How metabolic syndrome may increase the risk of Gout?
Obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and cardiovascular disease all seem to be more common in people with metabolic syndrome(MetS). This may make them more likely to develop in tandem.
The syndrome is a group of risk factors that have been linked to an elevated risk of acquiring additional disorders rather than a single, separate disease.
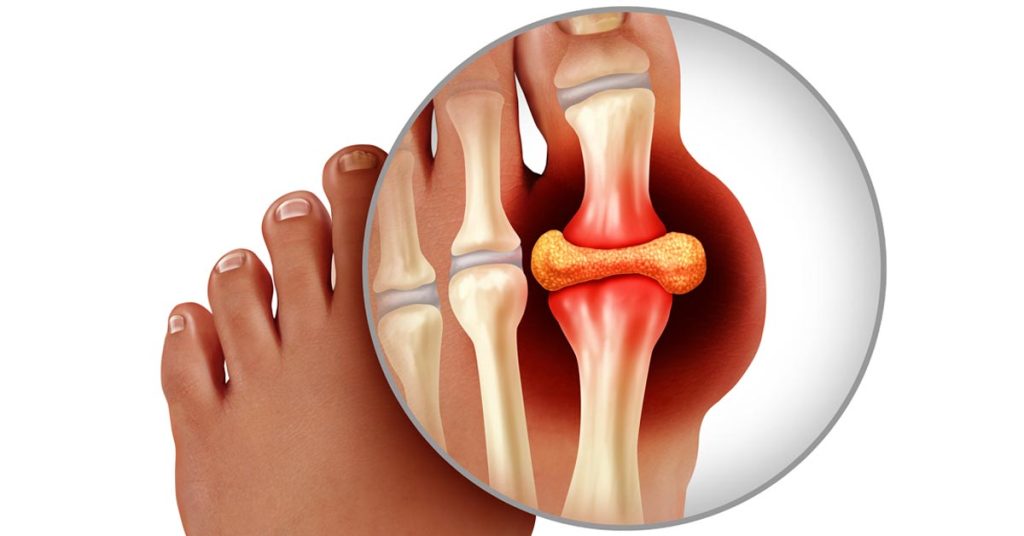
Metabolic syndrome have a higher risk of developing gout, according to research from the Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine in South Korea. Its a kind of arthritis that causes pain and swelling in the joints.
A recent study as per the journal Arthritis & Rheumatology, examined over 1.3 million men between the ages of 20 and 39 who had health examinations. The relationship between modifications in the participants’ METs and the onset of gout was examined.
They identified those who had gout using a database of diagnoses. Also, they utilised a statistical model to examine the connection between changes in metabolic syndrome and the onset of gout.
They found that males with metabolic syndrome or those who developed MetS had a higher risk of developing gout. Men who had high triglyceride levels and abdominal obesity—two factors associated with MetS—were at a substantially higher risk.
What is metabolic syndrome (MetS)?
A clinician may suspect metabolic syndrome if a patient displays at least three of the following five signs and symptoms:
- Specifically, a waist size of more than 40 inches for men and more than 35 inches for women is considered central, visceral, abdominal obesity.
- 100 mg/dL or more for fasting blood sugar.
- values of 130/85 mm/Hg or above for blood pressure.
- Blood triglyceride values of 150 mg/dL or higher.
- levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol at or below 50 mg/dL for women and 40 mg/dL or less for men.
What is gout?
An extremely painful, inflammatory, and inflexible form of arthritis known as gout causes the joints to become stiff.
The metatarsophalangeal joint, which is situated at the base of the big toe, is typically affected. An excessive buildup of uric acid in the body is the source of the disorder.
Researchers find
18,473 males in the recent study experienced gout. Compared to people having MetS, people having metabolic syndrome had a nearly four-fold increased risk of developing gout.
The researchers also noted that a participant’s probability of developing gout quadrupled if they had MetS. Yet, the likelihood of developing gout was practically cut in half for those who recovered from MetS.
High triglyceride levels and abdominal obesity were found to have the highest associations with gout risk. This is as per reports of metS factors.
Comparison was made for those in their 20s, 30s, and those who were underweight or had a normal weight. People with underweight were more likely to experience a connection between changes in MetS and gout.
This is the first extensive study to look at the relationship between alterations in the metabolic syndrome and the risk of gout. According to the study, young persons’ chance of developing gout can be greatly decreased by avoiding MetS or recovering from it.
Reports as per studies
Recent epidemiologic studies have revealed that, when compared to controls, those with hyperuricemia and gout had a higher prevalence of the metabolic syndrome.
In a cross-sectional research of 21,544 participants who completed work-related health examinations, those with serum urate levels 9 mg/dL had about a five-fold greater chance of developing metabolic syndrome. This is compared to those with serum urate levels 7 mg/dL.
Ford et al used data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) from 1999 to 2002. They conducted a cross-sectional analysis of 1370 children and adolescents to ascertain the relationship between serum urate and metabolic syndrome.
In the lowest to highest quartiles of serum urate, risk of metabolic syndrome was 1.0%, 3.7%, 10.3%, and 21.1%, respectively. The top quartile of urate had a roughly 15-fold higher risk of metabolic syndrome than the lowest two quartiles.
When comparing data from 1988-1994 to 1999-2006, NHANES also revealed that the prevalence of gout and metabolic syndrome were rising continuously and at comparable rates.
Rashad Barsoum, MD, FRCP, FRCPE, emeritus professor of medicine at Cairo University, and Rheumatology Advisor talked about the epidemiologic link between gout and metabolic syndrome. It is still disputed whether hyperuricemia is a surrogate marker or a confounding risk factor, but the statistical correlation does not suggest causality, he says, despite the significant evidence linking it to the metabolic syndrome.
Action to reduce risks
The findings of this study, according to Mitchell, “should at the very least act as a wake-up call for the children. Diabetes and hypertension are no longer considered “diseases of the elderly.”
“Gout is merely one of the numerous additional hazards that come with these chronic illnesses. In addition to lowering quality of life, early onset of these diseases may also shorten lifespans. This is over the next few decades, according to the expert.
To “promote the findings of this study to the general public and build a gout prevention programme,” Trinh made a number of recommendations, stating that the following actions may be taken:
Make educational materials that describe the connection between MetS and gout, such as pamphlets, posters, and infographics. Also, the information in these materials must to cover lifestyle modifications for managing MetS.
Join up with medical professionals including primary care doctors and endocrinologists to promote gout prevention strategies and share information about the study’s findings.
Use social media: Share information about the study’s findings and encourage healthy lifestyle choices. By using social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, this can be done.
To inform those who have MetS about the connection between the condition and gout and to offer advice on how to treat it with lifestyle changes, hold workshops or webinars for them.
To promote gout prevention practises to a larger audience, work with neighbourhood organisations like wellness centres or municipal health agencies.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gout-combining-2-existing-drugs-doubles-treatment-success-in-new-study
- https://www.rheumatologynetwork.com/view/rheumatoid-arthritis-year-in-review-2022
- https://www.rheumatologyadvisor.com/home/topics/gout/examining-the-connection-between-gout-and-metabolic-syndrome/
- https://rheumatology.medicinematters.com/gout/cardiovascular-disease/metabolic-syndrome-gout-risk/23767656
For more details, kindly visit below.