Important substancial factors to avoid Alzhiemer’s disease.
What is Alzhiemer’s disease?
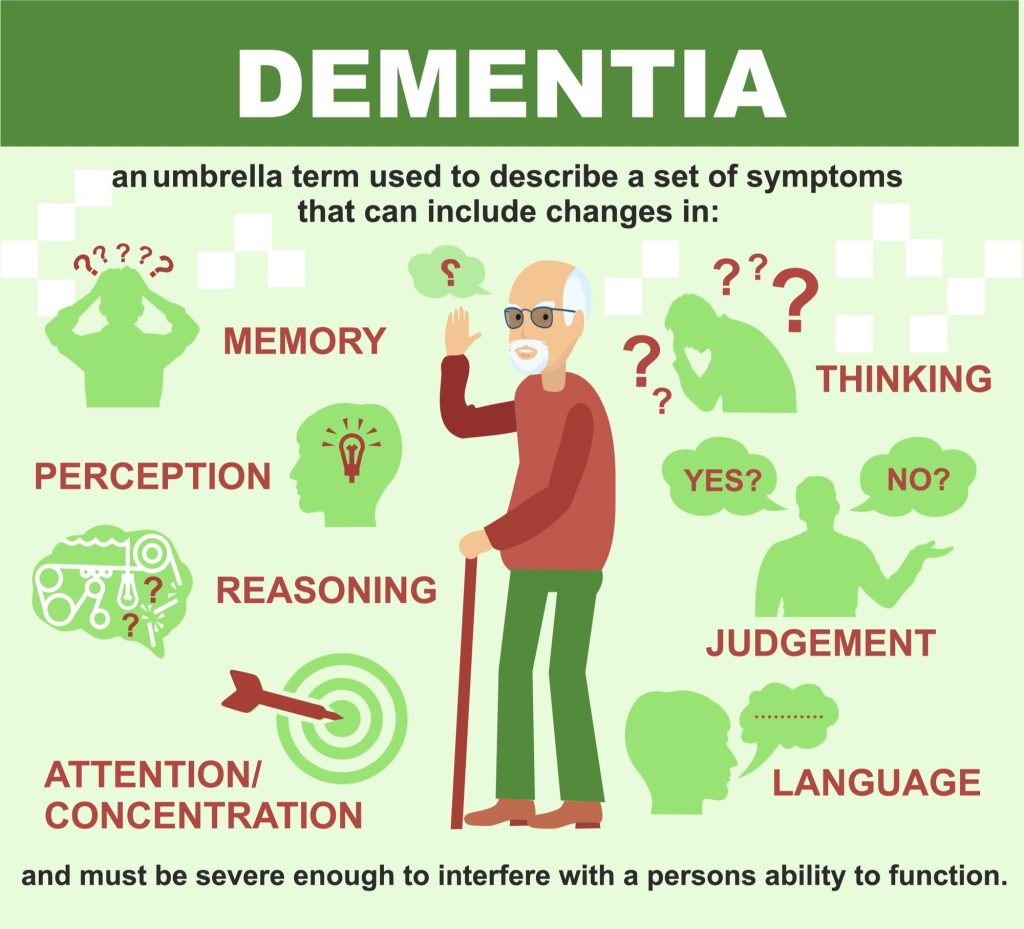
A form of dementia that progresses is Alzheimer’s disease. A condition that adversely impacts memory, thinking, and behaviour is referred to as dementia. The modifications make daily life more difficult. There are numerous possible causes of dementia, including diseases and brain traumas. Sometimes there is no known cause.
The Alzheimer’s Association estimates that 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases are caused by Alzheimer’s disease. The condition is typically diagnosed in patients over the age of 65. Alzheimer’s disease is typically described as having a “early onset” or “younger onset” if it is discovered earlier. Alzheimer’s has no known cure, but there are medications that can halt the disease’s growth.
Importants facts about Alzhiemer’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease is a persistent, chronic (long-term) illness. It is not a normal ageing symptom.
- Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are not the same thing. A form of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease.
- Its symptoms appear gradually, and its degenerative effects on the brain result in a steady decline.
- Alzheimer’s disease can affect anyone, but some people are more susceptible to it than others. People over 65 and those with a family history of the illness are included in this.
- Alzheimer’s patients cannot be predicted to have a particular outcome. While some persons experience a slower onset of symptoms and a faster rate of disease progression, others experience lengthy lifespans with minor cognitive impairment.
What does Alzheimer’s disease look like?
Even though the earliest symptoms of Alzheimer’s may differ from person to person, memory issues are often one of the first signs of the disease. The very early stages of Alzheimer’s disease may also be indicated by a deterioration in other cognitive abilities, including the ability to express oneself clearly, problems with vision or spatial awareness, and impaired reasoning or judgement. However, not everyone who has minor cognitive impairment (MCI) will go on to acquire Alzheimer’s. MCI is a condition that can be an early indicator of the disease.
Alzheimer’s patients struggle with simple tasks like driving a car, preparing food, and paying their bills. They might repeatedly ask the same questions, become disoriented quickly, misplace items or put them in strange places, and find even the most basic of tasks to be confusing.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
Everybody occasionally experiences moments of amnesia. However, those who have Alzheimer’s disease exhibit a number of persistent habits and symptoms that get worse with time. These may consist of:
- Memory loss that interferes with regular tasks like remembering appointments
- difficulty performing routine tasks, including using a microwave
- inability to solve problems
- difficulty speaking or writing
- becoming uncertain of the time or location
- reduced judgement
- lower level of personal hygiene
- changes in personality and mood
- retreat from the community, family, and friends
These symptoms do not always indicate Alzheimer’s disease. To ascertain the cause, it’s crucial to visit a doctor.
As the condition progresses, the symptoms change. People with Alzheimer’s frequently experience substantial difficulty speaking, moving, or reacting to events around them in the later stages of the disease.
Causes of Alzhiemer’s disease(Factors to avoid)
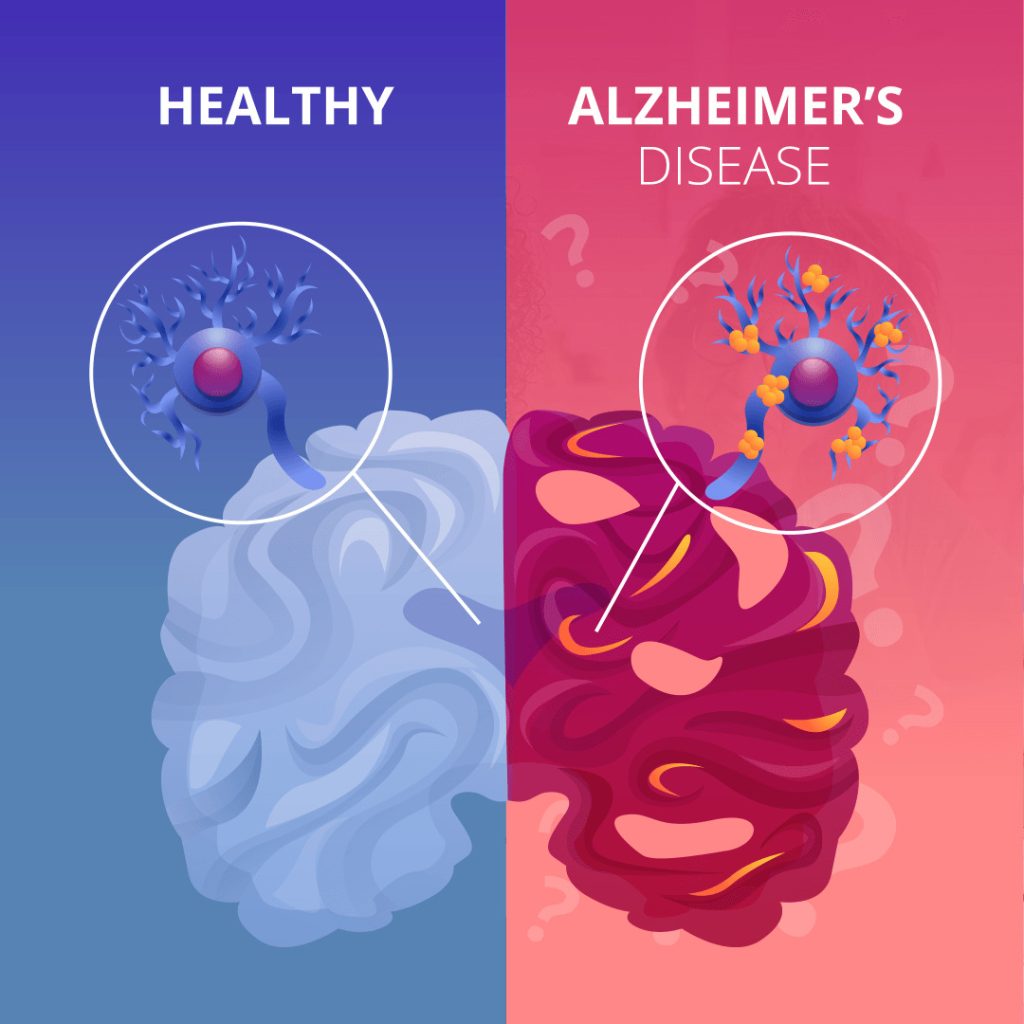
According to current theories, the aberrant protein buildup in and around brain cells is what causes Alzheimer’s disease. Amyloid is one of the proteins involved, and deposits of it create plaques around brain cells.
The other protein is tau, which builds up inside brain cells to form tangles. Scientists now know that this process starts many years before symptoms manifest, even if the exact cause is unknown.
The chemical messengers (known as neurotransmitters) used to communicate or send signals between brain cells decline as brain cells are damaged. The brains of those who have Alzheimer’s disease have notably low levels of one neurotransmitter, acetylcholine.
Different parts of the brain diminish throughout time. Memory-related areas are frequently the first to be damaged. Different parts of the brain are affected in more uncommon forms of Alzheimer’s disease. Instead of memory issues, the earliest signs may be issues with vision or language.
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease
Examining brain tissue after death is the only surefire technique to determine if someone has Alzheimer’s disease. However, a doctor can measure your mental capacity, identify dementia, and rule out other disorders using different examinations and tests.
Taking a medical history will probably be the doctor’s first step. They might inquire as to:
- symptoms
- family’s history of illness
- other health issues, present or previous
- Medications taken now or in the past
- alcohol consumption, nutrition, and other lifestyle choices
After that, your doctor will probably ask for a number of tests to see if you have Alzheimer’s disease.
What to do if you suspect Alzheimer’s disease
If you want to know if the symptoms you’re having are caused by Alzheimer’s disease or something more manageable like a vitamin deficiency or a drug side effect, make an appointment with your doctor.
A timely and correct diagnosis also gives you and your family the chance to think about financial preparation, create advance directives, sign up for clinical trials, and foresee care requirements.
REFERENCES:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/alzheimers-disease
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alzheimers-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350447
- https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-alzheimers-disease
- https://www.cdc.gov/aging/aginginfo/alzheimers.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9164-alzheimers-disease
For more details, kindly visit below.