Significance of high cholesterol level and its treatment.
Diet, smoking, and genetics are some of the root causes of elevated cholesterol. If you are at risk, it is crucial to have regular cholesterol examinations because high cholesterol rarely manifests as symptoms.
In the United States, high cholesterol is a rather prevalent problem. In fact, approximately 94 million American individuals age 20 and older have what can be referred to as borderline high cholesterol, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
You might not even be aware that you have this ailment until you see your doctor, though, as it frequently manifests without any obvious symptoms.
What is cholesterol?
Lipids include cholesterol. Your liver makes this waxy, fat-like substance on its own. It is essential for the production of some hormones, vitamin D, and cell membranes. Since cholesterol does not dissolve in water, it cannot independently move through your blood. Your liver generates lipoproteins to aid in the transportation of cholesterol.
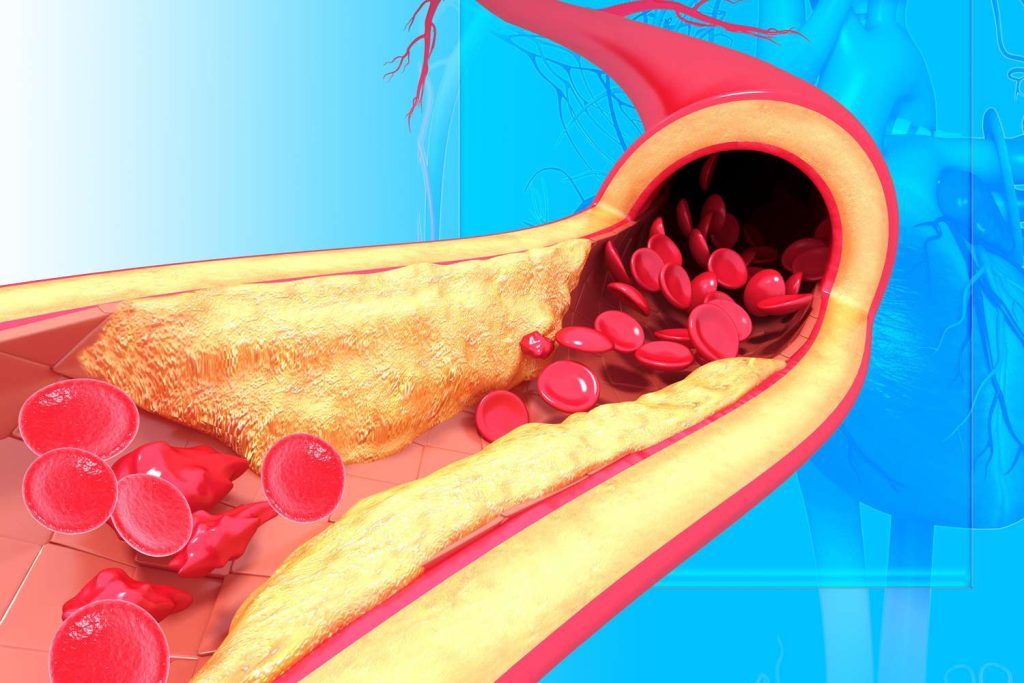
Particles called lipoproteins are comprised of protein and fat. They transport triglycerides, a different kind of lipid, and cholesterol through your bloodstream. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) are the two main types of lipoprotein.
Any cholesterol transported by low-density lipoproteins is referred to as LDL cholesterol. You might be given a high cholesterol diagnosis if your blood has an excessive amount of LDL cholesterol. High cholesterol can cause a number of health problems, such as heart attacks and strokes, if left untreated.
Cause of High cholesterol
Consuming an excessive amount of meals high in cholesterol, saturated fats, and trans fats may make you more likely to acquire high cholesterol. Additionally, your risk can go up if you are obese. Inactivity and smoking are two more lifestyle choices that might raise cholesterol.
Your likelihood of getting high cholesterol may also be influenced by your heredity. Parents pass on their genes to their offspring. Your body receives guidance from specific genes on how to digest lipids and cholesterol. You may be more likely to develop high cholesterol if your parents do.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a rare cause of elevated cholesterol. Your body is unable to eliminate LDL due to this hereditary condition. The majority of persons with this illness have total cholesterol levels above 300 milligrammes per deciliter and LDL levels above 200 milligrammes per deciliter, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute.
Your chance of acquiring high cholesterol and associated consequences may also be increased by other medical diseases like diabetes and hypothyroidism.
How does high cholesterol affect my body?
High cholesterol causes plaque to accumulate inside of your blood vessels over time. Atherosclerosis is the medical term for this plaque development. Atherosclerosis increases the likelihood of developing a wide range of illnesses. This is due to the crucial role that your blood vessels perform throughout your entire body. There are therefore consequences when there is an issue with one of your blood vessels.
Your body’s blood arteries are like a sophisticated system of pipes that keep blood flowing through it. Plaque is similar to the crud that clogs your home’s plumbing and causes your shower drain to run slowly. Your blood vessels’ inner walls become adhered with plaque, which reduces the amount of blood that can pass through.
Plaque begins to build inside your blood vessels when your cholesterol level is high. The plaque enlarges the longer you continue without treatment. Your blood arteries narrow or obstruct as the plaque grows larger. Your blood arteries could continue to function for a very long period even if they are partially obstructed. However, they won’t function as effectively as they ought to.
Depending on which blood vessels are blocked, high cholesterol increases your risk of developing various medical disorders.
Risk factors for high cholesterol
You can be more vulnerable to getting high cholesterol if you:
- are affected by obesity
- eat a lot of trans and saturated fats, such as those found in fast food
- have a minimal level of exercise
- tobacco products are smoked
- have a history of elevated cholesterol in your family
- have kidney problems, diabetes, or hypothyroidism
High cholesterol can affect people of various ages, genders, and ethnicities.
Complications of high cholesterol
Without therapy, elevated cholesterol can lead to artery plaque buildup. This plaque might constrict your arteries over time. Atherosclerosis is the name given to this condition.
A dangerous condition is atherosclerosis. It may restrict how much blood can flow through your arteries. Additionally, it increases your risk of getting harmful blood clots.
Many potentially fatal consequences from atherosclerosis include:
- stroke
- chest pain
- Chest pain, or angina
- blood pressure is high.
- disease of the peripheral vessels
- long-term kidney disease
A biliary imbalance brought on by high cholesterol increases your risk of gallstones. See how your body may be affected by high cholesterol in various ways.
How to lower cholesterol?
Your doctor could suggest lifestyle modifications if you have high cholesterol to help lower it. For instance, they can advise making adjustments to your daily schedule, exercise routines, or food. If you smoke, they’ll probably tell you to stop.
To assist lower your cholesterol levels, your doctor may also recommend drugs or other treatments. They might suggest you get extra care from a specialist in specific circumstances.
Dietary cholesterol reduction
Your doctor could suggest dietary adjustments to help you reach and maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
For instance, they might suggest that you:
- Limit the amount of cholesterol-, saturated-, and trans-fat-containing foods you eat.
- Pick lean protein sources including chicken, fish, and lentils.
- eat a variety of high-fiber foods, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- choose fried cuisine over baked, broiled, steaming, grilled, and roasted options.
- When possible, stay away from fast meals and sugary, pre-packaged foods.
High-cholesterol, saturated-fat, or trans-fat foods include:
- Red meat, organ meats, egg yolks, and dairy items with a high fat content
- prepared foods made with palm oil or cocoa butter
- meals that are deep-fried, including fried chicken, onion rings, and potato chips
- a few baked products, such a few cookies and muffins
Consuming fish and other meals high in omega-3 fatty acids may also assist in reducing your LDL cholesterol levels. For instance, omega-3s are abundant in fish like salmon, mackerel, and herring. Omega-3s can also be found in walnuts, almonds, ground flaxseeds, and avocados.
cholesterol-lowering drugs
Your doctor may occasionally recommend drugs to assist lower your cholesterol levels. The most frequently given drugs for elevated cholesterol are statins. They prevent your liver from making additional cholesterol.
Statin examples include:
- atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- fluvastatin (Lescol)
- rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- simvastatin (Zocor)
Other drugs for high cholesterol that your doctor might recommend include:
- niacin
- Bile acid resins or sequestrants such cholestyramine(Prevalite), colestipol, or colesevalam (Welchol)
- Inhibitors of cholesterol absorption, such as ezetimibe (Zetia)
- PCSK9 inhibitors like evolocumab (Repatha) and alirocumab (Praluent)
Some products comprise a mix of medications that work to lessen the amount of cholesterol your body absorbs from meals and the amount of cholesterol your liver produces. A combination of ezetimibe and simvastatin is one instance (Vytorin). Find out more about the prescription medications for high cholesterol.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/high-cholesterol
- https://www.healthline.com/health/high-cholesterol
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-cholesterol/symptoms-causes/syc-20350800
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/11918-cholesterol-high-cholesterol-diseases
- https://familydoctor.org/condition/cholesterol/
For more details, kindly visit below.