What is the reason behind white and formy Diarrhea?
What is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea is a common symptom, characterised by loose, watery, and possibly more frequent bowel movements. It can occur alone or in conjunction with other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or weight loss.
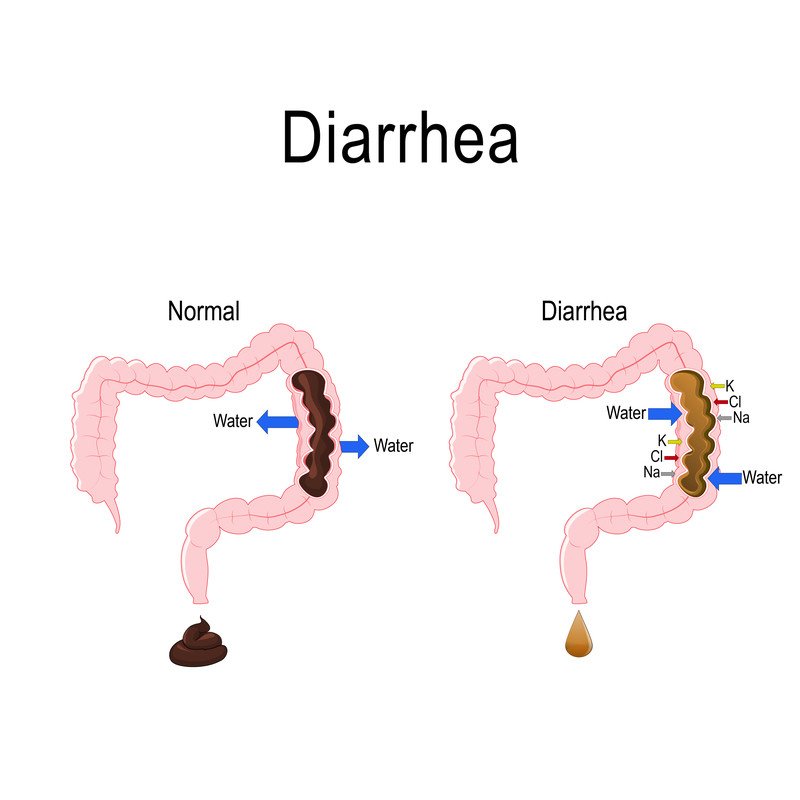
Fortunately, diarrhoea is usually only temporary, lasting only a few days. When diarrhoea lasts for several days or weeks, it usually indicates the presence of another problem, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or a more serious disorder, such as chronic infection, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Even while most instances of diarrhoea are self-limited (lasting a certain period of time and progressing at a constant rate of severity), it can occasionally cause life-threatening consequences. Dehydration (when your body loses a lot of water), electrolyte imbalance (loss of sodium, potassium, and magnesium), and renal failure (not enough blood or fluid is delivered to the kidneys) are all effects of diarrhoea.
Along with excrement, diarrhoea causes the loss of electrolytes and water. To replenish the lost fluids, you must consume enough of liquids. If dehydration does not improve, worsens, or is not properly treated, it may become dangerous.
What causes diarrhea?
There are various ailments or situations that might produce diarrhoea. Possible reasons Among the reliable sources of diarrhoea are:
- bacterial infections, such as Salmonella and E. coli, parasite infections, and viral gastroenteritis such as rotavirus, norovirus, and gastroenteritis
- intestinal conditions, food intolerances such lactose intolerance, and drug interactions
- stomach or gallbladder surgery
Globally, rotavirus is the most frequent cause of acute diarrhoea. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that this virus accounts for about 40% of hospitalizations among kids under the age of five. The majority of diarrhea-related deaths occur worldwide as a result of tainted water sources and inadequate sanitation.
A more serious disorder like irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease may show symptoms of chronic diarrhoea. Intestinal illness or a functional bowel dysfunction may be indicated by frequent and severe diarrhoea.
Symptoms of diarrhea
Frequent loose, watery stools and a strong urge to urinate are the two main signs of diarrhoea.
Diarrhea can cause a variety of distinct symptoms. Only one of these things might happen to you, or any combination of them might. The reason determines the symptoms. It’s normal to experience one or more of the followingTrusted Source feelings:
- Constant urges to urinate include nausea, abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, dehydration, and abdominal cramps.
- an abundance of stools
- dehydration
White and formy Diarrhea
While a standard stool is typically solid and brown, there are various variances that might occur. Stool that is foamy or frothy usually resembles diarrhoea and may even appear to have bubbles in it. It could also appear oily or have mucous in it.
Foamy stools are frequently a reaction to specific foods. If so, it will be a singular occurrence that gets better with time and fluids. Generally speaking, eating more fat than the body can break down can lead to frothy stools. Foamy stools, however, might also be an indication of a serious medical issue.
Causes
Disorder of malabsorption
The condition known as malabsorption disorder occurs when the body is unable to properly absorb or utilise nutrients from diet. Celiac disease is a prevalent malabsorption problem. This occurs when a person consumes gluten and experiences an autoimmune reaction, resulting in intestinal inflammation and other gastrointestinal symptoms like changes in faeces.
Similar symptoms can be brought on by dietary intolerances to different foods. These foods consist of Sugar alcohols such mannitol, sorbitol, and xylitol, as well as eggs, fructose, lactose, and shellfish.
After consuming a particular dish, a person could get frothy stools. They might also feel queasy or bloated.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can be either acute or chronic. It can impair one’s ability to digest fats.
This condition can cause severe pain, particularly in the upper abdomen, and the pain can spread to the back.Pancreatitis can cause the following symptoms in addition to foamy stools:
- fever, nausea, and rapid heartbeat
- exocrine pancreatic insufficiency swollen abdomen vomiting
Pancreatitis may necessitate hospitalisation for treatment.
Infection
Gas bubbles can be produced by a bacterial, parasite, or viral illness in the gastrointestinal tract, giving stool a foamy appearance.
Giardia is a parasite that is frequently the cause of infection. Consuming tainted water or food might make you sick. When swimming, for instance, a person could also come in contact with contaminated water.
Additional indications of an infection include:
- exhaustion, flatulence, nauseousness, and unexplained weight loss
- Symptoms of an infection can last for two to six weeks, on average.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) sufferers may have mucus in their stools, which might give the impression that it is frothy.
IBS additionally manifests as:
- stomach cramps and agony
- diarrhea
- bloating
- constipation
Abdominal operations
Digestion may be harmed by abdominal surgery. The removal of a section of the large or small intestine is one of these procedures.
Short bowel syndrome, which can result in persistent diarrhoea and frothy stools, can be brought on by surgery. This ailment could be transient and go away after the body heals.
However, if a patient has this syndrome for an extended period of time, a doctor will typically suggest supplements to make sure the patient gets enough nutrition.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321289
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diarrhea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352241
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4108-diarrhea
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diarrhea/symptoms-causes
- https://www.healthline.com/health/diarrhea
For more details, kindly visit below.