Important types of Cataract everyone need to know about.
What is Cataract?
A cataract is a hazy, thick region that develops in the eye’s lens. When proteins in the eye clump together, the lens is unable to transmit clear images to the retina. This leads to the development of a cataract. The retina functions by processing impulses from the light that enters via the lens. The optic nerve receives the signals from it and delivers them to the brain.
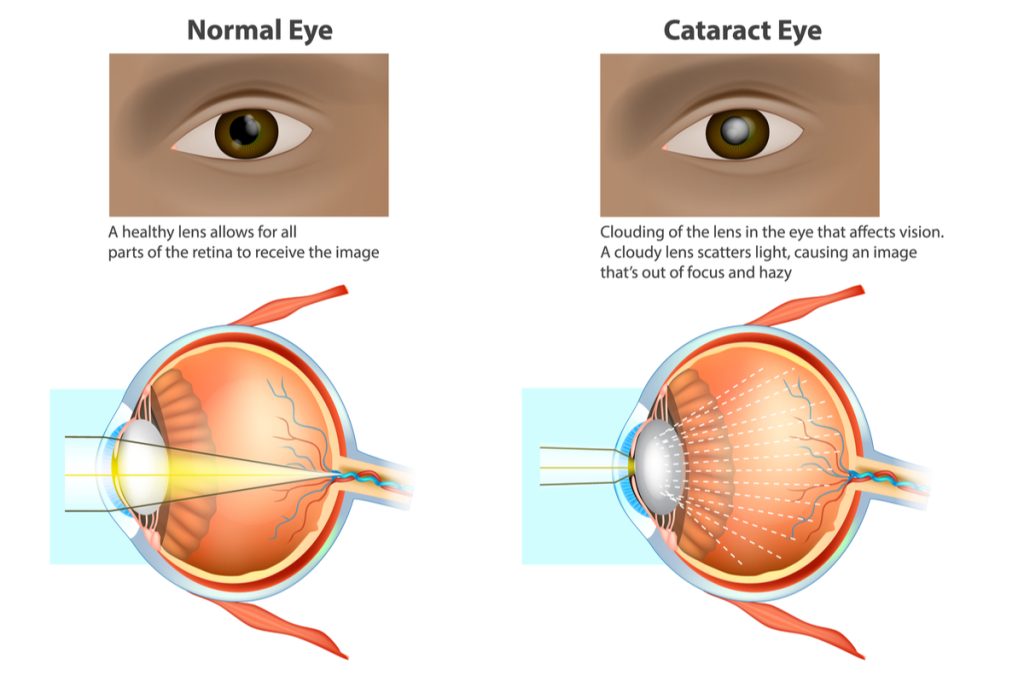
It gradually gets worse and eventually obstructs your eyesight. Cataracts can develop in both of your eyes, but they typically do not do so simultaneously. Older persons frequently develop cataracts. The National Eye Institute estimates that by the time people reach the age of 80, more than half of Americans either have cataracts or have had cataract surgery.
What Are the Symptoms?
Typically, cataracts form gradually. You might not even be aware of their presence until they begin to block light. Next, you might observe:
- hazy, fuzzy, foggy, or filmy vision
- Nearsightedness (in older persons)
- alterations in how you see colour
- driving issues at night (glare from oncoming headlights)
- glare issues during the day
- vision in the damaged eye is double.
- Problems with spectacles or poorly functioning contact lenses
What Causes Cataracts?
The most frequent reason is ageing. This results from typical eye changes that start to occur after the age of 40. Normal lens proteins begin to degrade at that point. The lens becomes clouded due to this. Most people over 60 begin to experience some lens clouding. However, visual issues can not appear for a few of years. There are more causes of cataracts, such as:
- having cataract-affected parents, siblings, or other family members
- having certain health issues, such diabetes
- smoking
- having undergone radiation therapy for your upper body, surgery, or sustained an eye injury
Types of Cataract
When protein accumulates in the eye’s lens, clouding it, cataracts grow. This prevents crystal-clear light from going through. It may result in some vision loss for you. Cataracts can take many different forms.
Atomic cataracts
This type of cataract, also known as a nuclear sclerotic cataract, is the most common one observed by physicians. Most people who live long enough acquire one.
They develop in the nucleus, or core, of the lens. Your reading vision may actually improve as they get worse. Second sight is referred to as such, yet it is transient.
The lens hardens and turns yellow or even brown over time. Small details are difficult to perceive, colours become less vibrant, and in the dark. Also, brilliant objects appear to have haloes surrounding them.
Cortical cataracts
These develop on the cortex, the outside edge of your lens. They initially appear as white triangle-shaped wedges that point in the direction of your eye’s centre. They emit light as they expand.
Glare is the major symptom. Driving at night could be challenging for you. They may also cause you to feel as though there is a fog in front of your eyes. Identifying distinct colours or determining an object’s distance may be challenging.
You usually get them removed at a young age since they can cause problems with both close and far vision.
Cataracts in the posterior capsule
These develop right inside the rear of your lens capsule, the structure in your eye that encloses and stabilises the lens. Directly in the path of the light as it travels through the lens, they are.
You may experience symptoms within months because they develop more quickly than other cataracts. Your close-up vision is impacted, and they make it more challenging to see in strong light.
Prior to the capsule cataracts
This type develops right inside the lens capsule’s front portion. One may be brought on by an eye injury or edoema. Atopic dermatitis, a kind of eczema, can also cause this.
They might not require treatment if they are tiny or located outside the centre of the lens, it can prevent the eye from learning to see because a doctor must remove one that limits vision after a newborn is born.
Accidental cataracts
A cataract can develop as a result of numerous traumas. You may suffer from one if a ball strikes your eye, or if you suffer burn, chemical, or splinter injuries. The cataract may manifest right after following the damage or years later.
Additional cataracts
Doctors refer to a cataract as secondary if it develops as a result of another illness or medical procedure. Possible causes include diabetes, the use of steroid medications like prednisone, and even cataract surgery.
Ray-induced cataracts
UV radiation from the sun can harm your eyes in addition to your skin. This is something you may already be aware of. If you spend too much time in the sun without eye protection, you could occasionally get cataracts.
This type of cataract is more common in people who work outside, such as farmers and fishermen. Wear sunglasses that offer 100% UVA and UVB protection to avoid it. Another adverse effect of radiation therapy for cancer is cataracts.
Cataracts with zonules or lamellae
This variety often affects both eyes and younger children. They are transferred from parent to child via the genes that cause them.
These cataracts may develop into a Y shape and appear as little white dots in the lens’s centre. It is possible that the lens’ entire centre will eventually turn white.
Polar cataracts in the back
These develop on the rear of your lens in the middle. They’re frequently brought on by genes that have been passed down through your family.
It’s fortunate that posterior polar cataracts frequently don’t show any symptoms because they are challenging to remove.
Cataracts on the polar front
They appear as tiny white dots that develop in the front and centre of your lens. Usually, these cataracts don’t impair your eyesight.
Cataracts following a vitrectomy
The clear gel at the centre of your eye is called vitreous. It is removed during a procedure called a vitrectomy. The procedure may cause a cataract but can help with some eye conditions.
Cataracts in Christmas trees
They develop in your lens and are also known as polychromatic cataracts. People with myotonic dystrophy are more likely to experience them.
Cataracts with a rusty hue
A nuclear cataract becomes extremely hard and brown if untreated. It is known as brunescent.
You find it difficult to distinguish between hues, especially blues and purples. Surgery to remove it is more difficult, time-consuming, and dangerous than when you receive early therapy.
Cataracts caused by diabetes
You may develop this uncommon form of cataract if you have diabetes. It quickly worsens and develops a snowflake-like gray-white pattern.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-are-cataracts
- https://www.healthline.com/health/cataract
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8589-cataracts
- https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/cataracts/what-are-cataracts
- https://www.dragarwal.com/diseases-conditions/cataract/
For more details, kindly visit below.