Dysuria: When It Hurts to Go With the ‘Flow
Dysuria, or painful urination, can occur for a number of causes. When someone urinates, it could ache because of an infection, kidney stones, a cyst, or another illness affecting the bladder or adjacent organs.
This symptom has a wide range of possible explanations, many of which are curable.
Individuals who experience dysuria should inform their doctor of any other symptoms. If these are associated with painful urination, it may be possible for doctors to diagnose the condition and suggest the best course of action.
Causes of painful urination
Urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection frequently manifests as painful urination (UTI). A bacterial infection may lead to a UTI. Urinary tract irritation may also be to blame.
The urinary tract is made up of the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. Urine travels from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters. Any of these organs that are inflamed can induce urinating pain.
UTIs are more common in those who have vagina than in those who have a penis. This is so because people with a vagina have shorter urethras. Bacteria need to travel less distance to reach the bladder if the urethra is shorter.
Urinary tract infections are also more likely to occur in menopausal or pregnant women.
Sexually transmissible diseases (STIs)
Also, if you have a sexually transmitted infection, you might feel pain when peeing (STI). Chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and genital herpes are a few STIs that can make urinating unpleasant.
Due to the fact that STIs are sometimes asymptomatic, it is crucial to get checked for them. STI testing should be done on a large number of sexually active individuals.
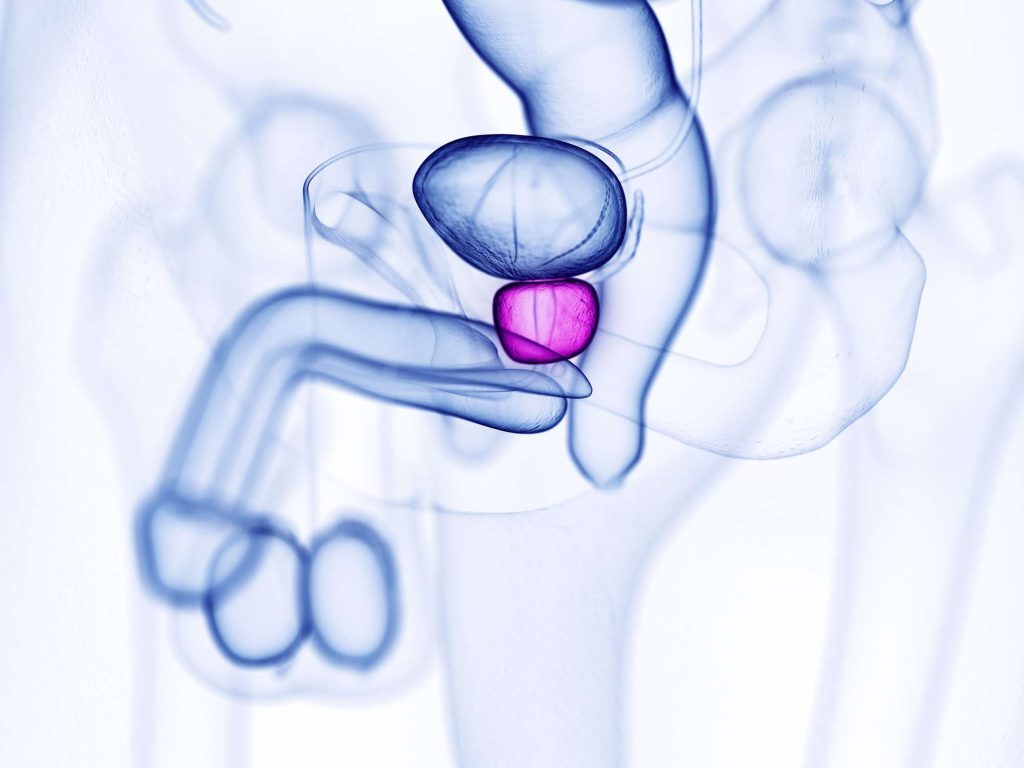
Prostatitis
Painful urination might be brought on by other medical disorders. Prostatitis, which affects the prostate, can cause painful urinating in men. The prostate gland is inflamed in this syndrome. It is the main source of burning, stinging, and pain in the urinary system.
Cystitis
Urination pain can also be brought on by cystitis, an inflammation of the bladder lining. The term “painful bladder syndrome” (PBS) is another name for interstitial cystitis (IC). The most typical kind of cystitis is this one. Pain and tenderness in the bladder and pelvic area are IC symptoms.
Radiation therapy occasionally results in pain in the bladder and urethra. Radiation cystitis is the name of this condition.
Urethritis
The condition known as urethritis denotes inflammation of the urethra, typically brought on by bacterial infection. In addition to frequently causing pain while urinating, urethritis can also increase the urge to urinate.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis, or inflammation of the epididymis in people with a penis, can also result in painful urination. Sperm from the testes are stored and transported by the epididymis, which is situated behind the testicles.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
PID can have an impact on the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Among other symptoms, it can lead to painful urination, painful intercourse, and abdominal pain.
PID is a severe infection that typically results from a bacterial infection that starts in the vagina and spreads to the reproductive organs.
Uropathy with obstruction
Urine flowing back into the kidneys is known as obstructive uropathy, which is caused by an obstruction in the ureter, bladder, or urethra. Regardless of the cause, it’s critical to get medical attention as soon as symptoms appear.
Similar problems with urination and pain can be brought on by another disorder called urethral stricture, which causes the urethra to narrow.
Renal stones
If you have kidney stones, it could be uncomfortable for you to urinate. The urinary tract contains masses of hardened material called kidney stones.
Medications
Painful urination is a side effect of various drugs, including some antibiotics and cancer treatments. Discuss any possible pharmaceutical side effects with your healthcare professional.
Hygiene items
It’s not always an infection that causes painful urinating. Moreover, it could be brought on by genital product use. Vaginal tissues can become particularly irritated by soaps, lotions, and bubble baths.
Dyes in laundry detergents and other personal care items can irritate and contribute to health problems such as dysuria.
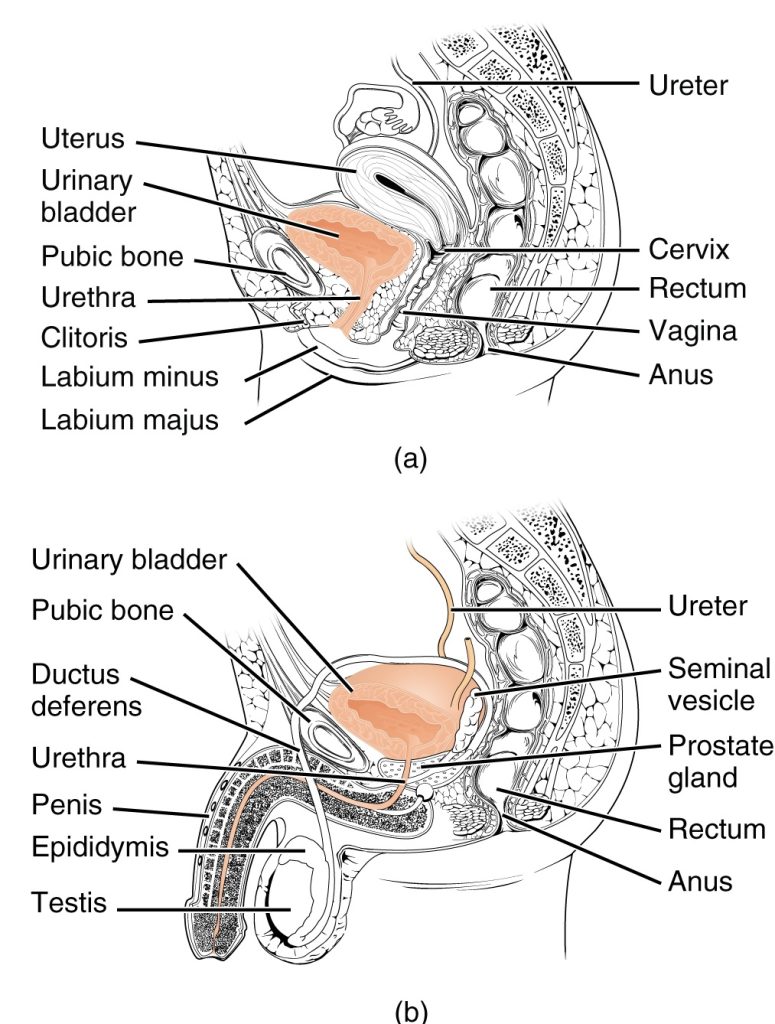
Differences in males and females
Both sexes can experience pain during urinating, and the causes may depend on the anatomy.
For instance, female urethras are shorter than male urethras. This makes it easier for germs to enter the bladder, which can result in UTIs.
A person might discuss with their doctor the likelihood that they will experience painful urinating based on their sex and medical history.
Treatment options for painful urination
The initial step before receiving therapy will be to identify the source of the pain.
To address painful urinating, your doctor could prescribe medication. UTIs, some bacterial infections, and some STIs can all be treated with antibiotics. Also, your doctor might prescribe you medicine to soothe your agitated bladder.
If you start taking medicine, painful urination brought on by a bacterial infection typically gets better quite soon. Take the medication exactly as directed by your doctor every time.
Certain infections, like interstitial cystitis, can cause pain that is more difficult to treat than others. The effects of pharmacological therapy could take longer. Before you start to feel better, you might need to take medicine for up to 4 months.
Prevent painful urination
There are lifestyle adjustments you can undertake to help with symptom relief.
- Avoid using scented toiletries and laundry detergents to lower your chance of irritation.
- When engaging in sexual activity, use condoms or other barrier techniques.
- Eliminate foods and beverages from your diet that can irritate the bladder (such as highly acidic foods, caffeine, and alcohol).
- Drink plenty of water.
When to see a doctor
Get in touch with your doctor:
- if the discomfort is ongoing or severe
- if you are expecting
- There is fever and ache together.
- if you develop vaginal or penile discharge
- your urine smells strange, contains blood, or is cloudy
- if abdominal discomfort is present along with the pain
- if you expel a kidney or bladder stone
To help identify the source of the pain, your doctor may request lab tests and inquire about any further symptoms.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323105
- https://www.healthline.com/health/urination-painful
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15176-dysuria-painful-urination
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/painful-urination/basics/causes/sym-20050772
- https://www.webmd.com/women/dysuria-causes-symptoms
For more details, kindly visit below.