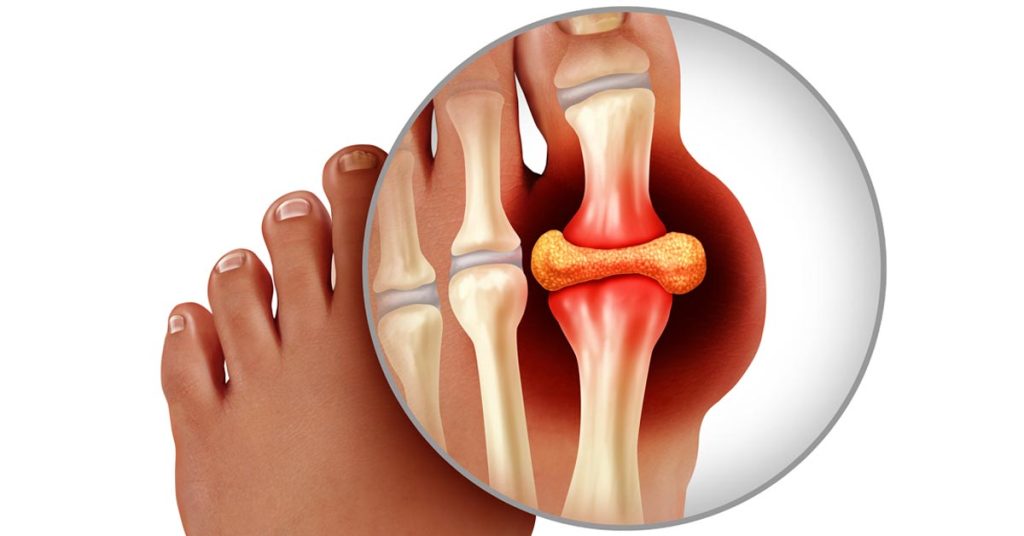
Gout due to deficiency of a protein found in joint fluid.
A multinational research team discovered a novel molecular route that is thought to be the origin of gout and the path it takes to joint tissue disintegration.
A protein called lubricin, which is present in joint fluid, may represent a unique therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of gout, according to researchers.
The discovery was made, in part, through research on a lady who had urate crystal formations and joint degradation but low blood urate levels.
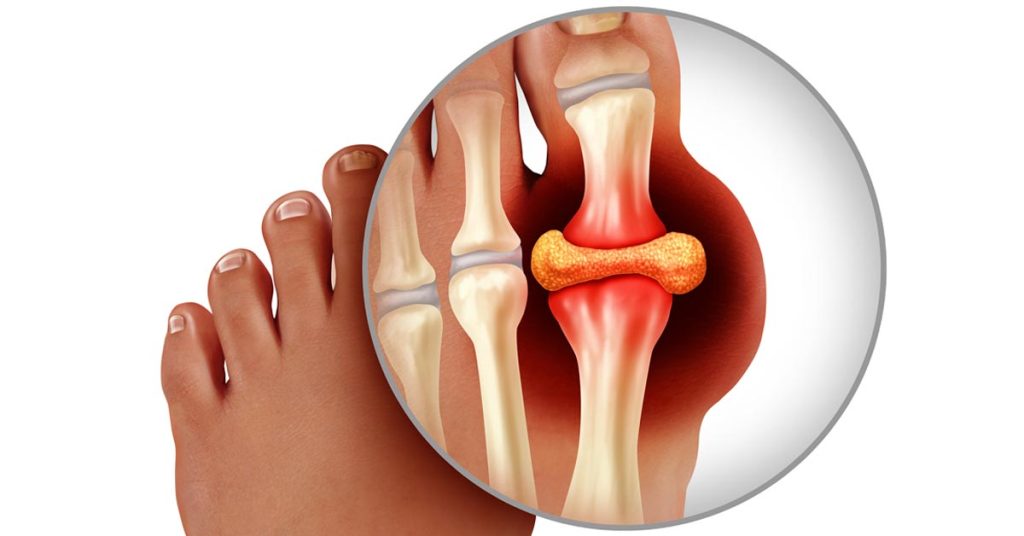
Gout, a common kind of inflammatory arthritis, can make joints extremely painful, swollen, and stiff. A punishment for those Gout has often affected one joint at a time since ancient times. Frequently the joint at the base of the big toe.
According to the American College of Rheumatology, the illness affects more than 3 million people in the US. Men. Also, postmenopausal women and persons with kidney problems are more prone to the condition.
An innovative molecular mechanism that causes gout and leads to the erosion of joint tissue has been discovered by an international research team headed by the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. The journal Arthritis & Rheumatology reported the researchers’ findings.
What is Gout?
An extremely painful, swollen, and stiffening form of arthritis known as gout generates these symptoms in the joints. The metatarsophalangeal joint, which is located at the base of the big toe, is typically affected. The body having too much uric acid is its main cause.
More than 3 million Americans suffer from gout, which is the most prevalent kind of inflammatory arthritis in men. Additionally, females are more prone to get gout after menopause despite the fact that disease is generally less likely to harm them.
Gout episodes can start suddenly and may continue to happen over time. This persistent recurrence can be quite painful and gradually destroy the tissue surrounding the inflammation. Obesity, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension are gout risk factors.
Unusual case study on gout
Purines, which are present in the body, meat, and some beverages, are broken down by the body to produce uric acid.
Uric acid crystals may grow inside a joint as a result of hyperuricemia. This is a high quantity of uric acid in the blood and promotes inflammation.
High uric acid levels are also frequently found in the joint fluid of gout sufferers. Although not invariably, gout can be caused by hyperuricemia. Up to 21% of the population may have asymptomatic hyperuricemia, according to one study.
Dr. Robert Terkeltaub is a professor at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. He is section chief of rheumatology at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System. Also, he is the study’s senior author, stated: “There are factors well beyond having a high serum rate to determine who gets gout, who doesn’t get gout.”
Factors that can cause gout
The researchers’ investigation of a 22-year-old lady with an atypical case of gout was included in their report. She had urate crystal formations and joint degradation, but her blood tests did not reveal elevated urate levels.
Researchers employed RNA-sequencing, a technology that gives a quantitative analysis of messenger RNA molecules in a biological sample, and whole genome sequencing, an investigation of an organism’s entire DNA composition, for their study.
In order to pinpoint a molecular route underlying the patient’s condition. They also used quantitative proteomic techniques, a method that enables a thorough examination of proteins. They examined samples from the young woman, her parents, and unrelated individuals.
Finally, scientists discovered a chemical route that had been damaged in the young woman. Their research focused on lubricin, a protein that lubricates joints.
Researchers found that the woman’s joint fluid had many proteins that were lower than those of her parents’ joint fluid. Also, lower than the combined results from four healthy controls.
“We searched for something that would either be tenfold decreased in the sick… related to the mother or father and the control or tenfold increased in the patient relative to the mother or father and the healthy control,” the researcher explained. And we discovered that the patient had roughly a dozen proteins that had significantly lower levels, Terkeltaub added.
Lubricin was one of those proteins. The following analysis focused on 18 individuals who had uncontrolled hyperuricemia and common gout. Five of them also showed low lubricin levels.
Lubricin inhibits inflammation
In a different section of the investigation, scientists employed mice with and without lubricin. Interleukin-1β, an inflammatory cytokine, was administered into the animals’ knee joints.
The main enzyme that really produces uric acid, xanthine oxidase, was enriched in the cells known as macrophages in the joint lining of the mice that didn’t produce lubricin, according to Terkeltaub.
According to the experiment, lubricin prevents urate from crystallising in joints and inhibits the release of xanthine oxidase and urate via stimulating white blood cells.
Dr. Puja Paul Khanna, an associate professor in the department of Internal Medicine at the University of Michigan Medical School. He stated that the study suggests lubricin may function as a biomarker for gout.
“With the mice models, they are observing that even if you did not have a high level of uric acid, but you are already experiencing damage from those small little, you know, monosodium urate crystals. We have identified lubricin as the cause, so we could block that pathway, Khanna added. “The [monosodium urate] crystals have a higher possibility of accumulating and harming that joint if the mice are deficient, meaning [they] lack lubricin. Right? More research on the same is required in people.
Terkeltaub emphasised that the findings demonstrates that lubricin’s function extends beyond just lubricating joint tissues.
In addition to inhibiting the inflammation brought on by the crystals and limiting the formation of new crystals, lubricin is something that is “actually involved in what we term the homeostasis of uric acid in the joint,” according to the expert.
Terkeltaub noted that the individual’s lubricin and other molecule-controlling lubricin gene variations may have an impact on whether or not a person with hyperuricemia develops gout.
The development of gout
This study shows that more can be learned about the pathophysiology of gout, according to Dr. Theodore Fields, a rheumatologist from Weill Cornell Medicine and Hospital for Special Surgery in New York who was not involved in the study.
He stated, “We continue to have big information gaps about why some patients get gout and some don’t, even if both have the same level of serum urate. It makes perfect sense that factors like lubricin deficiency play a role in certain patients.
Further studies by Terkeltaub will focus on lubricin’s potential as a novel therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of gout as well as gout biomarkers and biomarkers for other inflammatory diseases.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/new-look-at-an-ancient-disease-study-finds-novel-treatment-targets-for-gout
- https://www.healthline.com/health/synovial-fluid-analysis
- https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/synovial-fluid-analysis/
For more details, kindly visit below.