Important types and risk factors associated with Gout.
An extremely painful, swollen, and stiffening form of arthritis known as gout generates these symptoms in the joints. The metatarsophalangeal joint, which is located at the base of the big toe, is typically affected. The body having too much uric acid is its main cause.
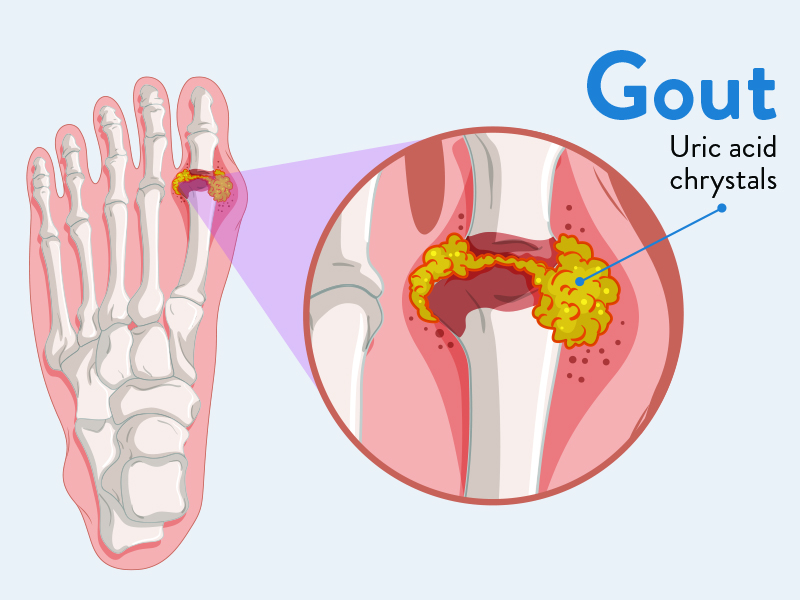
More than 3 million Americans suffer from gout, which is the most prevalent kind of inflammatory arthritis in men. Additionally, females are more prone to get gout after menopause despite the fact that disease is generally less likely to harm them.
Gout episodes can start suddenly and may continue to happen over time. This persistent recurrence can be quite painful and gradually destroy the tissue surrounding the inflammation. Obesity, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension are gout risk factors.
Types of gout
The progression of gout goes through a number of stages.
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Elevated uric acid levels might exist without any overt symptoms. Although there is now no need for treatment, tissue damage can occur as a result of elevated blood uric acid levels.
As a result, a doctor might advise someone with high uric acid levels to treat any potential causes.
Acute gout
This stage happens when urate crystals suddenly induce severe inflammation and excruciating pain in a joint. This sudden outbreak, known as a “flare,” may last for three days to two weeks. dependable source Events in life that are stressful and binge drinking may cause flare-ups.
Intercritical or interval gout
The time between acute gout attacks is referred to as this stage. These intervals get shorter as the gout gets worse. Urate crystals may continue to accumulate in tissue in between these times.
Chronic tophaceous gout
The most painful form of gout, chronic tophaceous gout, can permanently damage the kidneys and joints. At this point, the joints of the fingers and other colder parts of the body are susceptible to tophi and persistent arthritis.
Usually, acute gout attacks are followed by years of chronic tophaceous gout. Individuals who receive appropriate treatment are less likely to develop to this stage.
Pseudogout
One disorder that specialists frequently mistake for gout is calcium pyrophosphate deposition, also known as pseudogout. Although the flare-ups of pseudogout are typically milder, the symptoms are strikingly similar to those of gout.
The main distinction between gout and pseudogout is that calcium pyrophosphate crystals, not urate crystals, irritate the joints in the latter condition. Treatments for pseudogout differ from those for gout.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout attacks nearly often start quickly, and they frequently happen at night. They consist of:
- Intense joint pain. Although it can affect any joint, gout typically impacts the big toe. The elbows, wrists, fingers, ankles, and knees are other joints that are frequently impacted. Within the first four to twelve hours after it starts, the pain is likely to be at its worst.
- Persistent discomfort. Some joint discomfort may remain from a few days to a few weeks after the most intense pain disappears. Later episodes are probably more prolonged and likely to involve more joints.
- Swelling and redness. Affected joints develop swelling, tenderness, warmth, and redness.
- Limited range of motion. You might not be able to move your joints normally when gout worsens.
Causes of Gout
Gout is brought on by a buildup of uric acid in the blood, which results from purine breakdown. Your body overproduces uric acid when you have certain situations, like dehydration or problems with your blood and metabolism.
Your body may have a difficult time eliminating extra uric acid if you have a thyroid or renal condition, a genetic illness, or both.
Gout is more likely to develop in you if you:
- a middle-aged guy or a woman who has had menopause
- alcohol use among gout-suffering parents, siblings, or other family members
- take prescription drugs like cyclosporine and diuretics
- have a condition such as diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid illness, kidney disease, or sleep apnea
Consuming foods high in gout-producing purines can lead to gout in some persons.
Risk factors for gout
The following are a few reasons that can make hyperuricemia and gout more likely.
- Age: Children are infrequently affected by gout, which is more prevalent in elderly persons.
- Sex: Males are four times more likely than females to have gout in people under the age of 65. When a person is beyond 65, the ratio significantly drops to three times as likely.
- Genetics: A person’s chance of having gout may be increased by a family history of the ailment.
- Lifestyle choice: Alcohol use impedes the body’s ability to remove uric acid, according to lifestyle choices. A diet heavy in purines also raises the body’s uric acid levels. These two can both result in gout.
- Lead exposure: Chronic exposure to lead may boost your risk of developing gout, according to studies.
- Medication: Some drugs have the potential to raise the body’s uric acid levels. These include a few diuretics and salicylate-containing medications.
- Weight: Gout risk is associated with being overweight or obese and having high amounts of visceral body fat. Obesity, however, cannot be the direct cause of the illness.
- Other medical conditions: Kidney disease and renal insufficiency can impair the body’s capacity to eliminate waste, causing increased uric acid levels. Additionally, diabetes and high blood pressure are linked to gout.
Foods to avoid
Some meals naturally contain a lot of purines, which your body converts to uric acid. Most people can eat meals high in purines. However, if your body struggles to eliminate too much uric acid, you may want to stay away from things like:
- a red meat
- animal organs
- specific seafood
- alcohol
Despite the fact that they don’t contain purines, sugar-sweetened foods and beverages and beverages that include fructose can also be harmful. Some meals are beneficial if you have gout because they lower the body’s uric acid levels.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gout
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/144827
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gout/symptoms-causes/syc-20372897
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4755-gout
- https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/ss/slideshow-gout
For more details, kindy visit below.