Important Note on Hyperthyroidism you need to know.
Your thyroid develops and manufactures hormones that are involved in numerous bodily processes. Thyroid disease is characterised by the overproduction or underproduction of these critical hormones by your thyroid. Thyroid disease comes in a variety of forms, such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
When the thyroid gland overproduces hormone, it results in hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid. Diarrhea, respiratory problems, and weariness are just a few of the consequences that may spread throughout the body.
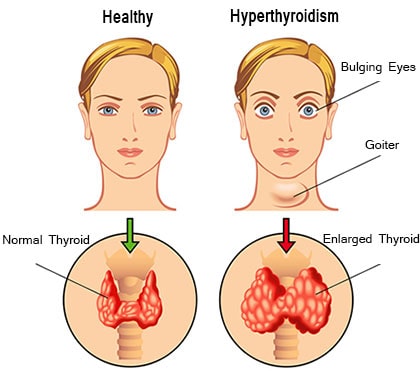
The thyroid is a neck gland with a butterfly form. The body’s growth and metabolism are regulated by the hormones it creates and releases into the bloodstream. In the US, hyperthyroidism affects about 1 in 100 adults over the age of 12. People over 60 are the ones most prone to experience it.
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, is distinct from hyperthyroidism. The terms “hyper” and “low” describe the amount of thyroid hormone in the body, respectively. Hyperthyroidism can have serious problems if left untreated. However, by lowering the synthesis of thyroid hormones, medicine can typically regulate it.
What causes hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism can be brought on by a number of circumstances. The most typical cause of hyperthyroidism is the autoimmune illness Graves’ disease. In Graves’ disease, your thyroid gland is attacked by antibodies produced by your immune system, which causes an excessive amount of hormone to be released.
Women experience Graves’ illness more frequently than males do. According to a 2011 research summary by Trusted Source, environmental circumstances do play a part in determining whether someone would acquire Graves’, but genetics account for the majority of the decision. Graves’ illness isn’t caused by a single gene deficiency, but rather by tiny mutations in a number of genes, according to studies of families and twins.
In order for your doctor to accurately assess your risk factors, you should let them know if any members of your family have been given a hyperthyroidism diagnosis.
Other causes of hyperthyroidism outside Graves’ disease include:
- Excess iodine. Iodine is a crucial component of T4 and T3, and too much of it might temporarily increase the thyroid hormone’s production. Fish and dairy products are two foods that contain iodine. It can also be found in some drugs, including cough syrups, medical contrast dyes, and amiodarone (for heart arrhythmia).
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid). Conditions known as thyroiditis cause the thyroid gland to enlarge and produce either an excessive amount or an insufficient amount of the hormone.
- Benign nodules on the thyroid. On the thyroid gland, nodules, which are lumps, frequently form for unclear reasons. Although the majority of thyroid nodules are benign, some do produce excessive thyroid hormones. Nodules are sometimes known as adenomas or benign tumours.
- Hazardous thyroid nodules (toxic adenoma). There are certain cancerous or malignant thyroid nodules. A nodule’s benignity or malignancy can be evaluated via ultrasound or a procedure known as fine needle aspiration tissue biopsy.
- Testicular or ovarian cancer.
- Blood has a lot of T4. Certain dietary supplements or excessive doses of the thyroid hormone drug levothyroxine can cause high levels of T4.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
While certain physical signs of hyperthyroidism may be clear, others may be more subtle and first difficult to detect. Sometimes anxiety and hyperthyroidism are confused.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) lists the following as hallmark signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism:
- Despite losing weight, your appetite has increased
- irregular or fast heartbeat
- feeling jittery or agitated
- Despite being worn out, I can’t sleep.
- Muscle tremors and shaking in the hands
- easily getting too hot
- several bowel motions
It is possible for the thyroid gland to enlarge and develop a symmetrical or unilateral goitre. An enlarged gland is known as a goitre, and it is frequently identifiable as a lump or swelling near the base of the neck. Iodine deficiency is the most typical cause of a goitre.
Complications of hyperthyroidism
Depending on how well the body can adapt to the changes brought on by the extra thyroid hormones and how strictly a person adheres to their treatment plan, hyperthyroidism and accompanying symptoms can vary in severity. Possible complications from the condition are listed below.
Graves’ ophthalmopathy
Light sensitivity, pain or discomfort in the eye, and specific visual issues can all be brought on by Graves’ ophthalmopathy. A person’s eyes could also protrude.
Sunglasses and eye medicines can both aid with symptoms relief. In extreme circumstances, certain medications—such as steroids or immunosuppressive ones—can reduce the puffiness under the eyes.
A thyroid storm
A thyroid storm is a rare reaction that can happen following an illness, injury, or physical trauma like childbirth or surgery. If the person has undetected hyperthyroidism or problems managing the illness, it may also happen during pregnancy.
Emergency medical care is necessary for this potentially fatal reaction. Thyroid storm warning signs and symptoms include:
- a pounding heart
- acute fever
- agitation
- jaundice
- vomiting
- diarrhoea
- dehydration
- hallucinations
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
While some drugs focus on addressing thyroid hormone production, others treat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as cardiac issues.
Beta-blockers
While beta-blockers cannot cure hyperthyroidism, they can lessen the symptoms while waiting for other treatments to work. It can take a few weeks or months, though.
Anthyroid medications
Antithyroid medication prevents the thyroid gland from overproducing thyroid hormone. Methimazole is a typical medication that doctors advise.
As methimazole may have adverse effects on the foetus, a doctor may advise propylthiouracil during a patient’s first trimester if the patient is pregnant. Later in the pregnancy, women who are pregnant may switch to methimazole.
The American Thyroid Association estimates that after using antithyroid medication for a period of 12 to 18 months, 20 to 30 percent of Graves’ disease patients have symptom remission. Medication side effects may include:
- allergy symptoms
- decreased white blood cells, which raises the risk of infection
- rarely, liver failure occurs.
- Iodine-131 radioactive
Active thyroid cells are destroyed when radioactive iodine penetrates them. There is only localised destruction and no adverse impacts that are felt widely. The radioiodine contains a very tiny dosage of radioactivity that is safe to consume.
However, women who are pregnant or nursing should not receive radioiodine treatment. Following therapy, doctors advise against getting pregnant for 6 to 12 months.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hyperthyroidism
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/9153
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14129-hyperthyroidism
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/overactive-thyroid-hyperthyroidism
- https://www.endocrineweb.com/conditions/hyperthyroidism
For more details, kindly visit below.