Characteristics and prevention of emphysema with symptoms.
A form of chronic obstructive pulmonary illness is emphysema (COPD). Lung air sacs deteriorate and stretch under these circumstances. This causes a persistent cough and respiratory problems.
Emphysema can be brought on by a variety of things, but smoking is by far the most common cause. Although there is no known cure, giving up smoking can better the prognosis.
Emphysema has been diagnosed in about 3.8 million Americans, or 1.5% of the total population. 7,085 persons (2.2 per 100,000) lost their lives to the illness in 2017.
What is emphysema?
A form of COPD is emphysema. Emphysema causes the air sacs and alveoli in the lungs to enlarge and the lung tissue to become less elastic.
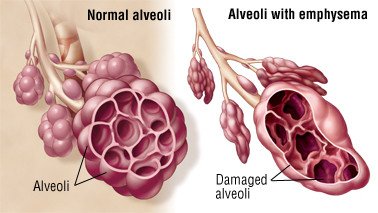
The air sacs’ walls deteriorate, are damaged, shortened, collapsed, stretched, or overinflated. This implies that the surface area available for the lungs to get oxygen into the blood and expel carbon dioxide from the body is reduced. Although the damage is irreparable and permanent, there are techniques to treat it.
Causes and risk factors of emphysema
Emphysema affected 2 million adults in 2018, or 1.6% of those who are 18 years of age or older, according to the American Lung Association.
Males, non-Hispanic white persons, and people over 65 had greater rates than other groups. The disparity between the sexes has, however, been closing as female rates have been rising over the past few decades.
Emphysema is primarily caused by tobacco usage. The likelihood of getting emphysema increases with the amount of smoking you do. This includes cannabis smoking.
More over 480,000 Americans die as a result of smoking each year, and COPD, including emphysema, is to blame for 80% of those fatalities. Emphysema risk is also increased by exposure to secondhand smoke.
The following are other causes of and potential risk factors for emphysema development:
- exposure to chemical vapours or lung irritants that are very polluting
- Alpha-1 deficiency-related emphysema is an uncommon form of emphysema that is caused by the genetic disorder alpha-1 deficiency.
- history of respiratory infections in children
- a weakened immune system, particularly due to HIV
- uncommon illnesses like Marfan syndrome.
Symptoms of emphysema
Emphysema’s main signs and symptoms include:
- breathing difficulty or dyspnea
- a persistent cough that is mucus-producing
- breathing that makes a whistling or squeaky sound and wheezing
- chest constriction
A person may initially experience these symptoms while engaging in physical activity. However, when the illness worsens, they may also begin to occur while you’re sleeping. COPD and emphysema both take time to develop.
Later on, an individual may have:
- flare-ups and frequent lung infections
- Wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath are some of the symptoms that are getting worse.
- reduction in weight and appetite
- exhaustion and a decline in energy
- Lack of oxygen can cause cyanosis, blue-tinged lips, or blue-tinged fingernail beds.
- sleep issues with sadness and anxiety
How is emphysema diagnosed?
The first thing your doctor will do is ask you about your background and medical history, namely whether you smoke and whether you regularly come into contact with dangerous gases or pollutants at work or at home.
Emphysema can be found using a variety of tests, such as:
- X-rays and CT scans are imaging procedures used to examine your lungs.
- blood tests to assess the efficiency of your lungs’ oxygen transport
- Using pulse oximetry, you can determine how much oxygen is in your blood.
- lung function tests, which gauge how well your lungs carry oxygen to your bloodstream and how much air your lungs can take in and out,
- tests to determine the amount of blood and carbon dioxide in your blood are known as arterial blood gas analyses.
- ECGs are used to evaluate heart health and rule out heart illness.
Complications of emphysema.
Emphysema can develop into a serious condition if it is not adequately managed or treated. These may consist of:
- either bacterial or viral pneumonia
- many respiratory infections
- failure of the right side of the heart is referred to as cor pulmonale.
- When air gathers between the lungs and the chest cavity, it causes a pneumothorax, which can cause the lungs to collapse.
- respiratory acidosis, or when the lungs are unable to get adequate oxygen, can result in coma
- When the lungs can’t effectively oxygenate the blood, it’s called hypoxemia.
Emphysema treatment
Emphysema does not have a treatment. The goal of treatment is to lessen symptoms and stop the spread of the illness using drugs, therapies, or operations.
If you smoke, quitting is the first step in curing your emphysema. To help you quit smoking, you could require medicine. Think about going over a strategy with your doctor.
Medications
The disease can be treated with a number of drugs, including:
- Breathing becomes easier and coughing and shortness of breath are reduced thanks to bronchodilators, which help open airways.
- steroids, which reduce breathlessness
- medicines, which combat infections that could worsen the situation
These drugs are all able to be breathed or given orally.
Therapies
By strengthening breathing muscles and reducing symptoms, pulmonary rehabilitation or light exercise like walking can improve breathing and make it easier to be physically active. Deep breathing techniques, yoga, and tai chi can all aid with symptom relief.
Breathing can be made simpler with oxygen therapy. People who have severe emphysema could require oxygen all the time.
Surgery
A lung transplant can replace the entire lung, and lung volume reduction surgery can be done to remove tiny portions of the diseased lung. Only those who have severe emphysema can undergo these uncommon operations.
Other therapies
You might lose weight if you have emphysema. It is advised to consume meals high in vitamins A, C, and E, such as fruits and vegetables, to boost your general health.
You can lessen your risk of contracting an infection that could aggravate emphysema by getting immunised against specific illnesses, such as pneumonia. These illnesses include COVID-19, influenza, and pneumonia.
If you don’t exercise as often as you used to, you can also feel anxious and depressed. You can connect with people who have the same ailment and go through similar experiences by joining a support group. This can make you more aware of the fact that you are not facing the sickness alone.
Perspective and prevention for Emphysema
Emphysema is primarily brought on by tobacco usage, thus quitting smoking is the best way to prevent it. Additionally, it’s critical to avoid exposure to toxic substances, gases, and areas with high pollution.
Depending on how severe their emphysema is, each person’s outlook is different. The condition has no known cure and just becomes worse with time, but you can stop it from getting worse.
Smoking cigarettes typically accelerates the condition, therefore stopping is crucial. Emphysema patients can experience life-threatening complications as their lungs and hearts deteriorate over time, making early disease detection crucial.
Maintaining good health requires a balanced diet and regular exercise. Emphysema can be managed with medications and treatments so that you can enjoy a long, healthy life.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/emphysema
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/8934
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/emphysema/symptoms-causes/syc-20355555
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9370-emphysema
For more details, kindly visit below.