anyplace in the body can experience them. The peripheral nervous system’s nerve sheaths generate schwannomas. Neurofibromas form on nerve tissue and can also spread deeper into the body, such the bladder, than the skin.
Osteomas
Exostosis, also name for osteomas, is the benign development of new bone over preexisting bone. Any bone in the body could be affected by this. It is known as an osteochondroma when the bone growth is coated in cartilage.
Some growths may not hurt and don’t require medical attention. However, some of them can hurt and may require surgery to be removed. They have no probability of developing into cancer.
Causes of benign tumors
A benign tumor’s precise cause is frequently unknown. It arises when the body’s cells divide and grow too quickly. The body usually manages to keep cell division and development in check. When a cell dies or becomes damaged, new, healthy cells are produced in its place. Tumors are growths that are created when dead cells are left behind and stick together.
The same processes govern cancer cell growth. Cancerous cells can invade neighbouring tissue and spread to other parts of the body, in contrast to the cells in benign tumours.
Although the exact cause of benign tumour development is unknown, there are some possible explanations. These consist of:
- environmental elements like chemicals, radiation, or poisons
- infection or inflammation
- diet
- localised ailment or damage
- stress
- genetics
Even children can acquire benign tumours, while adults are more prone to do so as they become older.
Symptoms of benign tumors
Neither benign nor malignant tumours always exhibit symptoms. The operation of critical organs or the senses may be impacted by a number of symptoms, depending on the location of the tumour.
Possible signs of a benign tumour, depending on the location, include:
- chills
- annoyance or pain
- fatigue
- fever
- reduced appetite
- morning sweats
- slim down
Even benign tumours that are close to the skin may be large enough to be noticed. The majority, nevertheless, aren’t painfully or discomfortingly enormous. If they are, they can be taken away. Lipomas, for instance, are often soft, moveable, and painless, yet they can be large enough to be detected.
Benign skin-surface tumours like nevi or hemangiomas may exhibit some degree of skin pigmentation. Anything that seems strange has to be examined by a physician. Depending on where they are growing, some benign tumours could produce particular symptoms. These consist of:
Benign brain tumour
A benign brain tumour may cause the following symptoms:
- headaches
- vision issues
- unclear memory
- seizures
A meningioma or other tumour pushing on the brain or spinal column causes these symptoms to appear. Your daily life may be impacted by symptoms, which may necessitate therapy.
Benign breast tumour
Although most alterations to breast tissue are benign, some tumours may still be large enough to be felt by hand. The following are signs of these benign breast growths:
- elevated lump beneath or on the skin
- If near the skin, it would be large enough to feel.
- EIther firm or soft, while pressing
- may change if you press
benign bone tumour
Osteomas and osteochondromas are benign bone tumours that rarely produce symptoms, but they can if they are large or close to joints. These signs comprise:
- notably in the muscles or joints
- bone or nerve pressure
- complete range of motion is challenging
- Shorter on one limb than the other
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/benign
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22121-benign-tumor
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/benign-tumors-causes-treatments
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/benign-tumor
For more details, kindly visit below.