Is it possible to have Angina with normal blood pressure?
What is Angina?
Angina is tightness, squeezing, pressure, or pain in the chest. It occurs when an area of the heart muscle receives less blood oxygen than usual. It is not a disease but a symptom. Angina usually happens due to ischemia, when one or more of the coronary arteries becomes narrow or blocked. It is often a symptom of coronary heart disease (CHD).
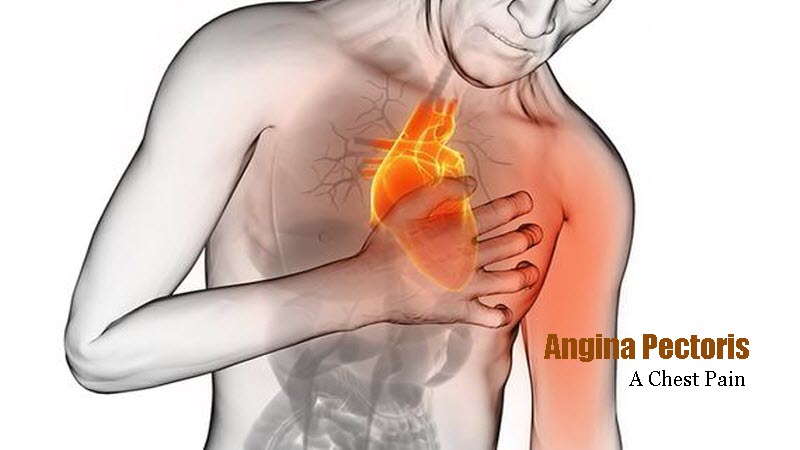
Alone, angina is not life threatening, but it can resemble the symptoms of a heart attack, and it is a sign of heart disease. Receive medical attention if angina occurs unexpectedly, does not go away, or does not respond to rest or medication.
What does angina feel like?
Most angina sufferers describe having pressure or pain in the chest. Or they describe a heaviness or squeezing in their chest. Some claim that it has the sensation of dyspepsia. Others claim that putting angina into words is difficult.
Usually, the pain starts behind your breastbone. You might not always be able to pinpoint the particular source of the pain. Your upper torso may experience upper chest pain or discomfort as well. Your neck, jaw, shoulders, arms, back, and belly are a few of these.
Other symptoms, referred to as “angina analogues,” can be brought on by a lack of oxygen to your heart. You may not feel any of these symptoms in your chest, such as:
- Fatigue.
- sickness or vomiting
- respiration difficulty.
- greatly perspiring.
Types of Angina
Enduring angina
When the heart is working harder than usual, such as during exercise, stable angina develops. Normally, it lasts for five minutes.
It has a predictable rhythm and might last for weeks, months, or even years. The symptoms can typically be reduced with rest or medicine.
Erratic angina
Unstable angina has no set rhythm and typically strikes while you’re at rest. Atherosclerosis, which involves a blockage preventing blood from reaching the heart, is the primary cause.
The pain may develop with time and linger for more than five minutes. Medication and rest may not be enough to reduce the symptoms.
Angina that is unstable can signal a possible heart attack. Anyone experiencing sudden angina should seek emergency medical attention.
Angina microvascular
Coronary microvascular disease can cause microvascular angina (MVD). The tiniest coronary arteries are impacted by this.
In addition to chest pain, a person may feel:
- low energy and weariness
- issues with sleep
- breathing difficulty
- Stable angina is more transient than microvascular angina. It frequently lasts for more than ten minutes. Trustworthy Source and occasionally takes more than 30 minutes.
Angina variant
Rare variant angina Prinzmetal angina is the name some doctors give to this condition, which can occur when the body is at rest, usually in the early morning or late at night.
It takes place when the coronary arteries spasm. Cold exposure, stress, medications, smoking, or cocaine usage are examples of potential triggers. Although the illness is chronic, medicines can help manage it.
What causes angina?
Angina is brought on by myocardial ischemia, which is reduced blood supply to the heart. Your coronary arteries may develop a number of issues that hinder your heart from getting adequate blood. These consist of:
Coronary artery disease: The most frequent cause of angina is coronary artery disease. When plaque (a fatty, waxy substance) accumulates in your coronary arteries, which carry blood to your heart, it causes heart disease. Your heart receives less blood as a result of these arteries’ narrowing or hardening (atherosclerosis).
Coronary microvascular disease: Compared to men and individuals designated male at birth, women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB) had a higher prevalence of coronary microvascular disease (AMAB). Small blood veins that branch off of your coronary arteries suffer damage to their walls.
Coronary artery spasm: Your coronary arteries repeatedly contract (tighten) and then relax during a coronary artery spasm. Your heart’s blood supply is momentarily restricted by these spams. Even without coronary artery disease, you can experience coronary spasms. Regular CAD testing may not be able to diagnose this, and it may be necessary to conduct specialised testing that not all hospitals offer.
Angina with normal blood pressure?
Even though the coronary arteries themselves are healthy, angina can occasionally develop when parts of the heart muscle are not getting enough oxygen.
The following conditions can cause angina without having coronary artery disease:
- extremely low blood pressure, which may happen in shock as a result of bleeding
- severe anaemia
- extremely active effort
- a lot of mental stress (as in broken heart syndrome)
- significant hyperthyroidism
- persistent tachycardia
- significant hypertension (high blood pressure)
- severely enlarged ventricles
- significant aortic stenosis
These disorders typically affect sicker people, and angina is typically just one symptom among many. Therefore, the absence of classic CAD is unlikely to mislead the healthcare professionals caring for these patients into a false sense of complacency.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/chest-pain-with-normal-coronary-arteries-1745819
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/angina/symptoms-causes/syc-20369373
- https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/heart-disease-angina
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21489-angina
For more details, kindly visit below.