Important causes of Stroke you need to know about.
What is a stroke?
A stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts and bleeds or when the blood supply to the brain is cut off. Blood and oxygen cannot reach the brain’s tissues because of the rupture or obstruction.
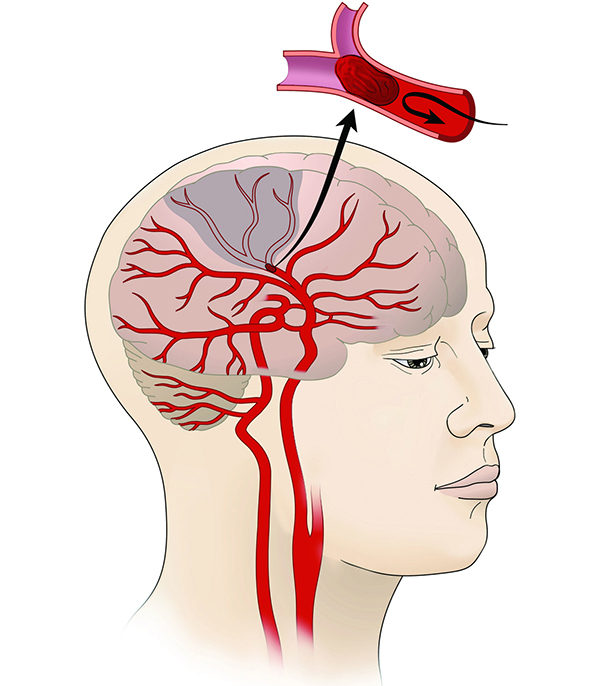
Stroke is a primary cause of death in the US, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). More than 795,000 Americans experience a stroke each year. Brain tissue and cells are damaged and start to die within minutes of being oxygen-deprived.
Strokes often come in three different forms:
- Temporary ischemia. A blood clot causes a transient ischemic attack (TIA), which normally resolves on its own.
- Ischemic stroke. It involves an obstruction in the artery brought on by a clot or plaque. The signs and problems of an ischemic stroke may persist permanently or linger longer than those of a TIA.
- Hemorrhagic stroke. A blood vessel that seeps into the brain either bursts or leaks, which is the source of the condition.
Strokes are often fatal. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), there were 37.6 age-adjusted deaths for every 100,000 stroke diagnosis in 2017. This fatality rate is 13.6% lower than it was in 2007 thanks to medical advances in the treatment of strokes.
How does a stroke affect my body?
What a heart attack is to your heart, strokes are to your brain. When you suffer a stroke, a portion of your brain loses blood flow, preventing that part of your brain from receiving oxygen. The afflicted brain cells become oxygen-starved and quit functioning correctly without oxygen.
Your brain cells will perish if you deprive them of oxygen for too long. If enough brain cells in a particular region perish, the damage is irreversible, and you risk losing the abilities that region used to regulate. Restoring blood flow, however, might stop that kind of harm from occurring or at least lessen how bad it is. Time is therefore very important when treating a stroke.
What causes a stroke?
Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes can occur for a variety of reasons. Blood clots are typically the cause of ischemic strokes. These can occur for a number of causes, including:
- Atherosclerosis.
- bleeding issues.
- Heart fibrillation (especially when it happens due to sleep apnea).
- Heart problems (atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect).
- ischemia microvascular disease (which can block smaller blood vessels in your brain).
There are other more causes of hemorrhagic strokes, including:
- High blood pressure, especially when it is present for an extended period of time, when it is extremely high, or both.
- Hemorrhagic strokes can occasionally result from brain aneurysms.
brain cancer (including cancer). - diseases like moyamoya disease can weaken or result in unexpected abnormalities in the blood vessels in your brain.
Related conditions
A person’s likelihood of having a stroke can also be influenced by various other ailments and elements. These consist of:
- a drinking disorder.
- elevated blood pressure (this can play a role in all types of strokes, not just hemorrhagic ones because it can contribute to blood vessel damage that makes a stroke more likely).
- High triglycerides (hyperlipidemia).
- Migraine headaches (they can resemble stroke symptoms, and sufferers of migraines, particularly those who experience auras, also have an increased lifetime chance of developing a stroke).
- diabetes type 2.
- smoking and using other tobacco products (including vaping and smokeless tobacco).
- drug addiction (including prescription and non-prescription drugs).
Stroke symptoms
Damage to brain tissues results from reduced blood supply to the brain. The body components that are regulated by the brain damage-related areas show signs of a stroke.
The better the prognosis for someone experiencing a stroke, the earlier they receive treatment. Because of this, being aware of the symptoms of a stroke will help you take prompt action. Some signs of a stroke include:
- paralysis
- Arm, face, or leg numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
- difficulty communicating or comprehending others
- muddled speech
- Lack of clarity, disorientation, or responsiveness
- abrupt behavioural alterations, particularly increased agitation
- visual issues, such as double vision or difficulty seeing with one or both eyes that are blurry or blacked out
- loss of coordination or balance
- dizziness
- strong headache that appears out of the blue
- seizures
- dizziness or vomiting
Any stroke victim needs to see a doctor right away. Call your local emergency services as soon as you suspect that you or someone else is experiencing a stroke. Early intervention is essential to avoiding the following consequences:
- brain injury
- long-term impairment
- death
Don’t be scared to seek emergency medical assistance if you believe you have seen the symptoms of a stroke because it’s best to be extra careful while dealing with a stroke.
Risk factors for stroke
You are more prone to stroke if you have certain risk factors. Risk factors for stroke include the following, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood InstituteTrusted Source:
- Diet
- Inactivity
- heavy drinking
- Tobacco use
Personal history
You have no control over a number of stroke risk factors, including:
- Family background. Some families have an increased risk of stroke due to inherited health issues including high blood pressure.
- Sex. Strokes can affect both men and women, although in all age categories, women are more likely to experience them than men, according to the CDCTrusted Source.
- Age. The probability of having a stroke increases with age.
- Ethnicity and race. Compared to other racial groups, African Americans, Alaska Natives, and American Indians are more likely to experience a stroke.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/about.htm
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
- https://www.healthline.com/health/stroke
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/5601-stroke
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/7624
For more details, kindly visit below.